The complement system occupies an irreplaceable position in the humoral immunity of mammals. As the vital enzymes of the complement cascade, C3 convertases and their proper regulation are critical for the protection of native tissues from complement-mediated destruction. Based on this, various complement modulators, such as factor H (FH), complement receptor 1 (CR1) and decay-accelerating factors prevent C3b opsonization by promoting the decay acceleration of C3 convertase. With rich experience in complement research, Creative Biolabs is committed to providing you with a one-stop solution as well as diversified products for complement research and drug development.
Decay-Accelerating Activity Assay Protocol
Here, we provide a brief introduction to the decay-accelerating activity assay by monitoring C3a production.
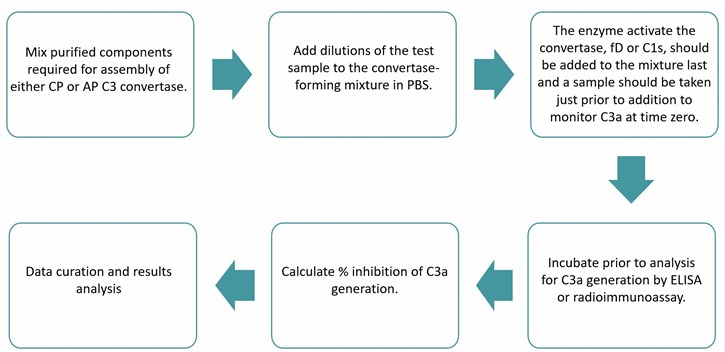 Fig.1 Flow chart of decay-accelerating activity assay. (Creative Biolabs)
Fig.1 Flow chart of decay-accelerating activity assay. (Creative Biolabs)
With decades of complement research experience and an advanced technology platform, Creative Biolabs provides a customized solution for complement research. Our diverse range of analytical services ensures you get the desired results and a better interpretation of complement function, which contributes to the exploitation of promising new complement therapies. Furthermore, our high-quality complement products provide a favorable guarantee for your complement research projects. Our featured complement products are listed below:
Published Data
 Fig. 2 Oxidative stress induces the increasing localization of C3aR on mitochondria.1
Fig. 2 Oxidative stress induces the increasing localization of C3aR on mitochondria.1
Complement component 3 fragment C3a serves as an anaphylatoxin that facilitates cellular responses and is integral to immune responses and host defense mechanisms. Its receptor, C3aR, is typically located on the plasma membrane; however, in immune cells, it is predominantly localized within the lysosome. Oxidative stress induces an increase in intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS), which subsequently activate complement signaling and lead to metabolic reprogramming in immune cells. This study investigated the interplay between oxidative stress and intracellular complement functions in mitochondrial dysfunction within retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells, employing high-resolution live cell imaging techniques. Although the levels of C3aR were not significantly altered by oxidative stress, a reduction in its presence on the plasma membrane was observed, coupled with an increase in its mitochondrial localization. The findings indicate that oxidative stress enhances mitochondrial C3aR levels, which subsequently influences mitochondrial calcium uptake and ATP production. These findings have significant implications for our understanding of the regulatory balance of complement signaling both intracellularly and extracellularly, particularly in the context of cellular health and dysfunction.
Services and Products at Creative Biolabs
Please feel free to contact us for solutions to your complement research.
Please note that our protocols are only for your reference.
Reference
-
Ishii, Masaaki, et al. "Mitochondrial C3a receptor activation in oxidatively stressed epithelial cells reduces mitochondrial respiration and metabolism." Frontiers in Immunology 12 (2021): 628062. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig.1 Flow chart of decay-accelerating activity assay. (Creative Biolabs)
Fig.1 Flow chart of decay-accelerating activity assay. (Creative Biolabs)
 Fig. 2 Oxidative stress induces the increasing localization of C3aR on mitochondria.1
Fig. 2 Oxidative stress induces the increasing localization of C3aR on mitochondria.1