Conjugation Based on Lysine Residues
Lysine is a nucleophilic amino acid with an ε-amino side chain that is highly abundant on protein surfaces. For example, an immunoglobulin (IgG) contains about 80-100 lysine residues and most of them are accessible, making lysine the most common target for random conjugation. Two primary chemical strategies are commonly employed for lysine conjugation. One is the formation of stable amide bonds using the active ester of the drug, such as N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS). The other approach is to form amidine bonds through cyclic thioiminate compounds, like Traut’s reagent, which introduce sulfhydryl groups while preserving the original amino group charge. These sulfhydryl groups are subsequently able to conjugate to drugs carrying specific active groups. Lysine has been extensively leveraged in the development of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). The following is a brief description of conjugation strategies for ADCs based on lysine residues.
Disclaimer
The processes and technologies outlined in this document are for reference only. Creative Biolabs makes no assurances or warranties regarding the outcomes that may result from the customer's implementation of this guideline.
Materials
 One-Step Conjugation
One-Step Conjugation
- O-succinimide-containing pyrrolobenzodiazepine (PBD) dimers.
- Target antibody.
- N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMA).
- Buffer 1 (pH 8, 50 mM potassium phosphate, 50 mM NaCl, and 2 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA)).
- Buffer 2 (pH 6.5, 10 mM phosphate, and 140 mM NaCl).
- Gel filtration column (200 pg).
- Syringe filter (0.45 μm).
- Ultracentrifugal filter (50 kDa MWCO).
 Two-Step Conjugation by Traut’s Reagents
Two-Step Conjugation by Traut’s Reagents
- Maleimide-modified drug.
- Target monoclonal antibody (mAb).
- 2-Iminothiolane (2-IT).
- Dextran 40.
- Buffer 3 (pH 6 ~ 8.5, 50 mM potassium phosphate, 50 mM NaCl, and 2 mM EDTA).
- Buffer 4 (pH 6.5, 10 mM phosphate and 140 mM NaCl).
- Buffer 5 (pH 8, 100 mM sodium phosphate, 50 mM NaCl, and 2 mM diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DPTA)).
- Buffer 6 (pH 5.5, 50 mM 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES), 5 mM glycine, and 2 mM DPTA).
- 4,4'-dithiodipyridine (DTDP).
- Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
- Syringe filter (0.2 μm).
- 10 kDa TFF cassette.
- Cation exchange (CEX) column.
Methods
 One-Step Conjugation
One-Step Conjugation
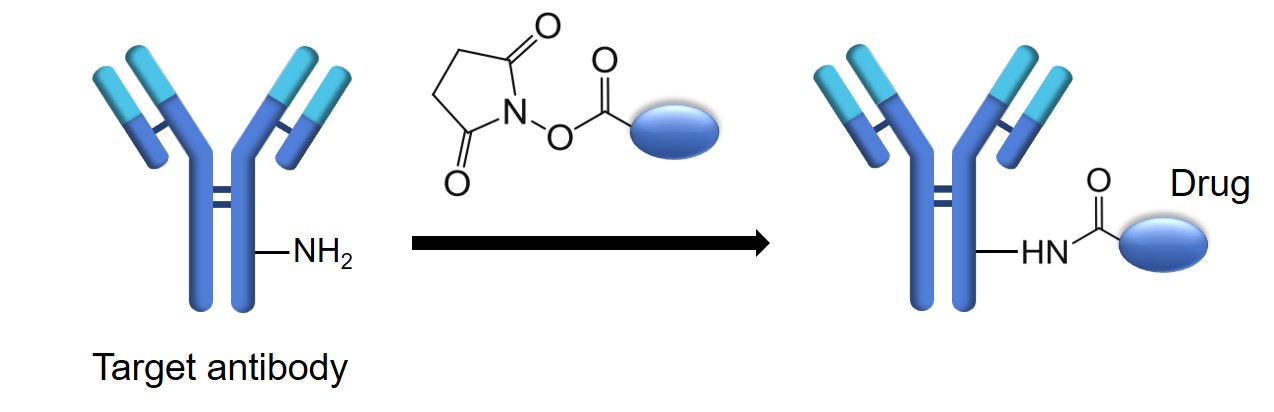
- Prepare 10 mM O-succinimide-containing drug stock solution in DMA.
