Lectin Pathway Basics Molecular Mechanisms Regulatory Mechanisms Experimental Approaches Resources
The complement system can be activated by three pathways, namely the classical pathway, the alternative pathway and the lectin pathway. The lectin pathway plays a critical role in the innate immune response. While the classical and alternative pathways are more commonly discussed, the lectin pathway offers unique insights into the immune response due to its distinct initiation process and regulatory mechanisms.
Overview of the Lectin Pathway
The lectin pathway of complement activation is a pattern recognition pathway that is triggered when specific lectins, such as mannose-binding lectin (MBL), bind to carbohydrate structures on the surface of pathogens or damaged host cells. Unlike the classical pathway, which is initiated by the binding of antibodies to antigens, or the alternative pathway, which is continuously active at low levels, the lectin pathway is unique in its reliance on carbohydrate patterns rather than immunoglobulins.
The lectin pathway shares many features with the classical pathway in terms of its downstream activation of complement proteins, but it does not require antibodies. This makes it particularly important in the early stages of the immune response, especially in individuals who have not yet generated adaptive immune responses to specific pathogens. The initiation process of the lectin pathway, involving the recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), allows for rapid detection and response to a wide variety of microbial threats.
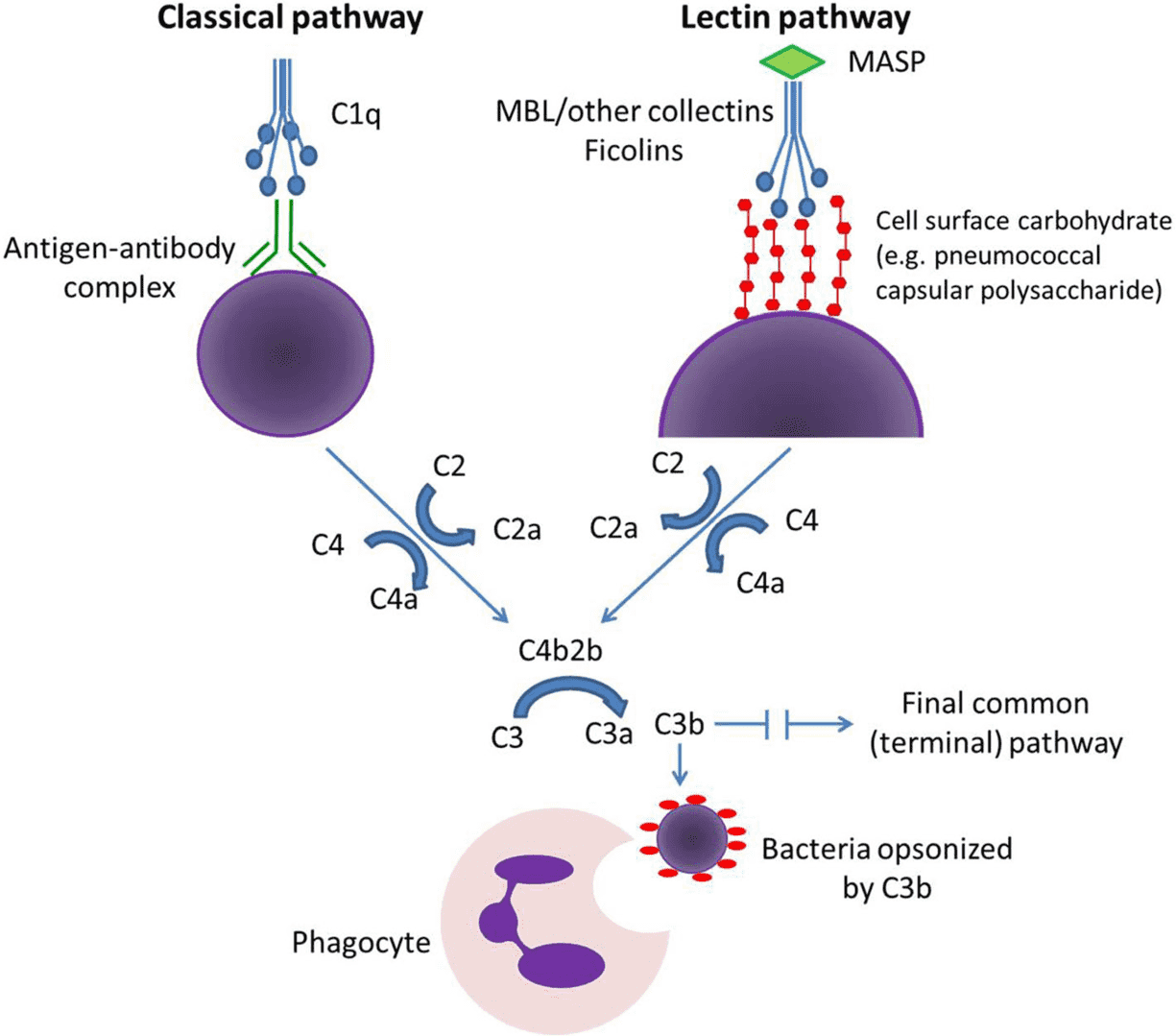
Fig. 1 Lectin pathway activation.1, 2
Key Components of the Lectin Pathway
The lectin pathway relies on several key components that are involved in its activation and downstream effects. These include MBL, collectins, MBL-associated serine proteases (MASPs), and the complement proteins C4, C2, and C3.
