The alternative pathway (AP) is one of the common opsonic complement pathways of pathogens. It is a cascade of the complement system, a component of the innate immune system that plays a vital role in natural defenses against infection. AP is spontaneously and slowly activated by hydrolysis of the internal C3 thioester bond and further triggered by contact with various protein, lipid and carbohydrate structures on microbes and other foreign surfaces, forming an integral defense mechanism independent of immune responses. As a leading international biotechnology company, Creative Biolabs has always focused on complement research. We have the expertise and capabilities to provide custom solutions for your complement research.
AP Hemolytic Assay Protocol
Here, we give a brief introduction to the procedure of the AP hemolytic assay.
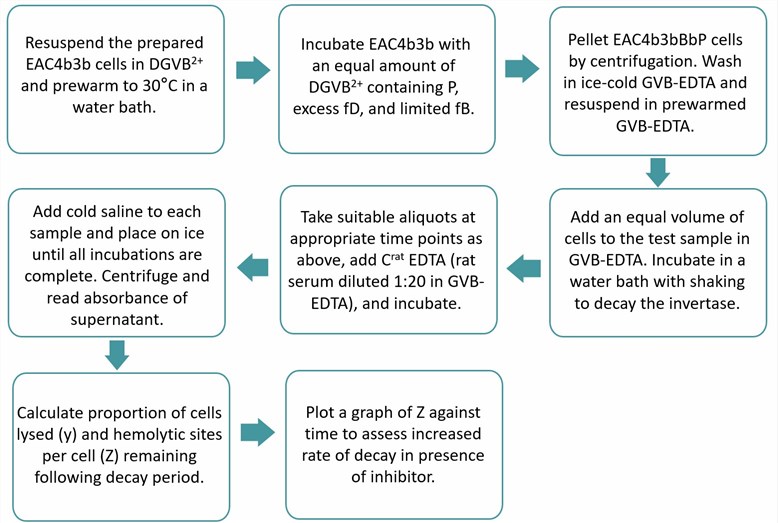 Fig.1 Flow chart of AP hemolytic assay protocol. (Creative Biolabs)
Fig.1 Flow chart of AP hemolytic assay protocol. (Creative Biolabs)
Creative Biolabs has been engaged in complement research for many years and has accumulated rich experience in complement testing. We are confident in offering a wide range of complement products including but not limited to proteins, inhibitors, kits and reagents. Based on these products, you can better conduct complement research. In addition, with our advanced detection platform, a variety of customized complement detection services can also escort your complement project.
Published Data
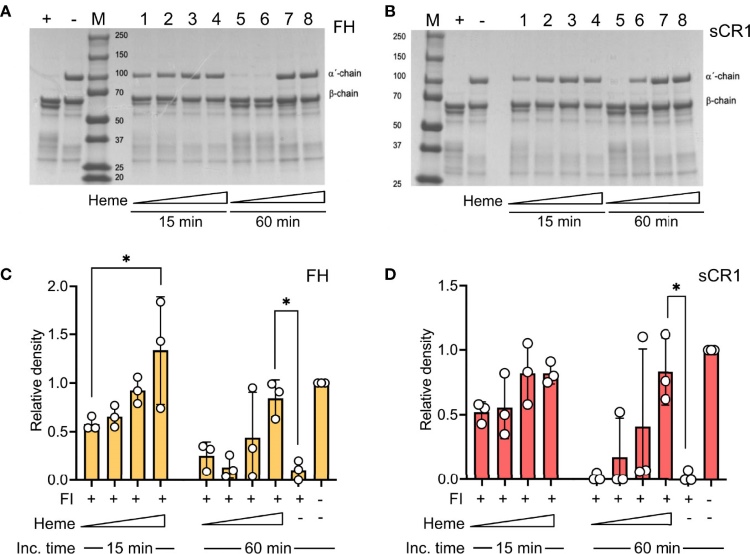 Fig. 2 Heme influences factor I-mediated degradation of soluble C3b.1
Fig. 2 Heme influences factor I-mediated degradation of soluble C3b.1
Activation of the alternative complement pathway can activate heme release Activation of the alternative complement pathway can activate heme release. The effects of heme on the regulatory functions of the complement system were investigated here. The degradation of C3b is mediated by factor I. When heme interacts with factor I, it interferes with the degradation of C3b. Heme demonstrated a dose-dependent ability to inhibit the activity of factor I, which is responsible for the degradation of C3b, both in its soluble form and when bound to the surface of cells. This inhibitory effect was observed during experiments where heme was incubated with complement regulatory proteins in either plasma or buffered solutions.
Services and Products at Creative Biolabs
If you are interested in our complement detection services and products, please feel free to contact us for more details.
Please note that our protocols are only for your reference.
Reference
-
Gerogianni, Alexandra, et al. "Heme interferes with complement factor I-dependent regulation by enhancing alternative pathway activation." Frontiers in Immunology 13 (2022): 901876. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig.1 Flow chart of AP hemolytic assay protocol. (Creative Biolabs)
Fig.1 Flow chart of AP hemolytic assay protocol. (Creative Biolabs)
 Fig. 2 Heme influences factor I-mediated degradation of soluble C3b.1
Fig. 2 Heme influences factor I-mediated degradation of soluble C3b.1