hNIS loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus Engineering Service
Introduction
Creative Biolabs hNIS-loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus service accelerates cancer therapy development for resistant tumors and complex models, integrating innovative oncolytic virotherapy with advanced molecular imaging. This cutting-edge approach enables selective tumor destruction and real-time treatment monitoring, delivering targeted therapeutic agents, comprehensive preclinical validation, molecular imaging support, drug resistance solutions, and advanced in vivo modeling.
[Discover How We Can Help - Request a Consultation]
hNIS-loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus
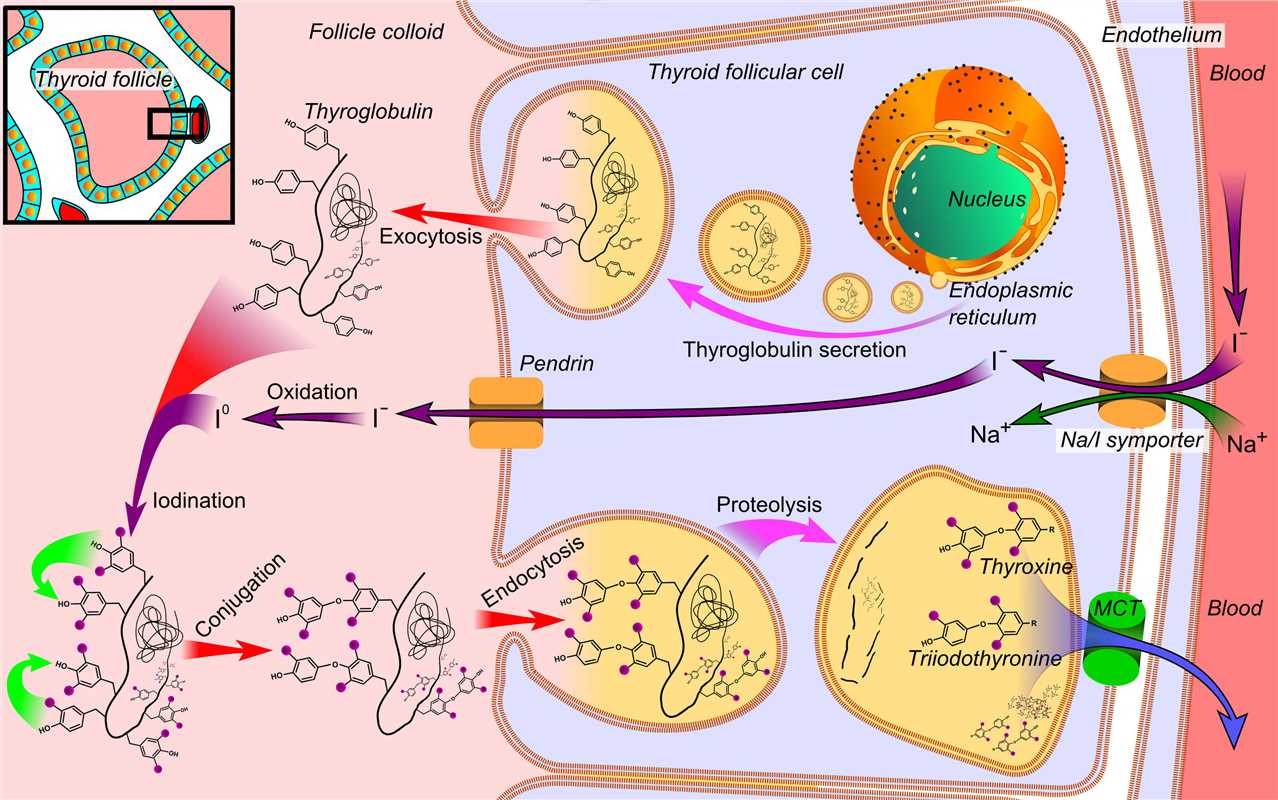 Fig.1 NIS is involved in the synthesis and transport of thyroid hormones (NIS is located on the right cell membrane).Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Fig.1 NIS is involved in the synthesis and transport of thyroid hormones (NIS is located on the right cell membrane).Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki, without modification.