- Dilute the antibody solution in buffer 1 (pH 8) and DMA. Then, slowly add a 5- to 20-fold molar excess of the drug solution (depending on the expected drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR) and drug reactivity) into the antibody solution under constant magnetic stirring to keep the final antibody concentration in the range of 2.5 ~ 5 mg/mL and the DMA content at no more than 20%.
- Stir the solution at room temperature for 2 ~ 4 h.
- Clarify the mixture using a 0.45 μm filter. Purify the final ADC by a 200 pg gel filtration column using buffer 2 (pH 6.5), and concentrate via a 50 kDa MWCO filter.
 Two-Step Conjugation by Traut’s Reagents
Two-Step Conjugation by Traut’s Reagents
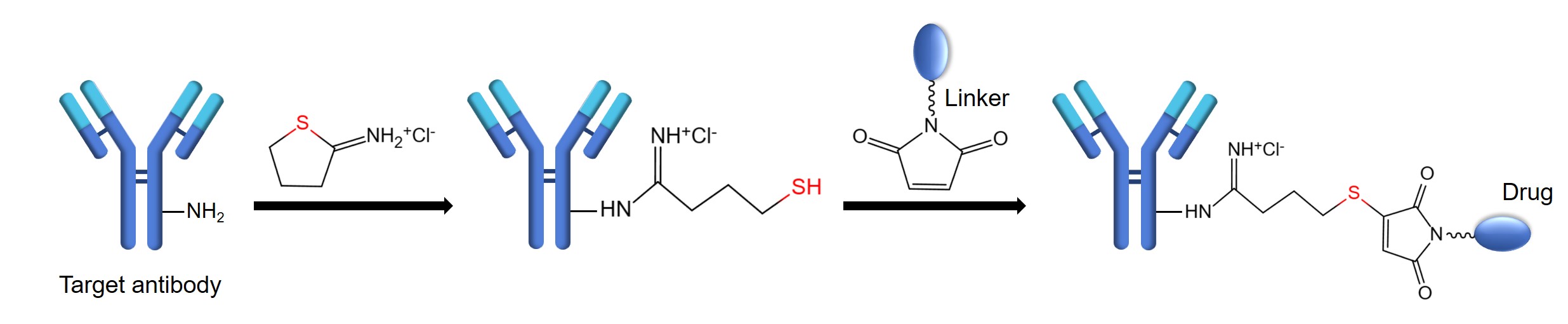
- Dilute the mAb solution at a concentration (>5 mg/mL) in buffer 3 (pH 6 ~ 8.5).
- Slowly add a 10-fold molar excess of 2-IT under constant stirring to a final mAb concentration of 5 mg/mL. Then, stir continuously at room temperature for 1 h.
- Use the 10 kDa TFF cartridge with buffer 4 (pH 6.5) for diafiltration to separate reaction by-products and excess reactants. Then, adjust the concentration of the modified mAb to 2.5 mg/mL.
- Use an excess of DTDP to treat a small aliquot of the modified mAb and measure the release of thiopyridine with UV (ε324 nm = 19,800/M/cm).
- Prepare a maleimide-modified drug stock solution (5 mM in DMSO).
- Add a 3-fold molar excess of the maleimide-modified drug solution per thiol under stirring. Then, stir continuously at room temperature for 1.5 h.
- Following filtration by a 0.2 μm filter, add a 10-fold molar excess per thiol of N-ethylmaleimide solution (100 mM in DMSO) to quench the conjugation reaction at room temperature for 1 h.
- Use a 0.2 μm filter to filtrate the ADC. Then, use a CEX column eluted with buffer 5 (pH 8) to further purify.
- Diafiltration by a 10 kDa TFF cassette with buffer 6 (pH 5.5) to formulate the ADC. Add Dextran 40 to a final concentration of 10 mg/mL, and then filtrate again using a 0.2 μm filter to “sterilize”.
Notes
- If the desired DAR is not achieved, an additional quantity of the O-succinimide-containing drug solution can be added, and the reaction can be continued for an additional 2 h. During this step, stirring may be replaced with gentle heating to 30°C, which can help facilitate the completion of the reaction.
Recommended products