Table 1 Key components of the lectin pathway.
|
|
Description
|
Key Components
|
|
PRRs
|
These receptors are specific to PAMPs and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), which are often found on microbial surfaces or injured tissues.
|
-
MBL: The central PRR in the lectin pathway is MBL, which binds to specific sugars, including mannose, N-acetylglucosamine, and fucose, on the surface of pathogens. MBL is a soluble protein that circulates in the plasma and is structurally similar to C1q of the classical pathway.
|
-
Ficolins: Similar to MBL, ficolins (ficolin-1, ficolin-2, and ficolin-3) are also soluble PRRs that recognize carbohydrate patterns on pathogens, including acetylated sugars, glycolipids, and lipopolysaccharides (LPS). Ficolins possess a collagen-like domain that is involved in binding to carbohydrates, and their activation of the complement system is closely related to their oligomeric structure.
|
|
Serine Protease Complexes
|
Upon recognition of pathogen surfaces, MBL and ficolins form complexes with serine proteases that mediate downstream complement activation. The most well-studied of these proteases are MASPs.
|
-
MASP-1 and MASP-2: MASP-1 and MASP-2 are serine proteases that bind to MBL and ficolins. Upon binding, they undergo activation, which triggers the cleavage of complement proteins, including C4 and C2. This results in the formation of the C3 convertase (C4b2a) of the lectin pathway.
|
-
MASP-3: While MASP-3 has a role in complement activation, it is less well understood. It appears to be involved in fine-tuning the activation process and may have an inhibitory role in some contexts.
|
|
Complement Proteins C4 and C2
|
Upon activation by MBL or ficolin, the associated MASPs cleave C4 and C2, leading to the formation of the C3 convertase (C4b2a). This enzyme complex is responsible for cleaving C3 into its active fragments, C3a and C3b, which are crucial for the amplification of the complement response.
|
-
C4: C4b, formed by the cleavage of C4, binds to the pathogen surface.
|
-
C2: C2a, formed by the cleavage of C2, binds to C4b.
|
Molecular Mechanisms of Lectin Pathway Activation
Similar to classical pathway activation, lectin pathway activation occurs through pattern recognition. The lectin pathway is initiated when pattern recognition molecules (PRM) bind to oligosaccharides and acetylated residues on the surface of microorganisms, respectively.
Recognition of Pathogen Surfaces
The lectin pathway is activated when MBL or ficolins bind to specific carbohydrate structures on the surface of pathogens. These include:
-
Mannan (mannose residues)
-
Glucans
-
Other microbial carbohydrates that are not typically found on host cells.
This recognition is highly specific and allows for the targeted activation of the immune system against foreign invaders while minimizing the risk of autoimmunity.
Activation of Complement Proteins
Upon binding to pathogens, MBL and ficolins recruit MASP-1 and MASP-2 to form a complex.
-
This activation cleaves C4 into C4a and C4b.
-
C4b then binds to the pathogen surface, while C2 is cleaved by MASP-2 into C2a and C2b.
-
C2a binds to C4b, forming the C3 convertase (C4b2a).
-
This enzyme complex cleaves C3 into C3a and C3b, leading to the amplification of the complement response.
C3b Binding and Opsonization
C3b plays a critical role in pathogen elimination. When deposited on the surface of pathogens, C3b acts as an opsonin, promoting the recognition and engulfment of pathogens by phagocytes. This is facilitated by receptors on phagocytes, such as CR1, which recognize C3b-tagged pathogens.
Formation of the MAC
-
C3b also participates in the formation of the C5 convertase (C4b2a3b), which cleaves C5 into C5a and C5b.
-
C5b then interacts with C6, C7, C8, and C9 to form the MAC.
-
The MAC creates pores in the pathogen membrane, leading to osmotic lysis and the destruction of the pathogen.
Inflammation and Immune Activation
In addition to direct pathogen elimination, the lectin pathway generates potent inflammatory mediators, such as C3a and C5a, known as anaphylatoxins. These molecules recruit immune cells to the site of infection, promote vascular permeability, and enhance the overall immune response. C5a, in particular, is a potent chemoattractant for neutrophils and other immune cells, amplifying the inflammatory response.
Regulation of the Lectin Pathway
The lectin pathway is tightly regulated to prevent excessive complement activation and tissue damage. Several regulatory proteins play a crucial role in controlling the activity of the lectin pathway.
Regulatory Proteins of the Lectin Pathway
Table 2 Regulatory proteins of the lectin pathway.
|
Regulatory Proteins
|
Description
|
Function
|
|
C1 Inhibitor (C1INH)
|
C1INH is a key regulator of the complement system, particularly in the classical and lectin pathways. It controls the activation of MASPs, which are crucial for initiating the lectin pathway.
|
-
C1INH functions by binding to and inactivating MASP-2 and other proteases in the cascade, thus preventing uncontrolled activation.
