Hi-Affi™ Humanized CD47 Immune Checkpoint Knockin Mouse Model
As the hard work of anticancer drug discovery, more accurate models to predict drug's efficacy is highly needed in preclinical drug discovery phase. The most widely used two immune checkpoint inhibitors are CTLA-4/B7 and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitory pathways, and both of them are now available for clinical use in cancer patients. Other interesting checkpoint inhibitors are also developed. CD47, which often expressed on tumor cells, is an important immune checkpoint in inhibition of macrophage phagocytosis, T cells, and dendritic cells. Creative Biolabs has successfully launched, commercialized and optimized an exclusive Hi-Affi™ “humanized” animal platform to provide specialty transgenic CD47 immune checkpoint knock-in mice to facilitate diverse immunotherapy development for our worldwide clients.
SIRP Alpha & CD47 Immune Checkpoint Pathway
Signal regulatory proteins (SIRP) are a multigene family of immune receptors encoded by a cluster of genes. The family includes five members: SIRPα, SIRPβ1, SIRPγ, SIRPβ2, and SIRPδ, of which SIRPα (also called CD172a) is the best-conserved member. SIRPα has an NH2-terminal CD47-ligand binding V-domain which can bind to CD47 to inhibitory signaling capacity.
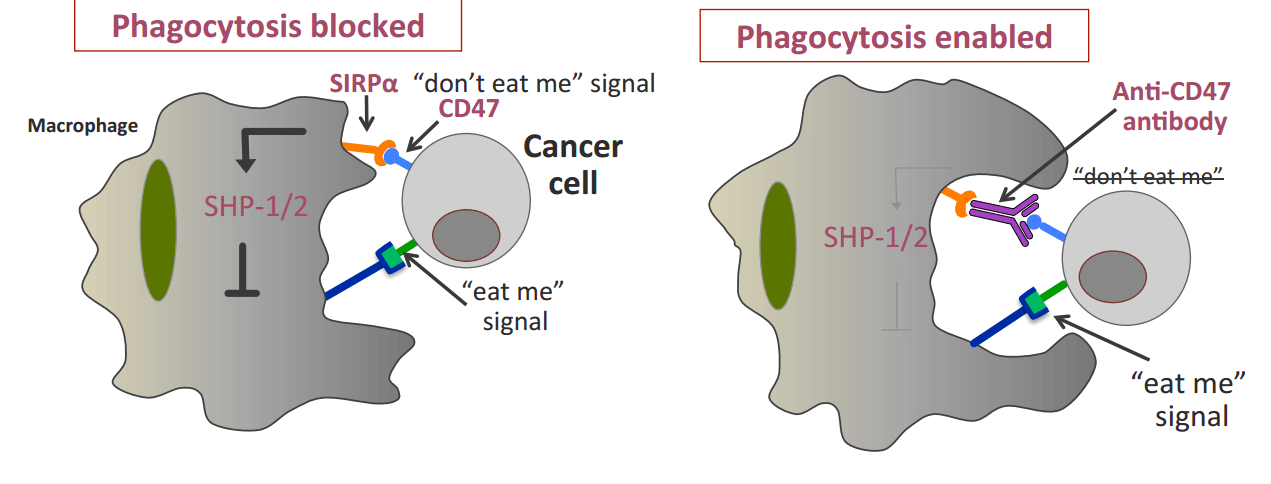 Fig.1 The CD47 immune checkpoint.
Fig.1 The CD47 immune checkpoint.
CD47 is a cell surface glycoprotein and is expressed on all normal cells in the body. It has a variety of functions including regulation of phagocytosis through binding to the macrophage and inhibition of T cells and dendritic cells. When CD47 binds to SIRPα, the immune checkpoint pathway sends a “don't eat me” message to macrophages by initiating signaling to inhibit phagocytosis. It has been demonstrated that many types of cancer cells [including acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), primary effusion lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leiomyosarcoma, and bladder cancer] increase the expression of CD47 to evade immune detection and phagocytosis. Therefore, many researchers use anti-CD47 blocking antibody to promote phagocytosis in vitro. The effect of reducing the growth of solid tumors of anti-CD47 blocking antibody has also been proven in animal models. Interestingly, it is also shown that anti-CD47 blocking antibody has synergy effect with anti-CD20 antibody to promote phagocytosis and to eliminate cancer cells in an in vivo xenograft model of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.

Development of Humanized CD47 Immune Checkpoint Knock-In Mice
Animal models, particularly rodents, provide possibilities to mimic many biological processes in humans. Recent studies of oncology rely on human tumor xenografts growing in immunodeficient mice. However, as immunodeficient mice lack a human immune system, it is inadequate to test immunotherapy. Given this, Creative Biolabs has developed a serial of well-established human immune checkpoint KI mouse models which allow researchers to study drugs that only recognize the human version of the checkpoint molecule. We also provide a full range of other Humanized Mouse Models to satisfy different needs:
Meanwhile, we can also provide a broad range of immune checkpoint mouse models, including but not limited to:
Please feel free to contact us for more details.
For Research Use Only.
