Definition Molecular Basis Biological Functions Regulatory Mechanisms Complement Analysis Resources
The complement system is composed of 30 different soluble proteins and glycoproteins which are mainly produced by hepatocytes, including serum proteins, serosal proteins, and cell membrane receptors. Complement activation is triggered by an antibody when it binds to the antigen. It can also be triggered by certain components of innate immunity. Therefore, the complement system plays a role in both innate and acquired immunity.
This article delves into the science behind the activation of complement, its mechanisms, and its critical role in immune defense.
What is Complement Activation?
The complement system is a pivotal component of innate immunity, serving as a first line of defense against pathogens. The process of complement system activation is a highly coordinated cascade of enzymatic reactions that bridges innate and adaptive immunity.
The complement system is activated only during an inflammatory response. After activation, it can enhance the ability of antibodies and phagocytes to remove microorganisms and damaged cells from the organism and promote inflammation. The complement system can be activated by three different pathways: the classical pathway, the alternative pathway and the lectin pathway. All three pathways converge at the C3 cleavage point, and then generate the membrane attack complex C5b-9, resulting in lysis of the cells (Fig.1).
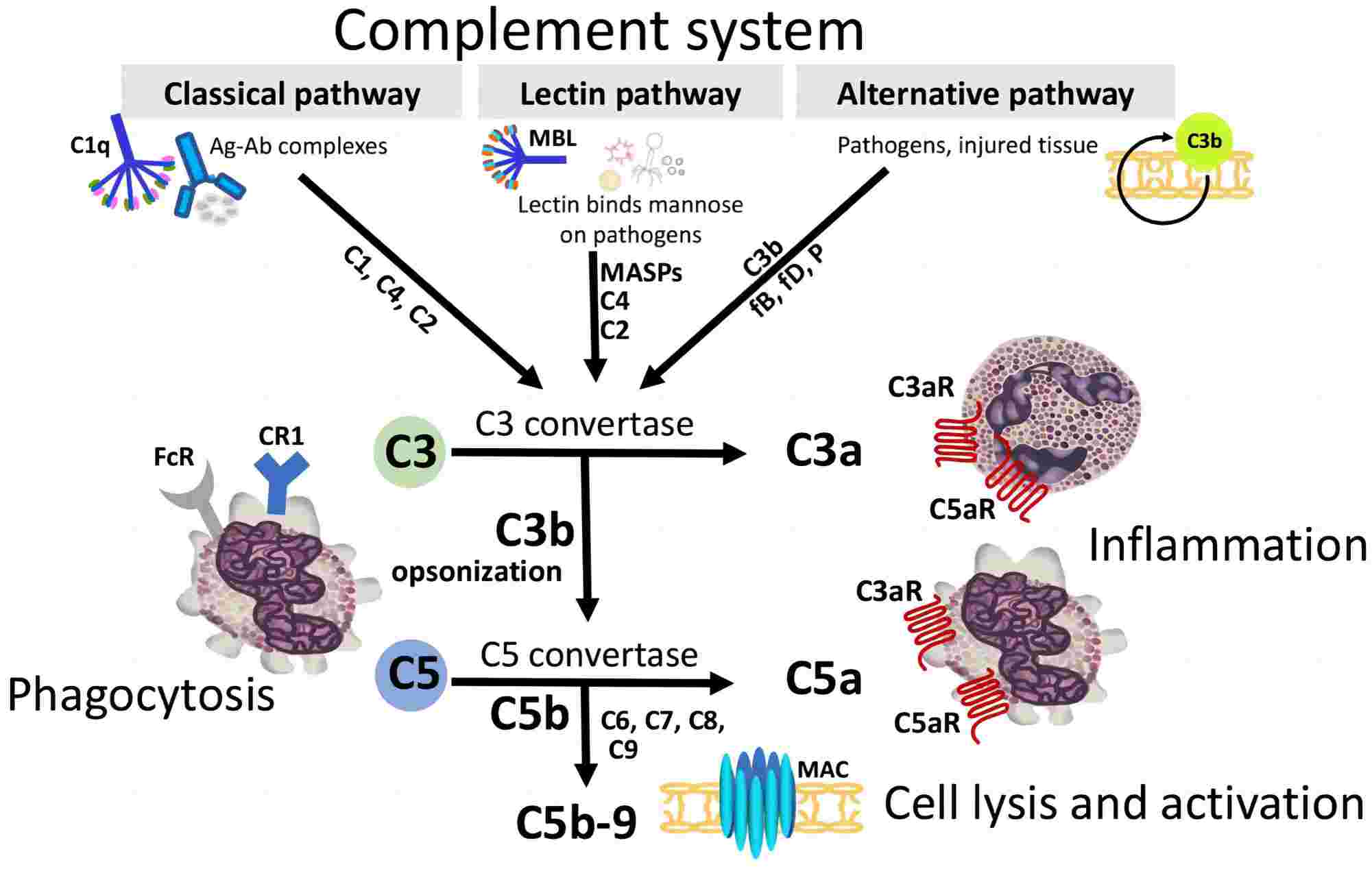
Fig. 1 Complement activation pathways.1, 2
Complement Activation in Classical Pathway
The classical pathway begins with the formation of the antigen-antibody complex. When the antibody (IgM/IgG) binds to the antigen, the Fc fragment of the antibody undergoes a conformational change, thereby exposing the binding site of the C1 protein. Therefore, antibodies activate the complement system only when they bind to an antigen.