-
This inhibitory action ensures that complement activation only occurs when necessary, protecting the host from excessive complement-mediated damage.
|
|
Factor H
|
Factor H plays a central role in modulating complement activity by regulating the alternative pathway and influencing the C3 convertase activity in both the classical and lectin pathways.
|
-
It primarily inhibits the deposition of C3b on host cells and promotes its degradation. Factor H binds to C3b and accelerates its decay, preventing the formation of the C3 convertase (C3bBb) complex.
-
In the context of the lectin pathway, Factor H helps to maintain a delicate balance between activating complement and protecting the host's own tissues from complement-mediated injury.
-
By controlling the activation of C3, Factor H ensures that the lectin pathway does not result in excessive immune responses that could lead to tissue damage or autoimmunity.
|
|
Factor I
|
Factor I is an essential regulator that works in concert with Factor H to control complement activation.
|
-
It cleaves C3b and C4b into inactive fragments, a process that prevents the formation and persistence of the C3 and C5 convertases.
-
Factor I requires co-factors, such as Factor H or C4-binding protein (C4BP), to facilitate its activity.
-
Factor I ensures that complement activation is tightly controlled, preventing tissue damage or autoimmune reactions.
|
Experimental Approaches to Study the Lectin Pathway
Understanding the mechanisms of the lectin pathway has broad implications for the development of therapeutic strategies for various infectious, inflammatory, and autoimmune diseases. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the experimental approaches used to study the lectin pathway, focusing on cutting-edge methodologies that allow for detailed characterization of its components and functions.
In Vitro Studies of the Lectin Pathway
In vitro studies provide a controlled environment to investigate specific interactions and mechanisms in detail. These models are commonly used to study the binding of lectins to carbohydrates and to identify the components involved in the lectin pathway activation.
Table 3 Techniques for detection and quantification
|
Assays
|
Techniques
|
|
Lectin Binding Assays
|
These assays typically involve incubating lectins with a target substrate, such as pathogen extracts or glycoproteins, followed by detection using various techniques, including:
-
ELISA: Used to detect and quantify the binding of lectins to specific carbohydrates.
-
SPR: A real-time analytical technique that measures the interaction between lectins and carbohydrate ligands on a sensor surface, providing detailed kinetic data.
-
Fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry: These techniques are used to observe the binding of fluorescently labeled lectins to cells or particles and to quantify binding events at the single-cell level.
|
|
Complement Activation Assays
|
Complement activation assays measure the functional consequences of lectin binding, including the activation of complement components and the formation of the MAC. Common approaches include:
-
Hemolytic assays : These assays use red blood cells (RBCs) coated with pathogen-like molecules to assess complement-mediated lysis.
-
Western blotting: This method can be used to monitor the cleavage of complement proteins such as C4 and C3, indicating complement activation through the lectin pathway.
-
C3 deposition assays : Flow cytometry-based assays can be used to quantify the deposition of C3 fragments on the surface of pathogen-like particles or cells, providing a measure of complement activation.
|
In Vivo Studies of the Lectin Pathway
While in vitro assays provide valuable mechanistic insights, in vivo models are essential for understanding the physiological relevance of the lectin pathway in a living organism. These models are particularly useful for studying the immune response to infections and the role of the lectin pathway in immune regulation.
-
MBL-deficient mice - exhibit increased susceptibility to a variety of infections, which helps to elucidate the importance of MBL in pathogen clearance.
-
MASP-deficient mice - provide insights into the proteolytic activation steps in the lectin pathway.
-
C4-deficient mice - for studying the downstream effects of lectin pathway activation, including inflammation and immune responses.
-
Bacterial infection models: mice infected with Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, or Pseudomonas aeruginosa are often used to study the role of the lectin pathway in bacterial clearance and sepsis.
-
Viral infection models: the role of the lectin pathway in antiviral immunity can be studied in mouse models of influenza virus, herpes simplex virus (HSV), and other viral pathogens.
Molecular Techniques for Investigating the Lectin Pathway
Molecular biology techniques are integral to identifying and characterizing the genes and proteins involved in the lectin pathway.
-
Quantitative PCR (qPCR) and RNA sequencing
These techniques are used to measure the expression levels of lectin pathway components, including lectins, MASPs, and other regulatory proteins, in various tissues or cells.
-
Proteomics and mass spectrometry
These techniques are used to analyze complex protein mixtures, providing detailed insights into the protein composition of the complement activation complexes and the identification of novel lectin pathway components.
-
Advanced imaging techniques
These techniques are used to visualize the spatial and temporal dynamics of lectin pathway activation and its effects on immune cells and pathogens.
You can contact us to take advantage of these cutting-edge experimental approaches, where researchers can continue to unravel the nuances of the lectin pathway and explore its potential as a therapeutic target for immune diseases.
Creative Biolabs offers a range of complement test services and complement products related to the lectin pathway, including:
If you are interested in our products or services, please feel free to contact us.
Resources
References
-
LaFon, David C., et al. "Classical and lectin complement pathways and markers of inflammation for investigation of susceptibility to infections among healthy older adults." Immunity & Ageing 17 (2020): 1-9.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections: