Hi-Affi™ hPD-1/hPD-L1/hCTLA-4 Triple Humanized Mouse Model
Studies have confirmed several different immune checkpoints, such as PD-1, PD-L1, and CTLA-4. Antibodies that target these three immune checkpoints have been approved for clinical use. Nowadays, the combinational use of them becomes the focus of cancer treatment. Creative Biolabs has successfully established an optimized Hi-Affi™ “humanized” animal platform to offer specialty manipulated hPD-1/hPD-L1/hCTLA-4 triple humanized mice for our clients all over the world.
hPD-1/hPD-L1/hCTLA-4 Molecule
Human programmed cell death protein-1 (hPD-1) and its ligand human programmed cell death ligand-1 (hPD-L1) are a pair of immunoregulatory molecules presenting on immune cells and tissue cells. The interactions of them down-regulate the immune system's response to human cells and promote self-tolerance, thus preventing the autoimmune diseases. Studies demonstrated that the tumor cells utilize this mechanism via expressing hPD-L1 to escape the killing from the immune system.
Human cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (hCTLA-4), also known as differentiation cluster 152 (CD152), is a protein receptor that acts as an immune checkpoint and down-regulates the immune response. hCTLA4 is constitutively expressed in regulatory T cells (Tregs) and memory CD4+ cells, but is only upregulated in conventional T cells after activation (a phenomenon that is particularly pronounced in cancer). When combined with CD80 or CD86 on the surface of antigen-presenting cells (APCs), it acts as a "close" switch for immune activation.
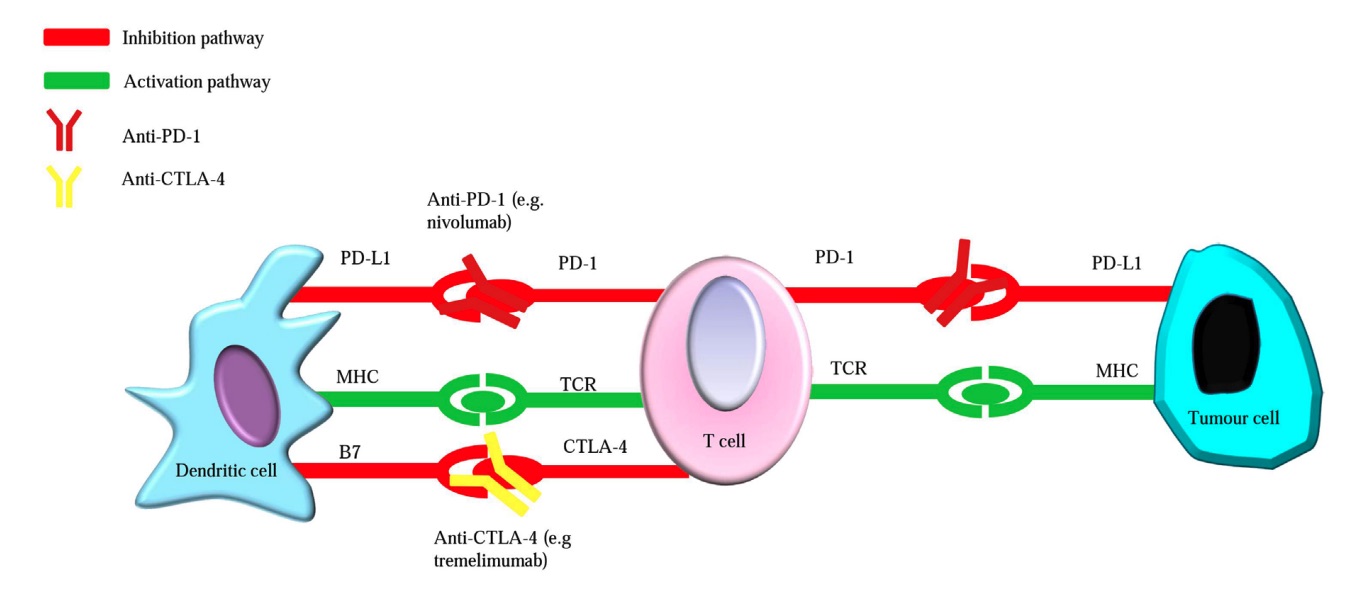 Fig. 1 Simplified mechanism of CTLA-4 and PD-1 inhibitors in tumor immunotherapy.1
Fig. 1 Simplified mechanism of CTLA-4 and PD-1 inhibitors in tumor immunotherapy.1
hPD-1/hPD-L1/hCTLA-4 Signal Pathway
Accumulated evidences suggest that hPD-1 and its ligands negatively regulate the immune response. hPD-L1 expression in tumors is associated with reduced survival rates of patients diagnosed with esophageal cancer, pancreatic cancer, and other types of cancer, highlighting this pathway as a target for immunotherapy. Triggering hPD-1, expressed on monocytes and up-regulated when monocytes are activated, its ligand hPD-L1 induces IL-10 production, which inhibits T cell function. hCTLA-4 is another inhibitory receptor on the surface of T cells. hCTLA-4 mainly regulates T cells during the initial activation of T cells by dendritic cells (DCs) and other APCs. Because hCTLA-4 has a higher binding affinity to the ligand CD86, hCTLA-4 is superior to the stimulatory receptor CD28 binding to CD86. hCTLA-4 and CD86 combine to transmit negative regulatory signals to T cells, thereby inhibiting the activation and expansion of T cells.
Development of hPD-1/hPD-L1/hCTLA-4 Triple Humanized Mice
The combination of anti-PD1, anti-PD-L1, and anti-CTLA-4 antibodies are more effective in treating multiple cancers than either antibody alone. The combined treatment with anti-PD1, anti-PD-L1, and anti-CTLA-4 therapeutic agents has become an important tumor therapy in the field of checkpoint suppression. To expand the number of beneficiaries and avoid drug resistance, the triple combination might be more effective and worthy of investigation. Creative Biolabs provides multiple Hi-Affi™ “humanized” animal models, including the hPD-1/hPD-L1/hCTLA-4 triple humanized mice. Our scientists have much experience in preclinical novel drug development and will assist you in your research implementation. If you have any problems about our study, please feel free to contact us for further discussions.
Creative Biolabs also offers other various Humanized Mouse Models you may be interested in:
Reference
- Wang, Shanshan, et al. "Brain metastases from hepatocellular carcinoma: recent advances and future avenues." Oncotarget 8.15 (2017): 25814. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