Complement Activation in Alternative Pathway
Unlike classical pathway, alternative pathway does not require the antigen-antibody complex for the initiation of the complement activation. Alternative pathway is initiated by cell surface components that are foreign to the host. These surface molecules include lipopolysaccharide etc. The alternative pathway begins with the activation of C3 and requires the participation of factor B and factor D.
Complement Activation in Lectin Pathway
The lectin pathway is initiated when mannose-binding lectin (MBL) binds to mannose residues on glycoproteins or carbohydrates on the surface of microorganisms. The microorganisms that induce the lectin pathway are bacteria, including Salmonella, Listeria, and Neisseria strains, some fungi, and certain viruses, such as HIV-1. The lectin recognizes and binds the carbohydrate of the target cell and then activates complements.
Molecular Basis of Complement Activation
The complement system consists of a series of proteins that work in a cascading manner to detect, tag, and eliminate threats. The complement cascade refers to a sequential activation of proteins, amplifying the immune response. These proteins work together to recognize pathogens, facilitate their destruction, and trigger inflammation. The process of activating complement culminates in the formation of complement activation pores in membranes, leading to cell lysis.
Three Primary Activation Pathways
Complement activation occurs via three main pathways. Each pathway has distinct triggers but converges at the formation of C3 convertase, which amplifies the cascade.
Table 1 Three primary activation pathways.
|
Activation Pathways
|
How to Trigger
|
Molecules Involved in the Pathway
|
|
Classical Pathway
|
The classical pathway for complement activation is initiated by immune complexes formed between antigens and IgG or IgM antibodies.
|
-
Initiated by the binding of C1q to antigen-antibody complexes
-
leads to the cleavage of C4 and C2
-
Forms the C3 convertase
|
|
Alternative Pathway
|
The alternative pathway complement does not rely on antibodies for activation. Instead, it is triggered by the spontaneous hydrolysis of C3 in the plasma.
|
-
Begins with spontaneous hydrolysis of C3 to form C3(H2O)
-
Enables factor B binding and subsequent cleavage by factor D
-
Ultimately generates the alternative pathway C3 convertase C3bBb
|
|
Lectin Pathway
|
The lectin pathway of complement system is activated by MBL binding to carbohydrate structures on microbial surfaces.
|
-
MBL recognizes specific glycan structures on the surface of pathogenic microorganisms to initiate complement activation
-
MASP-1 binds to pattern recognition molecules and initiates complement cascade
-
MASP-2 as effector enzymes and key mediators
|
Convergence Point of Pathways
Regardless of the initiating pathway, all complement pathways converge to activate C3, leading to the complement cascade classical pathway and downstream effects. These include:
Biological Functions of Complement Activation
The complement system is a cornerstone of the innate immune response, serving as one of the first lines of defense against pathogens. Its activation plays a pivotal role in immune surveillance, inflammation, and homeostasis.
Table 2 Biological functions of complement activation.
|
Key Biological Functions
|
Pathological Conditions
|
|
Pathogen Elimination
|
-
Opsonization: C3b and C4b deposition on pathogen surfaces enhances phagocytic recognition and clearance, significantly improving the efficiency of cellular immune responses.
-
Formation of the MAC: The terminal complement components (C5b-C9) assemble into the MAC, creating transmembrane pores that compromise pathogen membrane integrity and lead to osmotic lysis.
