Hi-Affi™ hPD-1/hVISTA Dual Humanized Mouse Model
Clinical evidences have shown that in pancreatic cancer therapy, the response rate of existing immune checkpoint inhibitors is unmet, and treatment options for pancreatic cancer are already limited. The human V-domain immunoglobulin suppressor of T-cell activation (hVISTA) might be the promising target for pancreatic cancer therapy. The combinational use of anti-hVISTA drugs (small molecule or monoclonal antibody) and anti-hPD-1 antibody could be the effective treatment for patients with pancreatic cancer. Creative Biolabs has successfully established an optimized Hi-Affi™ “humanized” animal platform to offer specialty manipulated hPD-1/hVISTA dual humanized mice for our clients all over the world.
hPD-1/hVISTA Molecule
It is well known that in many human tumors, various special molecules are expressed on the surface of tumor cells. These molecules are as receptors and can interact with the corresponding ligands on the surface of immune cells, which will decrease the anti-cancer function of tumor-specific lymphocytes, thereby realizing tumor cells immune evasion. The human programmed cell death protein 1 (hPD-L1) we often mention is such a molecule.
hVISTA is one of these immune regulatory molecules and mainly expressed on macrophages. It is a newly discovered inhibitory immune checkpoint protein that prevents T cells in the immune system from being activated by self-antigens (such as those in cancer cells). hVISTA inhibits T cell proliferation and cytokine production in tumor cells and reduces tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells. CD68+ macrophages in pancreatic cancer have higher levels of hVISTA expression. Thus, the hVISTA pathway plays a role in suppressing immune responses, which results in the failure of anti-hPD-1 antibodies in pancreatic cancer therapy.
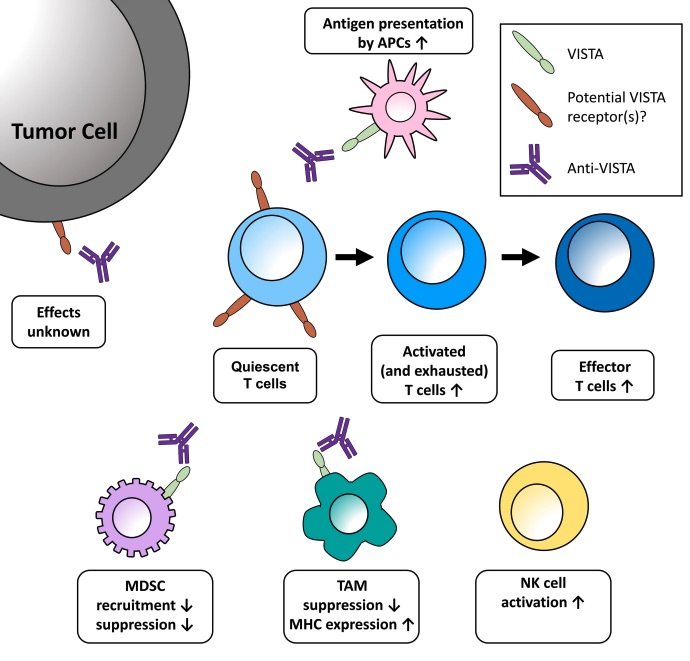 Fig. 1 Potential effects of VISTA blockade in the tumor microenvironment. 1
Fig. 1 Potential effects of VISTA blockade in the tumor microenvironment. 1
hPD-1/hVISTA Signal Pathway
Through the combination of hPD-1 and human programmed cell death ligand 1 (hPD-L1), tumor cells can cover the eyes of the immune system and escape the immune killing. Recent studies found that the deletion of hVISTA gene will lead to the redistribution of naïve T cell subsets: the silent (inactive) subpopulation is significantly reduced, and the memory-like activated T cell subpopulation is increased. In the absence of inherent hVISTA expression, naïve T cells behave more strongly at T cell receptor and cytokine stimulation at epigenetic and transcriptional levels. Deletion of hVISTA gene or blocking hVISTA with antibodies will result in significant expansion of antigen-specific T cells and reduced tolerance. However, under inflammatory conditions, hVISTA expression on antigen-specific T cells is reduced, and its ability to limit naïve T cell responses will disappear. The researchers believe that these findings indicate that hVISTA is a unique negative checkpoint receptor for naïve T cells. hVISTA may be a valuable target for regulating immune responses in cancer. Like other negative checkpoint regulators, blocking hVISTA in cancer may enhance the host's ability to generate an anti-tumor specific immune response. Previous animal studies have shown that the combined blocking of hPD-1 and hVISTA can improve the anti-tumor response in some tumor models.
Development of hPD-1/hVISTA Dual Humanized Mice
Monotherapy by blocking the hPD-1 pathway is unlikely to restore an effective T cell response because the untreated hVISTA inhibition pathway is also highly expressed and can suppress the T cell response in pancreatic cancer. Therefore, the combination of anti-hVISTA drug and anti-hPD-1 antibody may be an effective immunotherapy strategy for patients with pancreatic cancer. With advanced technology, Creative Biolabs has provided preclinical CRO services for many years and advanced lots of drug development projects for our global clients using our Hi-Affi™ “humanized” animal models. If you re interested in these humanized models, please feel free to contact us for more details.
Creative Biolabs also offers other various Humanized Mouse Models you may be interested in:
Reference
- Noelle, Randolph J., et al. "Clinical and research updates on the VISTA immune checkpoint: immuno-oncology themes and highlights." Frontiers in Oncology 13 (2023): 1225081. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
