Hi-Affi™ hPD-1/hCD40 Dual Humanized Mouse Model
As a promising target in cancer therapy, human CD40 (hCD40) plays an important role in the function of cytotoxic T cells and adaptive immune response. Stimulating the hCD40 using anti-hCD40 agonist antibody could augment the immune response. Recent clinical trials adopt both anti-hCD40 agonist antibody and anti-hPD-1 antibody, trying to increase the response rate in cancer patients. Creative Biolabs has successfully established an optimized Hi-Affi™ "humanized" animal platform to offer specialty manipulated hPD-1/hCD40 dual humanized mice for our clients all over the world.
hPD-1/hCD40 Molecule
Human programmed cell death protein 1 (hPD-1) is a protein on the surface of normal human cells. It binds to human programmed cell death ligand 1 (hPD-L1) and then prevents immune cells from activating and killing normal cells. It is a self-protect mechanism for the autologous organs and tissues. Some special types of malignant tumors can express a large amount of hPD-L1 on the surface of the cells, and vigorously suppress the activation of immune cells to escape the attack of immune cells.
The hCD40 (also called TNFRSF5) receptor and its ligand CD40L (also called CD154) belong to the TNF/TNFR family. hCD40 has a total length of 277 amino acids, including the extra-cytoplasmic region (193 amino acids), transmembrane region (22 amino acids), and cytoplasmic region (62 amino acids). The extra-cytoplasmic region of hCD40 is composed of four 22-cysteine-rich domains, which constitute a region that binds to its ligand hCD40L. hCD40 is a type I membrane glycoprotein that was initially identified as a surface marker of bladder cancer cells and B cells. The hCD40 is broadly expressed on a variety of cells, including antigen-presenting cells (APCs), B cells, platelets, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells.
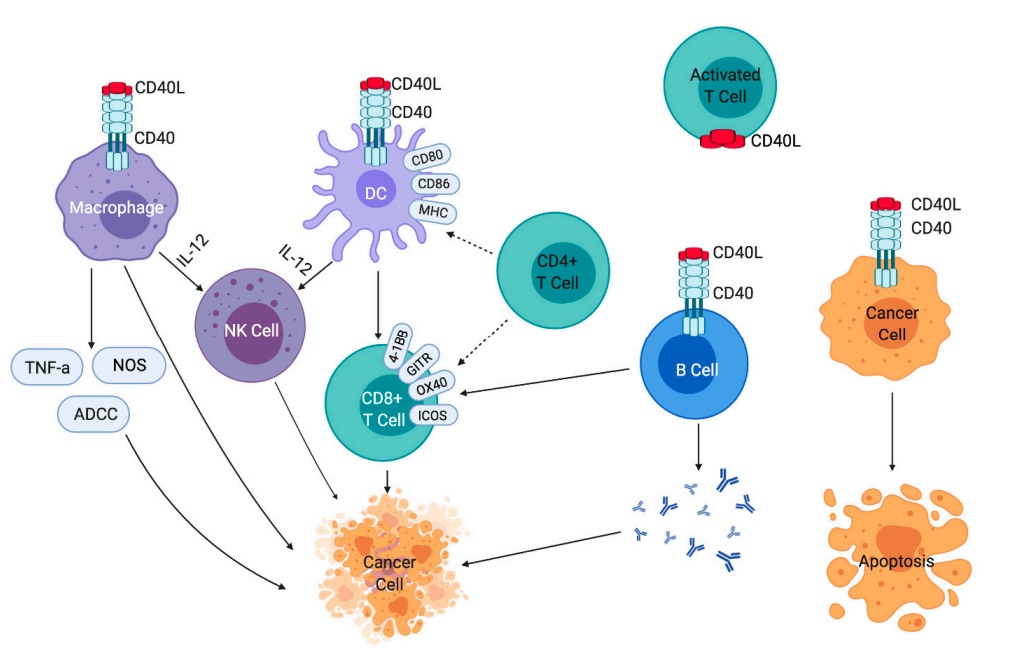 Fig. 1 Effects of CD40-CD40L signaling on immune cells and cancer cells. 1
Fig. 1 Effects of CD40-CD40L signaling on immune cells and cancer cells. 1
hPD-1/hCD40 Signal Pathway
hPD-L1 is up-regulated on T cells in the tumor microenvironment and binds to hPD-1 on the surface of T cells. After binding, it transmits negative regulatory signals to T cells, thereby inhibiting the activation of T cells, so that T cells will not attack tumor cells. The tumor cells, therefore adopt this mechanism to keep the immune system blind and avoid the attack from immune cells.
Upon binding to its ligand hCD40L, the membrane hCD40 molecules can be cross-linked and cultured. Subsequently, hCD40 is polymerized, which constitutes the structural basis and initiating factor of hCD40 signaling. They recruit TNFR-related factors (TRAF) in the inner membrane to promote intracellular signaling, thereby activating different signaling pathways, such as classical and non-classical nuclear factor κB (NF-κB), mitogen-activated protein kinase, phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K) pathways. hCD40/hCD40L occupies an important upstream position in the specific immune response. The main functions mainly include the regulatory effects on B cells, T cells, and dendritic cells (DCs). For example, the binding of hCD40 and hCD40L could promote the proliferation and differentiation of B cells, T cells and DCs. Besides, it participates in the secretion of immunoglobulins and type conversion.
Development of hPD-1/hCD40 Dual Humanized Mice
Anti-hCD40 agonist antibody has been used in combination with a variety of immunosuppressive agents, such as anti-hPD-1 antibody, to enhance the immune response. Nowadays, it becomes another potential unit of cellular immunotherapy. With advanced technology, Creative Biolabs provides the well-established hPD-1/hCD40 dual humanized mice and the related analysis services to advance your drug development. We have years of providing CRO services for our global clients and greatly advanced their project implementation. If you are about to carry out the study project evaluating your potential drugs, we will provide you with one-stop services. Please feel free to contact us for further discussions.
Creative Biolabs also offers other various Humanized Mouse Models you may be interested in:
Reference
- Djureinovic, Dijana, Meina Wang, and Harriet M. Kluger. "Agonistic CD40 antibodies in cancer treatment." Cancers 13.6 (2021): 1302. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
