Classical Pathway Basics Mechanism of Activation Regulatory Mechanisms Experimental Approaches Resources
The complement system is a critical component of innate and adaptive immunity, functioning as a proteolytic cascade to eliminate pathogens and modulate immune responses. Among its three primary activation routes - the classical pathway, the lectin pathway, and the alternative pathway - the classical pathway stands out due to its antibody-dependent nature.
Overview of the Classical Pathway
The classical pathway is one of the main pathways of complement activation. It is primarily triggered by the binding of C1 to antigen-antibody complexes containing IgG or IgM in the presence of complement components C1, C4, C2, Ca2+ and Mg2+ cations. IgG and IgM are the most effective activators of this pathway. They combine with antigens to form antigen-antibody complexes, which react in the order of C1q, C1r, C1s, C4, C2, C3, C5, C6, C7, C8 and C9. Different IgG subclasses have different abilities to activate the classical pathway. Although IgG1, IgG2, and IgG3 (most effective) can activate complement, IgG4 is not able to activate at all.
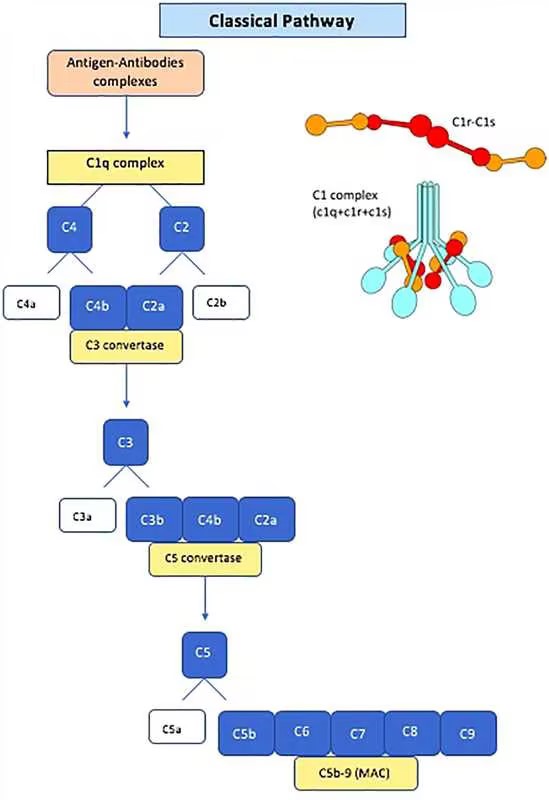
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the classical pathway of the complement system.1,2
Activation of this pathway amplifies immune defense by:
-
Opsonization: Tagging pathogens for phagocytosis.
-
Inflammation: Recruiting immune cells to the site of infection.
-
Membrane Attack Complex (MAC): Direct lysis of target cells.
Key Components of the Classical Pathway
The classical complement system is a well-coordinated interplay of proteins that function sequentially to propagate the complement cascade. Each component plays a distinct role in the pathway's activation and amplification.
The classical pathway begins with the formation and activation of C1qr2s2 by the antigen-antibody complex and ends with the formation of a MAC. The whole process can be divided into the following parts.
Table 1 The whole process of the classical pathway.
|
Process
|
Description
|
Key Components
|
|
Initiation
|
The activation of the classical pathway begins with the binding of at least two globular heads of the C1qr2s2 complex to the antigen-antibody complex through the Fc fragment of the antibody.
|
C1 is the first complement component involved in the classical pathway. It is a complex composed of three polypeptide chains (C1q, C1r and C1s).
-
C1q: A hexameric recognition protein that binds to the Fc region of IgG or IgM antibodies. The interaction requires a minimum of two antibody molecules for stable binding.
-
C1r and C1s: These are serine proteases. Upon C1q binding to immune complexes, C1r is auto-activated, which subsequently activates C1s, initiating downstream cleavage events.
|
|
Formation of C3 Convertase
|
The binding of the Cqr2s2 globular head results in a conformational change in the C1q stem. This change is transmitted to C1r2 and C1s2 in turn, causing C1r to be activated by auto-cleavage and cleaving C1s. At this stage, the Cqr2s2 complex has been fully activated.
|
The cleaved C1s can cleave C4 and C2.
-
C4: C1s cleaves C4 into C4a and C4b, which covalently binds to the pathogen surface or immune complex.
