Hi-Affi™ Humanized CD27 Immune Checkpoint Knockin Mouse Model
Cancer immunotherapy is now in the center stage of oncology due to the outcome of clinical trials with blocking antibodies to the T-cell co-inhibitory receptors such as CTLA-4 and PD-1. Apart from blocking T-cell coinhibitory receptors, deliberate stimulation of T-cell co-stimulatory receptors, including CD27, is expected to increase the success of cancer immunotherapy with immunomodulatory monoclonal antibodies. With years of experience, Creative Biolabs has successfully launched a series of well-characterized Hi-Affi™ “humanized” animal models to provide the most appropriate platform for your research on evaluating potential tumor immunotherapy.
CD27 Immune Checkpoint Pathway
CD27, a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily (TNFRSF7), can promote the antigen-specific expansion of naive T cells and is required for the generation of T cell memory. Unlike certain other TNFR family members, CD27 is already present on naive CD4+ and CD8+ T cells while most of other co-stimulatory TNFRs are only synthesized after T cell activation. Upon activation, naive CD4+ and CD8+ T cells transiently up-regulate the expression of CD27. When activated, T cells would proteolytically shed CD27 from the cell surface, thus leading to circulating soluble CD27 which can be regarded as a diagnostic marker of T-cell activation. It has been proved that CD27 costimulation may suppress Th17 effector cell function. The activity of CD27 is restricted by the transient availability of its ligand CD70/TNFSF7, which is constitutively expressed on medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTECs) and dendritic cells. Apart from this, CD70/TNFSF7 is specifically expressed after immune activation, as it is found on activated DCs, B cells, conventional- and regulatory T cells and NK cells. The expression of CD70/TNFSF7 is exceedingly regulated by antigen since it is under control of PRRs, T cell and B cell antigen receptors, and its expression is further tuned by cytokines such as IL-1α, IL-12, TNFα, prostaglandin E2 and by CD28- and CD40 co-stimulation. Epithelial cells and other cell types may acquire CD70/TNFSF7 upon malignant transformation. The CD27 ligand CD70/TNFSF7 was similarly presented to promote TCR/CD3-induced proliferation of naive CD4+ and CD8+ human T cells as well as the generation of effector cells.
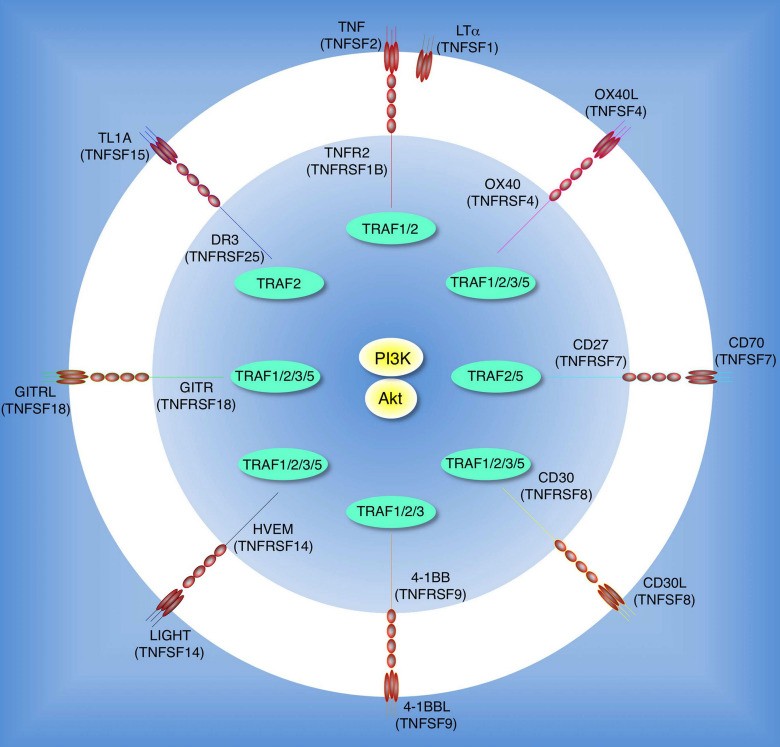 Fig. 1 CD27, CD30, and GITR promote activation of the PI3K or Akt pathway. 1
Fig. 1 CD27, CD30, and GITR promote activation of the PI3K or Akt pathway. 1
Distinguishingly from other TNFR family members, CD27 and related co-stimulatory TNFRs do not have a proapoptotic death domain. Instead, they have cytoplasmic tail motifs that bind to TNFR associated factors (TRAFs), which are adaptor molecules that link to the NF-κB and JNK signaling pathways. Adaptor proteins TRAF2 and TRAF5 have been confirmed to mediate the signaling process of CD27. Additionally, SIVA, a proapoptotic protein, also can bind to CD27 and is supposed to be critical in apoptosis induced by CD27.
Development of Humanized CD27 Immune Checkpoint Knock-In Mice
According to the previous experimental evidence, the CD27/CD70 co-stimulatory system is believed to play a vital role in immune regulation, by promoting T, B and NK cell responses and particularly the CTL response, which motivates its targeting in cancer immunotherapy. CD27 agonism is now expected to be most successful when used in combination with other forms of treatment that specially targeted this bottleneck. What's more, CD27 agonist mAb may also be applied in therapeutic vaccination against cancer.
At Creative Biolabs, our experienced scientists have established a full-fledged and stable Hi-Affi™ platform, aiming at providing an array of validated human immune checkpoint KI mouse models. We also established comprehensive in vitro immunomodulation assessment service using various approaches. Please feel free to contact us for more details.
Creative Biolabs also offers other Humanized Mouse Models you may be interested in:
Reference
- So, Takanori, and Michael Croft. "Regulation of PI-3-Kinase and Akt Signaling in T Lymphocytes and Other Cells by TNFR Family Molecules." Frontiers in immunology vol. 4 139. 7 Jun. 2013, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2013.00139.
For Research Use Only.