The human Sodium Iodide Symporter (hNIS) is a crucial membrane protein naturally expressed in thyroid follicular cells, where its primary function is the active transport of iodide into the cell. This integral role in thyroid physiology has long made hNIS an invaluable tool in nuclear medicine for thyroid diagnostics and therapy. In the innovative context of oncolytic virotherapy, hNIS is ingeniously repurposed to serve as a dual-purpose therapeutic gene, offering both therapeutic and diagnostic capabilities within a single platform.
Principle
By genetically engineering oncolytic adenoviruses to express hNIS, these sophisticated viral vectors, upon selectively infecting and replicating within cancer cells, introduce the hNIS gene into the tumor microenvironment. The infected tumor cells then begin to express functional hNIS proteins on their cell surface. This expression provides two critical advantages:
- Targeted Radioiodine Therapy
hNIS-expressing cancer cells actively import radioiodide (e.g.,131I), delivering localized high-dose radiation to destroy tumor cells while sparing healthy tissues. This is effective for eradicating large solid tumors or disseminated disease refractory to conventional methods.
- Non-invasive Imaging and Monitoring
hNIS-mediated iodide uptake enables real-time imaging with radioisotopes like 124I (PET) or 99mTcO4- (SPECT). This allows precise tracking of viral distribution, replication, and treatment efficacy, as well as tumor regression monitoring to guide therapeutic optimization.
Advantages
- Enhanced Specificity and Efficacy: Oncolytic adenoviruses are engineered for cancer cell selectivity (e.g., tropism modifications, hTERT promoter), with hNIS integration enabling precise radioiodine therapy for potent anti-tumor activity.
- Real-time Theranostic Capability: Combines therapeutic radioiodine uptake with diagnostic imaging (PET/SPECT) for personalized "theranostic" strategies, allowing immediate assessment of treatment efficacy.
- Overcoming Drug Resistance: Preclinical data shows hNIS-loaded adenoviruses target drug-resistant cancer stem cells (e.g., paclitaxel-resistant breast cancer), addressing tumor recurrence mechanisms.
- Reduced Systemic Toxicity: Tumor-specific viral replication and localized hNIS-mediated radiation minimize off-target effects, offering a safer alternative to systemic chemotherapy.
- Versatility and Adaptability: Adenoviral platform supports co-expression of immunomodulatory genes (e.g., cytokines) to enhance anti-tumor immunity, expanding therapeutic applications.
Workflow
| Required Starting Materials | Project Consultation & Design |
|---|---|
|
Initial discussion to understand therapeutic goals, select viral constructs, and define project scope. Collaborative design of a customized experimental protocol aligned with research objectives, resulting in a comprehensive project plan. |
| Viral Production & Engineering | In Vivo Efficacy Studies |
| Expert production of high-titer, quality-controlled hNIS-loaded oncolytic adenoviruses with potential custom modifications (e.g., capsid alterations, therapeutic gene incorporation) to meet precise specifications. | Thorough in vitro studies in cancer cell lines to evaluate viral replication kinetics, cytopathic effect, hNIS expression, and radioiodine uptake capacity. Provides foundational data on viral performance and cellular response. |
| In Vivo Preclinical Studies | Data Analysis and Reporting |
| Comprehensive assessments in animal models, including tumor regression monitoring, in vivo hNIS expression quantification via SPECT/CT imaging, and overall survival analysis. Insights into therapeutic potential and viral biodistribution. | Comprehensive analysis of imaging, tumor burden, molecular, and histopathological data. Delivery of detailed reports with statistical validations, expert interpretations, and actionable recommendations for subsequent development phases. |
| Final Deliverables | Estimated Timeframe |
|
The typical timeframe for this service ranges from 12 to 18 weeks, depending on the complexity of the viral construct, the inclusion of optional preclinical evaluation, and the specific requirements of your project. More intricate designs or extensive in vivo studies may extend the duration. |
[Contact us to get more information]
What we can offer
Our service delivers unparalleled capabilities for advancing your cancer research. Our offerings are meticulously designed to provide precise, effective, and customizable solutions, directly supporting your therapeutic development goals.
