The complement system consists of dozens of proteins that are present in different forms in the blood or bound to cells. These proteins are intimately linked to complement activation. The system is divided into three pathways of activation: the lectin pathway (LP), the classical pathway (CP) and the alternative pathway (AP), each with different recognition molecules. Here Creative Biolabs shares a brief introduction to the CP hemolytic assay protocol.
Classical Pathway of Hemolytic Assay Protocol
In CP assays, the time required for the maximum amount of C3 convertase to present on the cell surface is referred to as Tmax. Tmax is closely related to the amount of functionally active C4b on the cell surface and should usually be less than 6 minutes. Tmax was determined by incubating EAC14b cells with C2 and measuring the number of functionally active sites (Z) of the cells at specific times after the addition of C2.
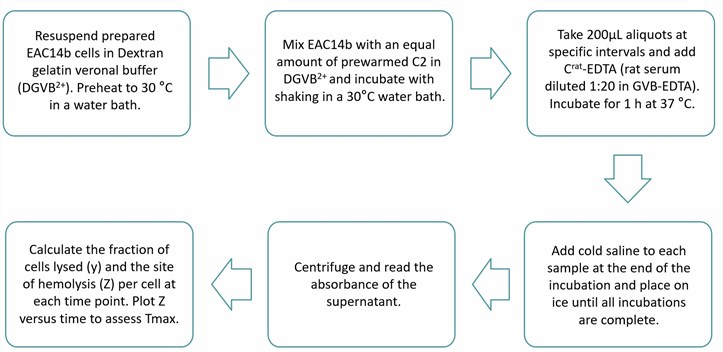 Fig.1 Flow chart of determination of Tmax assay.
Fig.1 Flow chart of determination of Tmax assay.
After Tmax was determined by the above assay, decay activity can be determined by the following procedure.
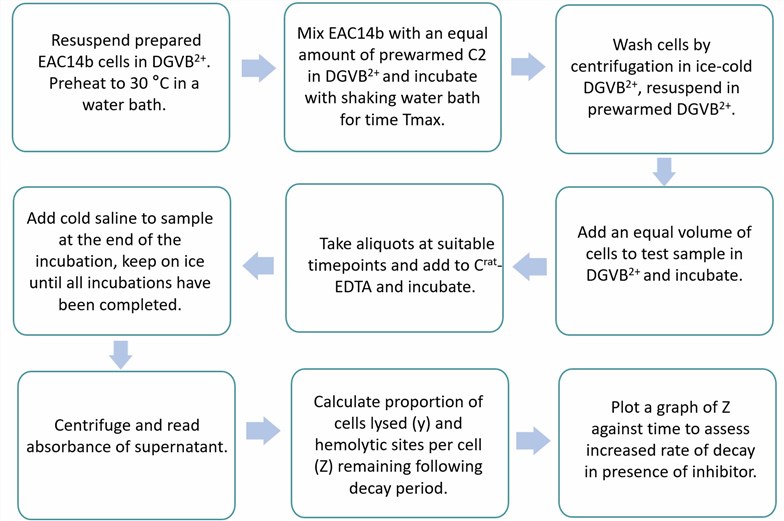 Fig.2 Assay of decay activity.
Fig.2 Assay of decay activity.
The diverse complement detection services provided by Creative Biolabs can deepen the understanding of the mechanism of disease development and promote the progress of complement-related drug development projects. Our professional team will provide customized solutions for your complement program according to your unique needs, and help your drug development progress in the early stage. In addition, rigorously tested complement products are also the best choice for your complement research.
Published Data
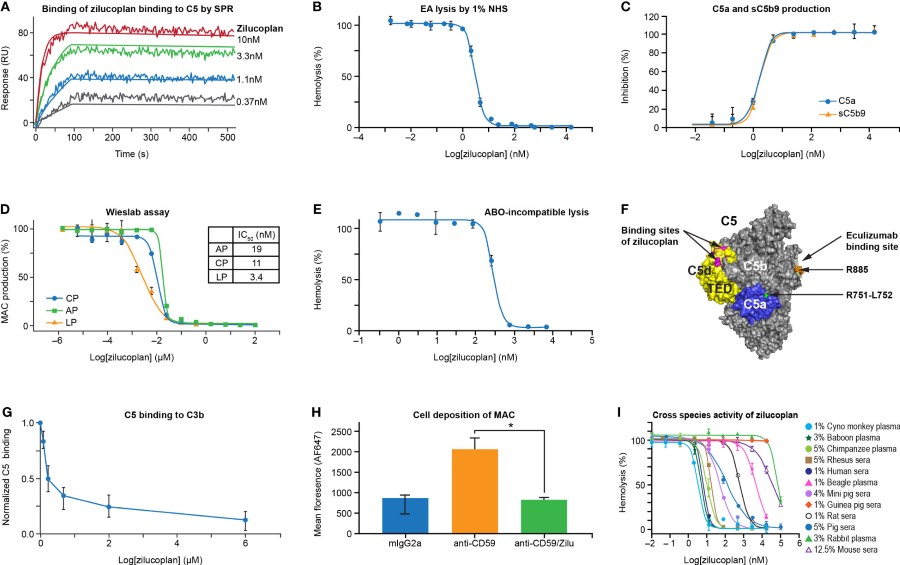 Fig. 3 Zilucoplan binds human C5 and blocks complement-mediated hemolysis in vitro.1
Fig. 3 Zilucoplan binds human C5 and blocks complement-mediated hemolysis in vitro.1
Zilucoplan is a kind of macrocyclic peptide that can bind to human complement component 5 (C5), and effectively inhibit its lysis and activation. The interactions between zilucoplan and C5, including the clinically relevant C5 R885 variant, were investigated using surface plasmon resonance (SPR), hemolysis assays, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). The capacity of zilucoplan to obstruct the activation of the terminal complement cascade (TCC) was evaluated through the lysis of antibody-sensitized sheep erythrocytes (EA) exposed to 1% normal human serum (NHS), both in the absence and presence of serial concentrations of zilucoplan. In the complement classical pathway-mediated hemolysis assay, zilucoplan exhibited dose-dependent inhibition, preventing lysis from reaching completion. Furthermore, zilucoplan demonstrates a high-affinity binding to C5 and inhibits the production of the anaphylatoxin C5a as well as the cytolytic membrane attack complex (MAC) formed by the C5 convertase. It is capable of dissociating the stable C5b6 complex and impeding the non-classical TCC activation pathway mediated by plasmin, indicating that zilucoplan possesses a novel mechanism of action by competing with C6 for binding to C5b.
Services and Products at Creative Biolabs
If you are interested in more information about our complement detection services and products, please contact us directly.
Please note that our protocols are only for your reference.
Reference
-
Tang, Guo-Qing, et al. "Zilucoplan, a macrocyclic peptide inhibitor of human complement component 5, uses a dual mode of action to prevent terminal complement pathway activation." Frontiers in Immunology 14 (2023): 1213920. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig.1 Flow chart of determination of Tmax assay.
Fig.1 Flow chart of determination of Tmax assay.
 Fig.2 Assay of decay activity.
Fig.2 Assay of decay activity.
 Fig. 3 Zilucoplan binds human C5 and blocks complement-mediated hemolysis in vitro.1
Fig. 3 Zilucoplan binds human C5 and blocks complement-mediated hemolysis in vitro.1