-
C2: C1s also cleaves C2 into C2a and C2b. C2a associates with C4b, forming the C3 convertase (C4b2a).
|
|
Formation of C5 Convertase
|
In the presence of Mg2+, C3 convertase cleaves C3 into C3a and C3b. C3b binds to the membrane to form C4b2a3b complex while C3a remains in the microenvironment. The C4b2a3b complex functions as C5 convertase, which cleaves C5 into C5a and C5b. The production of the C5 convertase marks the end of the classical pathway.
|
-
C3 convertase: The C3 convertase cleaves C3 into C3a and C3b, amplifying the cascade and leading to robust complement activation.
-
C5 convertase: The binding of C3b to the C3 convertase forms the C5 convertase (C4b2a3b), which cleaves C5 into C5a and C5b.
|
|
Formation of MAC
|
C5b initiates the assembly of the MAC, resulting in lysis of the target cell.
|
-
C5b: C5b combines with the C5 convertase to form a C4b2a3b5b complex, which acts as the catalyst to form the MAC.
-
C6, C7: C5b binds to C6 and C7 sequentially to form the complex C5b67.
-
C8: The membrane-bound C5b67 serves as a receptor for C8 and binds to it. C8 also inserts itself into the membrane.
-
C9: The membrane-inserted complex C5b678 binds the C9 molecule and polymerizes it into a 12-15 unit tubular channel of about 10 nm diameter.
|
Mechanism of Activation of the Classical Pathway
The classical pathway of complement activation is a meticulously regulated cascade that bridges innate and adaptive immunity. From the initial recognition of immune complexes by C1q to the formation of the lytic MAC, each step underscores the precision and amplification inherent in the complement system. Understanding this pathway offers insights into its role in host defense, as well as its implications in autoimmune and inflammatory conditions.
The classical pathway is initiated by the recognition of an antigen-antibody complex by the C1 complex. Among these, C1q is the recognition molecule that binds to the Fc region of Ig molecules.
-
C1q has a bouquet-like structure with six globular heads. Each head can bind to the Fc domain of IgM or IgG.
-
IgM, being pentameric, provides multiple binding sites for C1q, making it a more potent activator compared to IgG, which requires two or more molecules for effective C1q engagement.
-
Upon binding to the antigen-antibody complex, conformational changes are induced in C1q. The conformational shift in C1q exposes C1r's active site, allowing it to autoactivate through cleavage.
-
Activated C1r then cleaves and activates C1s, initiating its enzymatic activity.
Cleavage of C4 and C2
Activated C1s enzymatically cleaves C4, a plasma glycoprotein, into two fragments:
-
C4a: A small peptide with anaphylatoxin activity.
-
C4b: C4b contains reactive thioester groups that facilitate its attachment to surfaces. Once anchored, it serves as a scaffold for the assembly of the C4b2 complex.
C1s also cleaves C2, generating:
-
C2a: The enzymatically active component.
-
C2b: A smaller fragment with no known enzymatic function.
C4b and C2a are associated with forming the C4b2a complex, which is also known as the classical pathway C3 convertase. This enzyme complex is pivotal for the amplification of the complement cascade.
C3 Cleavage and Amplification Loop
The C4b2a complex functions as a C3 convertase, cleaving C3, the most abundant complement protein in plasma, into:
-
C3a: A potent anaphylatoxin that recruits immune cells.
-
C3b: A versatile opsonin that binds covalently to pathogens and immune complexes.
C3b deposition on surfaces significantly enhances the efficiency of complement activation by forming additional C3 convertase complexes. This amplification loop ensures a robust response to even small amounts of immune complex or antigen.
Terminal Pathway Progression
When additional C3b molecules associate with the C4b2a complex, it forms the C5 convertase (C4b2a3b). This complex cleaves C5 into:
-
C5a: A strong chemoattractant and anaphylatoxin.
-
C5b: The initiating molecule of the terminal complement pathway.
C5b binds sequentially to C6, C7, C8, and multiple C9 molecules. The polymerization of C9 forms a pore-like structure in the membrane of the target cell, resulting in osmotic lysis and cell death.
Regulatory Mechanisms of the Classical Pathway
The classical pathway relies on the sequential activation of complement components, starting with C1q, C1r, and C1s, and leading to the formation of the MAC. While this cascade is essential for pathogen clearance, unchecked activation can result in severe collateral damage to host tissues. Regulatory proteins play a critical role in maintaining balance within the classical pathway.