Customizable Viral Engineering
Tailored hNIS-loaded oncolytic adenovirus constructs with tumor tropism modifications, promoter selection, and co-expression of therapeutic genes for unique research needs.
Comprehensive Preclinical Evaluation
In vitro/in vivo studies assessing viral replication, tumor selectivity, efficacy, and biodistribution for thorough performance analysis.
Advanced Molecular Imaging Integration
SPECT/CT and PET imaging protocols for real-time monitoring of viral kinetics and therapeutic response to optimize treatment strategies.
Strategies for Therapy Resistance
Specialized approaches to design and test hNIS-loaded adenoviruses against drug resistance mechanisms in refractory tumors and cancer stem cells.
High-Quality Viral Production
State-of-the-art facilities for high-titer, high-purity viral production with rigorous quality control.
Expert Scientific Consultation
Collaborative guidance from virologists and oncologists for project design, optimization, and data interpretation.
[Experience the Creative Biolabs Advantage - Get a Quote Today]
Case Study
The employment of hNIS-loaded oncolytic adenoviruses in preclinical experimental models and neoplastic cell lines amplifies tumor-targeted lytic potency. Research findings authenticate its utility for treating solid malignancies, emphasizing the virus's dual-action mechanism strategy.
| NIS Expression | 125I uptake |
|---|---|
|
|
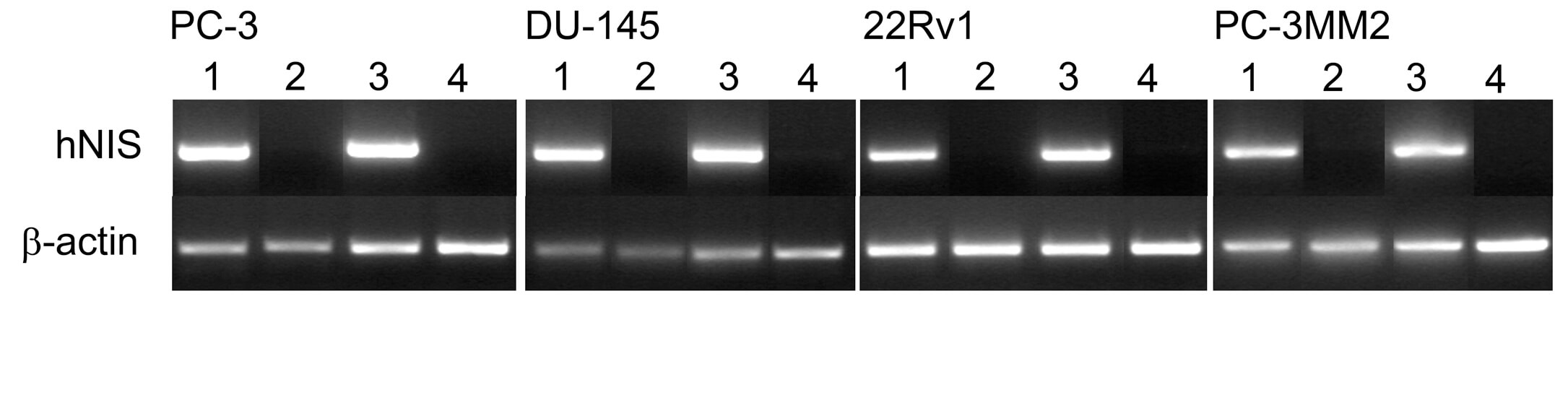
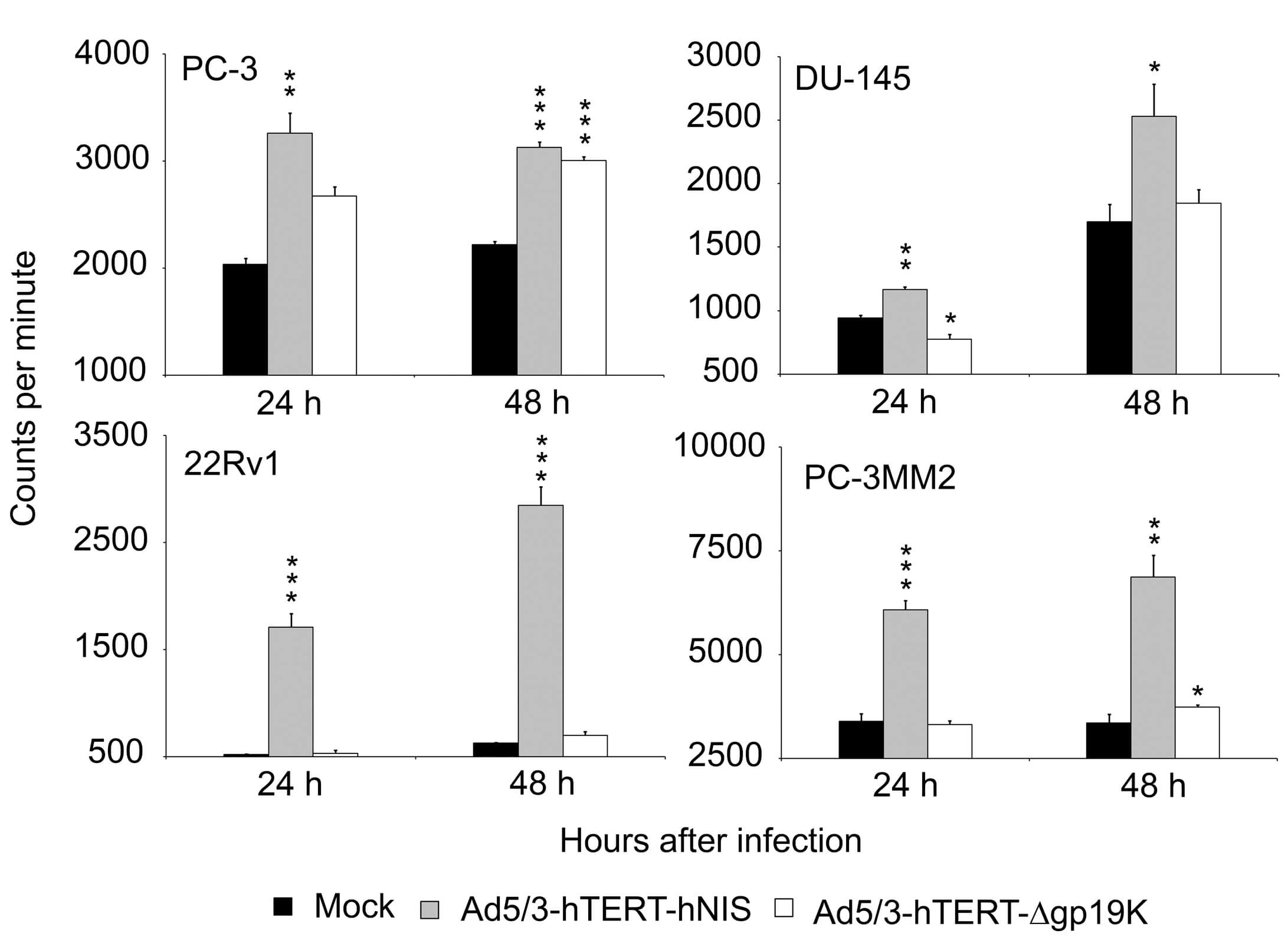
| Fig.2 Agarose gel electrophoresis was used to detect NIS expression in tumor cells after administration of oncolytic virus loaded with hNIS and the control group.1 | Fig.3 Iodide uptake of tumor cells treated with adenoviruses loaded with hNIS and control adenoviruses was analyzed using a gamma counter.1 |
| Cell Cytotoxicity | Gamma Camera Imaging |
|
|
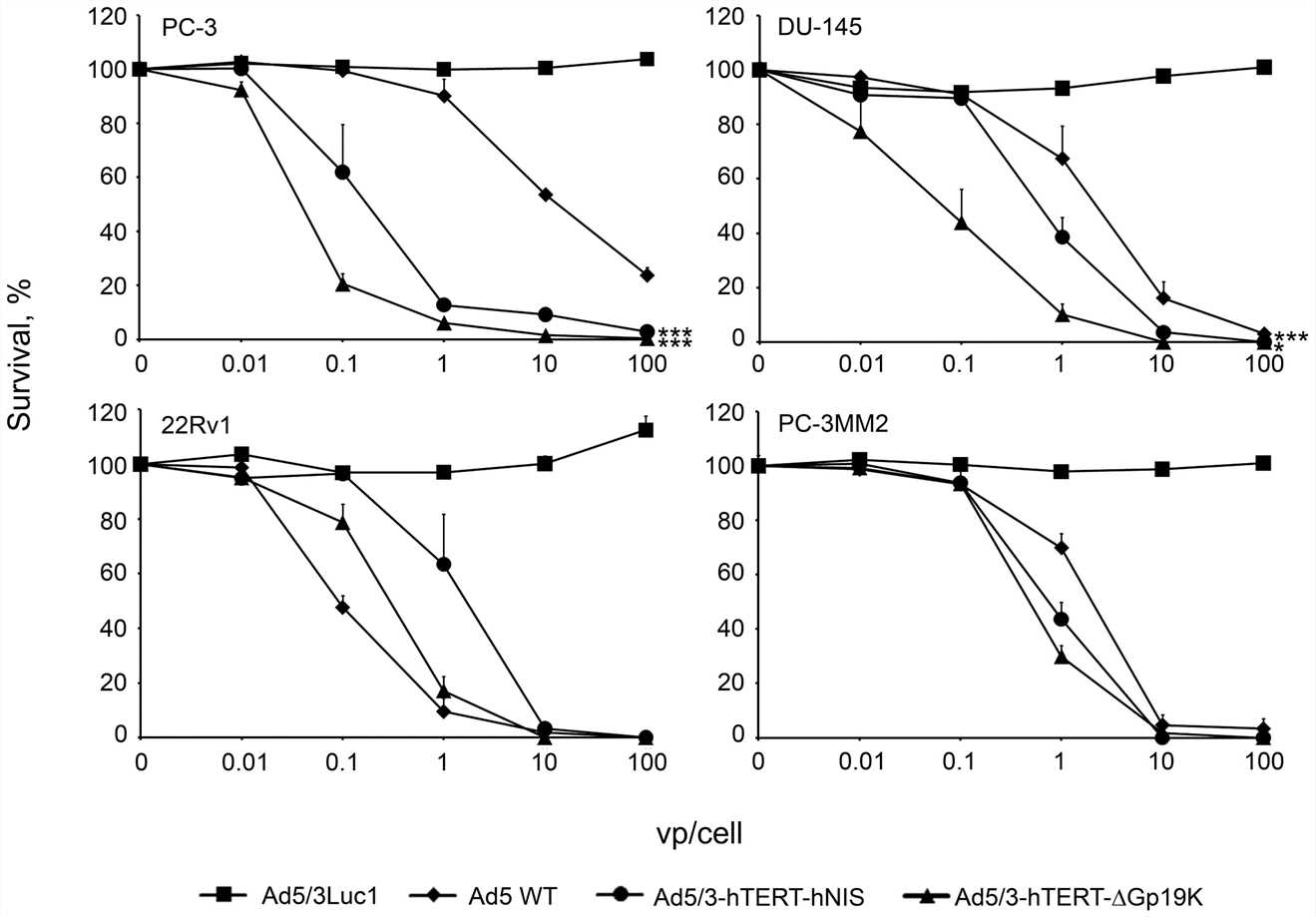
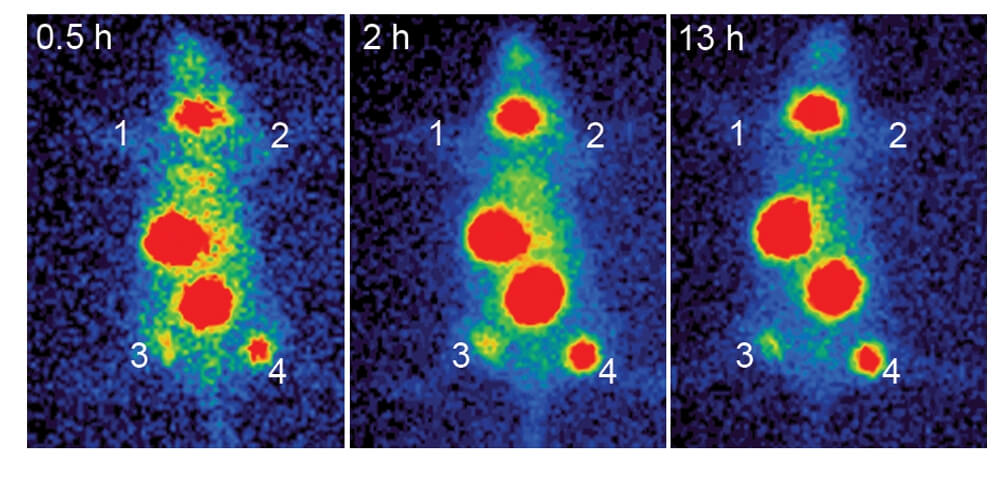
| Fig.4 Tumor cell survival after treatment with hNIS-loaded oncolytic adenovirus.1 | Fig.5 The ability of oncolytic adenovirus loaded with hNIS to guide iodine uptake into tumors in vivo was evaluated.1 |
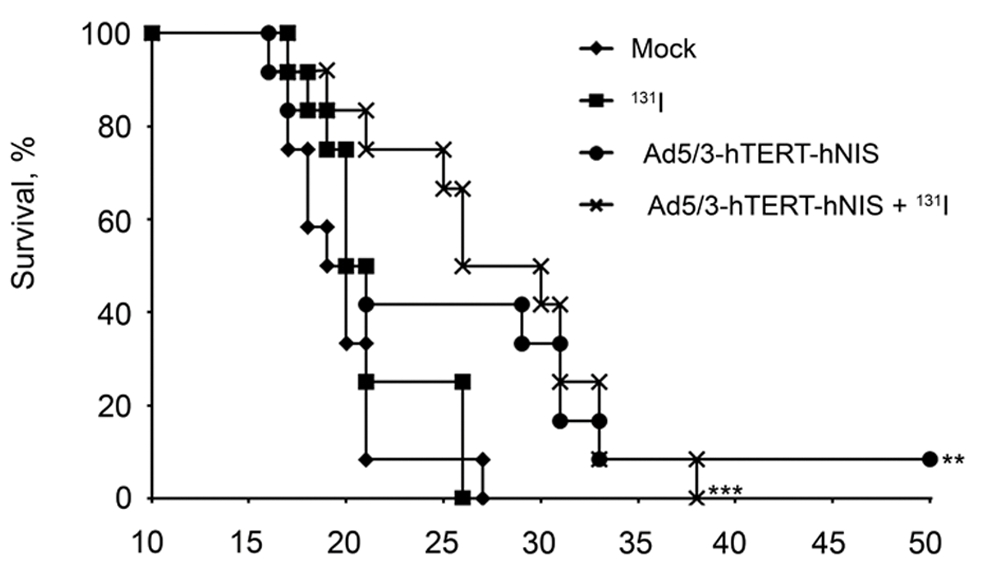
| Survival Curve | Biodistribution |
|
|
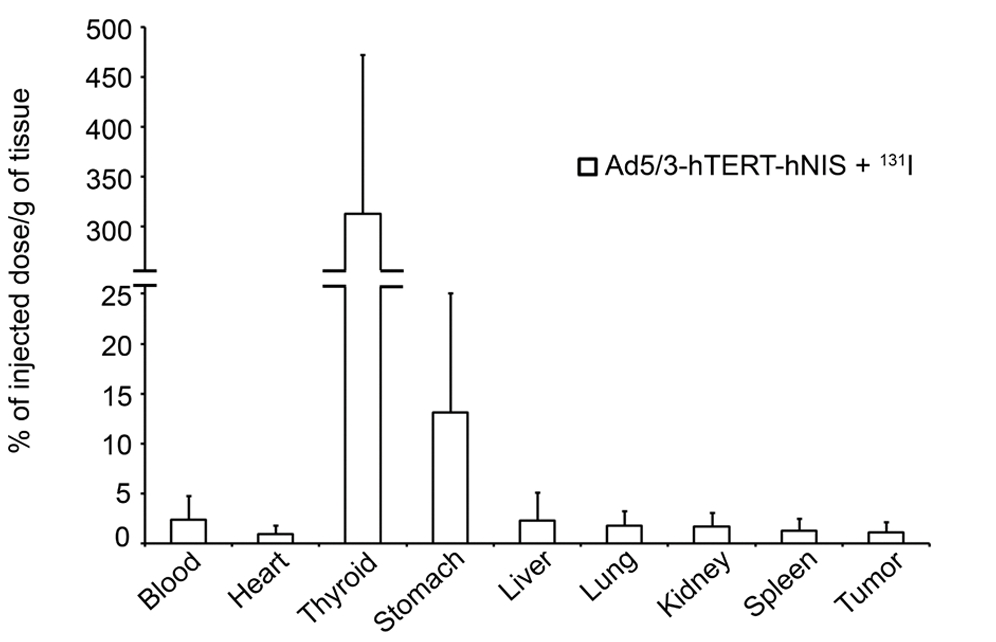
| Fig.6 Oncolytic adenovirus loaded with hNIS prolonged the survival time of tumor-bearing mice.1 | Fig.7 An automated gamma counter is used to measure the distribution of iodine in each organ tissue of mice.1 |
FAQs