-
Inflammatory Response Modulation: Anaphylatoxins C3a, C4a, and C5a generate localized inflammatory responses, recruiting immune cells and enhancing vascular permeability.
|
|
Immune Complex Clearance
|
-
Solubilization of immune complexes, preventing their pathological deposition in tissues
-
Enhancement of immune complex transport to specialized clearance organs
-
Facilitation of efficient removal by phagocytic cells
|
|
Bridge Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
|
-
Enhancement of B cell activation and antibody production
-
Modulation of T cell responses and immune synapse formation
-
Augmentation of antigen presentation efficiency
|
Understanding complement activation's biological functions has led to significant therapeutic developments. Modern therapeutic approaches focus on:
-
Complement inhibition in autoimmune conditions
-
Enhancement of complement-dependent cytotoxicity in cancer treatment
-
Regulation of complement activation in inflammatory diseases
In addition to targeted therapeutic applications, complement activation is commonly used in diagnostics. Complement activation markers serve as valuable diagnostic tools for:
-
Monitoring disease progression
-
Assessing treatment efficacy
-
Predicting clinical outcomes
Regulatory Mechanisms of Complement Activation
Precise regulation of the activation pathways of the complement system is essential for normal immune function and tissue homeostasis.
Fluid-Phase Regulatory Proteins
Several plasma proteins act as regulators to prevent excessive or inappropriate complement activation:
Table 3 Soluble regulators
|
Regulatory Proteins
|
Short Descriptions
|
Functions
|
|
C1 Inhibitor (C1-INH)
|
C1-INH serves as a critical regulator of both the classical and lectin pathways. It is a 105-kDa serine protease inhibitor.
|
-
Binding to and inactivating C1r and C1s components of the C1 complex
-
Inhibiting MASP-1 and MASP-2 proteases in the lectin pathway
-
Preventing spontaneous activation of the classical pathway
|
|
Factor H
|
Factor H is pivotal in regulating the alternative pathway. By binding to C3b, it prevents the formation of C3 convertase and accelerates the decay of existing convertases. Additionally, Factor H serves as a cofactor for factor I-mediated cleavage of C3b into its inactive form, iC3b.
|
-
Acting as a cofactor for factor I-mediated C3b cleavage
-
Accelerating the decay of the C3bBb convertase
-
Competing with factor B for C3b binding
|
|
Factor I
|
Factor I is a serine protease that inactivates C3b and C4b by cleaving them in the presence of cofactors such as factor H and complement receptor 1 (CR1) .
|
-
Factor I-mediated C3b cleavage
|
Membrane-Bound Regulators
Host cells are equipped with membrane-bound complement regulatory proteins that protect them from autologous complement-mediated damage.
-
Decay-Accelerating Factor (DAF/CD55): DAF destabilizes C3 and C5 convertases on the cell surface, preventing complement-mediated cytotoxicity.
-
Membrane Cofactor Protein (MCP/CD46): MCP functions as a cofactor for Factor I, facilitating the cleavage of C3b and C4b.
-
Protectin (CD59): CD59 inhibits the assembly of the MAC by preventing the incorporation of C9, thereby protecting host cells from lysis.
-
CR1/CD35: CR1 acts as both a decay-accelerating factor and a cofactor for Factor I, regulating C3b and C4b activity.
Cellular Regulation of Complement Activation
Host cells employ sophisticated mechanisms to regulate complement protein expression.
-
Post-translational modifications affecting protein function
-
Tissue-specific expression patterns of regulatory proteins
-
Cross-talk between complement receptors and other immune receptors
-
Regulation of inflammatory mediator production
-
Modulation of cellular activation thresholds
Complement Analysis
Analyzing complement activation is vital to understanding immune dynamics in disease and therapeutic contexts. Such assessments typically involve:
-
Quantifying activation products
Biomarkers such as C3a, C4a, C5a, and sC5b-9 are measured to evaluate the extent and type of complement activation.
-
Assessing pathway-specific activation
ELISA-based assays tailored for individual pathways (e.g., CH50 for classical and AP50 for alternative pathways) offer critical insights into pathway-specific dysfunctions or overactivation.
-
Kinetic analysis
Time-resolved assays monitor the progression of complement activation, providing insights into regulatory mechanisms and potential inhibitors.
-
Cell-based complement deposition assays
Utilizing flow cytometry or microscopy, these assays assess the deposition of complement components (e.g., C3b or MAC) on cell surfaces, offering spatial and quantitative data.
Complement activation analysis provides unparalleled insights into the dynamics of the immune system. Advances in analytical methods and applications continue to expand the scope of this critical field. For customized solutions for complement activation analysis, Creative Biolabs offers a wide range of cutting-edge assays and expert consulting. Contact us today to learn how our expertise can enhance your research or preclinical program.
Creative Biolabs offers comprehensive complement-related products and complement test services, including:
Resources
References
-
Girardi, Guillermina, et al. "Essential role of complement in pregnancy: from implantation to parturition and beyond." Frontiers in immunology 11 (2020): 1681.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections: