Hi-Affi™ hPD-L1/hCD40 Dual Humanized Mouse Model
The anti-PD-L1 antibody is a well-known effective cancer treatment drug while still has some limitations. Its combination with the anti-CD40 agonist antibody is considered as a promising alternative to enhance the anti-tumor immunity, which has been investigated in preclinical and clinical studies. Creative Biolabs has successfully established an optimized Hi-Affi™ “humanized” animal platform to offer specialty manipulated hPD-L1/hCD40 dual humanized mice for our clients all over the world.
hPD-L1/hCD40 Molecule
The well-known immune checkpoint, human programmed cell death-ligand 1 (hPD-L1) is a transmembrane protein in various tumor cells. The hPD-L1 and its receptor human programmed cell death protein-1 (hPD-1) involve in the negative regulation of immune responses. hPD-L1 in tumor cells inhibits the activation and function of T cells, which results in immune evasion of tumor cells.
Human CD40 (hCD40, also known as TNFRSF5) belongs to the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily (TNFRSF). hCD40 is a type I membrane glycoprotein that was initially identified as a surface marker of bladder cancer cells and B cells. It was later found that hCD40 is expressed on antigen-presenting cells (APCs), including monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells (DCs). hCD40 is also expressed by platelets and some non-hematopoietic cell types such as fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells.
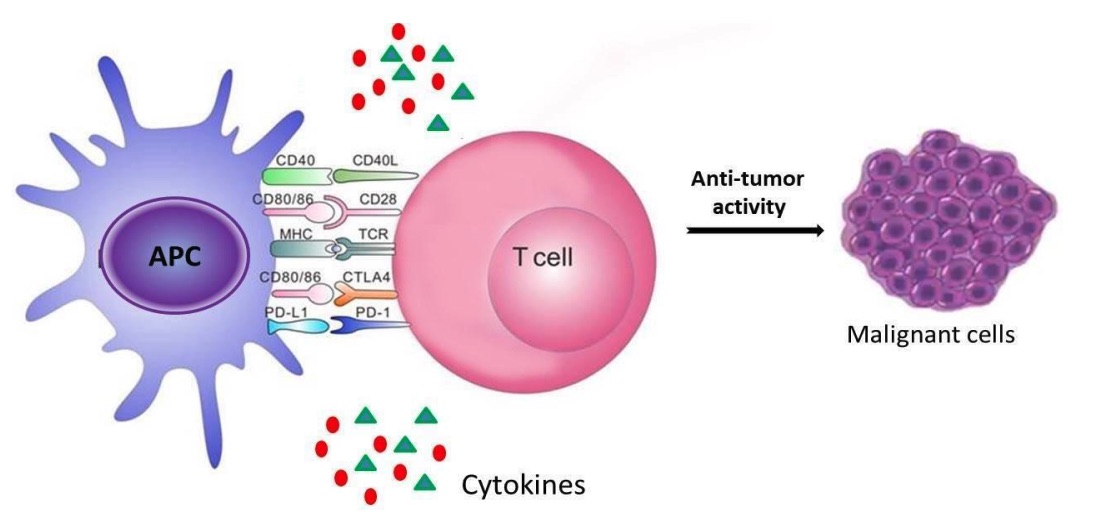 Fig. 1 The main immune cells recruited for tumor defense. 1
Fig. 1 The main immune cells recruited for tumor defense. 1
hPD-L1/hCD40 Signal Pathway
Under normal circumstances, to prevent activated T cells from attacking normal human cells, the immune system can regulate the activation process of T cells through negative regulatory pathways, such as the hPD-L1/hPD-1 signaling pathway. The hPD-L1/hPD-1 signaling pathway can adjust the strength of its immune response to maintain immune tolerance, thereby preventing the accidental injury by T cells. However, tumor cells adopt this signal pathway to suppress the immune activity of T cells, which is conducive to immune escape and uncontrolled growth of tumor cells.
hCD40 and its ligand hCD40L is a pair of costimulatory molecules. After interacting on the cell surface, they recruit TNFR-related factors (TRAF) in the inner cell membrane to promote intracellular signaling. The ligation of hCD40 and hCD40L could activate different signaling pathways, such as classical and non-classical NF-κB pathways, mitogen-activated protein kinase, phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K), and phospholipase Cγ pathway, etc. The hCD40/hCD40L axis participates in the body's humoral and cellular immune responses. It plays a key role in the regulation of B and T cells function, specifically in secretion of effector cytokines, production of antibody, switching of Ig class, and activation, proliferation, and differentiation of cells.
Development of hPD-L1/hCD40 Dual Humanized Mice
Many studies have demonstrated the key role of hCD40 in regulating the function of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells which is necessary for attacking tumor cells. Also, it has been confirmed in various tumor models that the anti-CD40 agonist antibody can promote the immune responses. Thus, the combination of anti-hPD-L1 antibody and anti-hCD40 agonist antibody is expected to be a promising cancer treatment. Creative Biolabs is a professional CRO company and has been recognized by our global clients. We have assisted our clients in their research using our stable and verified Hi-Affi™ “humanized” animal models you are interested in these models, please feel free to contact us for more details.
Creative Biolabs also offers other various Humanized Mouse Models you may be interested in:
Reference
- Nuzzo, Genoveffa, et al. "Antitumor potential of immunomodulatory natural products." Marine Drugs 20.6 (2022): 386. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