Q1. How does Creative Biolabs ensure the specificity of hNIS-loaded oncolytic adenoviruses for cancer cells?
A1: Our hNIS-loaded oncolytic adenoviruses feature precise genetic modifications: tumor-specific promoters restrict replication to cancer cells, enhancing specificity and sparing healthy tissues. Capsid modifications optimize tumor transduction for diverse cancer types. Contact us to explore our engineering strategies and project benefits.
Q2. What type of imaging modalities can be used with hNIS-loaded oncolytic adenovirus for monitoring?
A2: The hNIS gene enables non-invasive SPECT/CT or PET imaging with radioisotopes to track viral distribution, assess tumor response, and evaluate treatment efficacy in real time. Our team offers imaging protocol guidance and result interpretation for optimal therapeutic insights.
Q3. Can hNIS-loaded oncolytic adenovirus be combined with other cancer therapies?
A3: hNIS-loaded oncolytic adenoviruses show strong synergistic potential with chemotherapy, external beam radiation, and immunotherapy. Radioiodine-delivered localized radiation sensitizes tumor cells to other treatments, while viral lysis enhances anti-tumor immune responses. Discuss your combination therapy ideas with our scientists to explore full potential.
Q4. What starting materials are typically required to initiate a project with Creative Biolabs' hNIS-loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus service?
A4: Project initiation typically requires: relevant cancer cell lines (primary/tumor/drug-resistant variants), target gene sequences for custom viral modifications, and existing preliminary efficacy data. Our team will collaborate with you during initial consultations to identify all necessary materials for seamless project start-up.
Q5. How long does a typical hNIS-loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus project take, and what are the key deliverables?
A5: Project timelines vary by scope but typically range from 12-18 weeks for comprehensive studies. Deliverables include detailed reports, SPECT/CT imaging data, statistically validated efficacy results, and expert development recommendations. Schedule a consultation to discuss your specific timeline and deliverables.
[Contact Our Team for More Information and to Discuss Your Project]
Related Sections
| Cytosine Deaminase loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus | Thymidine Kinase loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus |
| Prodrugs loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus | GMCSF loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus |
| CD40L loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus | TNF-α loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus |
| IL-2 loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus | 41BBL loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus |
| PH20 Hyaluronidase loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus | Anti-CTLA4 loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus |
| Anti-PD1 loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus | IL-12 loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus |
| Decorin loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus | OX40L loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus |
| EGFR loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus | FRα loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus |
| FAP loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus | CD44v6 loaded Oncolytic Adenovirus |
Reference
- Rajecki, Maria, et al. "SPECT/CT imaging of hNIS-expression after intravenous delivery of an oncolytic adenovirus and 131I." PloS one 7.3 (2012): e32871. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032871. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
