Hi-Affi™ Humanized CD80 Immune Checkpoint Knockin Mouse Model
CD80 (B7-1), one of the immune checkpoint proteins, is expressed on dendritic cells, activated B cells and monocytes. CD80 is required to provide a costimulatory signal which is necessary for T cell activation and survival. As a world leader in the industry of drug discovery, Creative Biolabs has developed a well-established Hi-Affi™ platform including a series of well-established human immune checkpoint KI mouse models, which can provide you this humanized CD80 immune checkpoint knock-in mice with extensive experience and legendary transgenic techniques.
CD80 Immune Checkpoint Pathway
CD80 (cluster of differentiation 80), also known as B7-1 (referred to as B7), is a type I membrane protein which is a member of the surface immunoglobulin superfamily that is expressed by activated B cells, activated T cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Like the related protein CD86, CD80 is the ligand for CD28 (for autoregulation and intercellular association) and CTLA-4 (for autoregulation and intercellular association) at the cell surface of T cells. CD80 has a greater affinity for CTLA-4 over CD28 and works in concert with CD86 to prime T cells. The bond of CD80 with CD28 antigen is a costimulatory signal for activation of the T-cell and induces T-cell proliferation and cytokine production. CD80 plays a role in the induction of innate immune responses by activating the NF-κB-signaling pathway in macrophages. Thus, CD80 has been regarded as promising therapeutic targets for autoimmune diseases and various carcinomas.
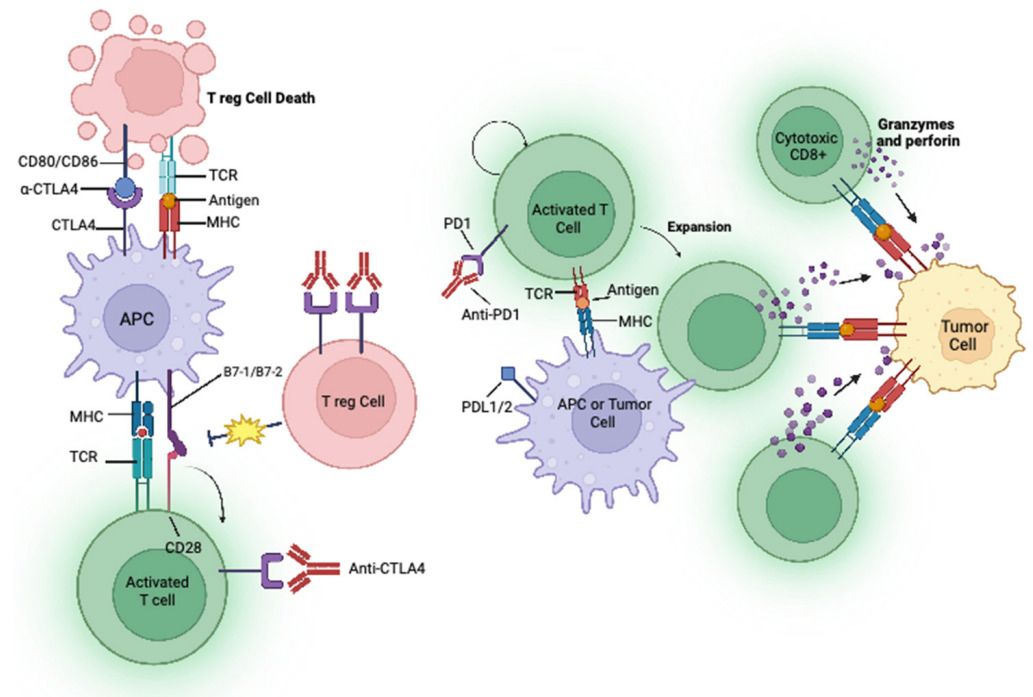 Fig. 1 Mechanisms of action of immune checkpoint inhibitors. 1
Fig. 1 Mechanisms of action of immune checkpoint inhibitors. 1
Development of Humanized CD80 Immune Checkpoint Knock-In Mice
Given their role in suppressing effector T-cell responses, immune checkpoints are being targeted for the treatment of cancer. What's more, immune checkpoint inhibitors have been demonstrated to enhance ex vivo effector T-cell responses from patients with chronic viral, bacterial, or parasitic infection, including HIV, tuberculosis, and malaria. Although the data from clinical trials in infectious diseases are still sparse, these inhibitors have great potential for treating chronic infections, especially when combined with therapeutic vaccines. Creative Biolabs, who always focus on the research spotlight of anti-tumor novel drug discovery, has successfully established a series of well-characterized Hi-Affi™ “humanized” animal models, including CD80. Our experienced scientists focused on humanized mouse models are willing to assist you in your studies of anti-tumor immunotherapies. What's more, we also established comprehensive in vitro immunomodulation assessment service using various approaches. Please feel free to contact us for more details.
Creative Biolabs also offers other Humanized Mouse Models you may be interested in:
Reference
- Stanley, Robyn et al. "Immunotherapy through the Lens of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer." Cancers vol. 15,11 2996. 30 May. 2023, doi:10.3390/cancers15112996. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