Preventing Overactivation of the Classical Pathway
Table 2 Regulatory proteins in maintaining balance within the classical pathway.
|
Regulatory Proteins
|
Function
|
Mechanism
|
Clinical Significance
|
|
Decay-Accelerating Factor (DAF)
|
DAF, also known as CD55, inhibits the formation and activity of the C3 and C5 convertases. By accelerating the decay of these convertases, it prevents the amplification of the complement cascade.
|
DAF interacts with C3b and C4b, displacing the enzymatic components (Bb or C2a) from the convertases. This action halts the cascade before the terminal effector mechanisms are triggered.
|
Deficiencies in DAF are associated with conditions such as PNH, where complement-mediated red blood cell lysis occurs.
|
|
CD59 (Protectin)
|
CD59 directly inhibits the formation of the MAC by binding to C8 and C9, the final components of the pathway.
|
By preventing C9 polymerization, CD59 ensures that the MAC does not indiscriminately lyse host cell membranes.
|
Insufficient CD59 expression is linked to increased susceptibility to hemolytic diseases and other complement-mediated disorders.
|
|
Factor I
|
Factor I is a serine protease that degrades activated complement components, particularly C3b and C4b, in the presence of cofactors.
|
Factor I requires cofactors such as factor H, C4-binding protein (C4BP), or membrane cofactor protein (MCP/CD46) to inactivate C3b and C4b. This action prevents further complement activation and amplification.
|
Mutations or deficiencies in factor I can lead to uncontrolled complement activity, predisposing individuals to autoimmune diseases and inflammatory conditions.
|
Experimental Approaches to Study the Classical Pathway
The classical pathway of the complement system plays a pivotal role in host defense and immune regulation. Its intricate cascade of events, from C1 complex activation to the formation of the MAC, requires precise methodologies for analysis and evaluation.
Techniques for Detection and Quantification
A comprehensive understanding of the classical pathway necessitates the use of robust and sensitive assays. These techniques not only elucidate the activation status of complement components but also evaluate functional outcomes essential for preclinical and therapeutic research.
Table 3 Techniques for detection and quantification
|
Techniques
|
Applications
|
|
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
|
ELISA is particularly effective for detecting activation markers , such as:
-
C1q: Indicates early activation of the classical pathway.
-
C4b/C4d: Reflects subsequent cleavage events.
-
C5a: A potent anaphylatoxin produced downstream.
|
|
Hemolytic Assays
|
These assays measure the ability of serum to lyse antibody-sensitized erythrocytes, providing a direct readout of complement activity.
-
CH50 Assay : Quantifies the overall activity of the classical pathway by determining the serum dilution required to achieve 50% hemolysis.
-
Modified Hemolytic Assays: Employ alternative target cells, such as sheep erythrocytes, to evaluate specific inhibitory effects or therapeutic candidates.
|
|
Complement Functional Assays
|
Beyond hemolytic assays, complement functional assays encompass a range of techniques to measure specific component activities. These include:
-
C1 Inhibitor Functional Assays: Evaluate the regulation of C1 complex activation.
-
C3 and C5 Convertase Assays: Focus on enzyme activity at pivotal junctions in the cascade.
-
Alternative Readouts: Employ fluorescence, chemiluminescence, or other advanced detection modalities for higher sensitivity.
|
Creative Biolabs' Expertise in Complement Analysis
Creative Biolabs is at the forefront of complement research, offering an extensive suite of services tailored to studying the classical pathway. Recognizing the diverse needs of complement research, we specialize in custom assay development. We provide:
-
Tailored ELISA Kits: Designed for precise quantification of complement activation markers in serum, plasma, or tissue samples.
-
High-Throughput Hemolytic Assays: Optimized for large-scale drug screening or biomarker discovery.
-
Multiplex Assays : Simultaneously evaluate multiple components of the classical pathway, enhancing data richness and efficiency.
Applications in Complement Therapeutics
Creative Biolabs is deeply invested in complement therapeutics, leveraging our expertise to develop novel inhibitors targeting the classical pathway. Our services span:
-
Preclinical Evaluation: Functional assays for drug efficacy and specificity.
-
Biomarker Discovery: Identification of complement activation signatures in disease states.
-
Therapeutic Antibody Development: Generation of monoclonal antibodies against key complement proteins, such as C1q and C4.
Creative Biolabs offers a range of complement-related products and complement testing services, including:
If you have any questions about our complement testing services and products, please feel free to contact us.
Resources
References
-
Calatroni, Marta, et al. "Anti-C1q antibodies: a biomarker for diagnosis and management of lupus nephritis. A narrative review." Frontiers in Immunology 15 (2024): 1410032.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections: