Introduction Published Data What We Can Offer? Workflow Why Choose Us? FAQs Featured Services Featured Products
Accelerate Your Research and Development!
Are you currently facing complex challenges in developing targeted therapies for complement-mediated diseases, such as the difficulty in engineering and producing high-quality proteins or navigating a lengthy development cycle? Creative Biolabs' Soluble Complement Regulators Development services are designed to help you overcome these hurdles. We help you accelerate drug discovery and obtain potent, high-quality recombinant proteins through advanced protein engineering techniques and robust expression platforms. Our end-to-end solutions are crafted to streamline your project from initial concept to lead candidate selection, ensuring a clear path to success.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Introduction
The complement system is a vital component of the innate immune system, consisting of a cascade of proteins that work together to protect the host from pathogens and clear damaged cells. While this system is crucial for immune defense, its dysregulation can lead to chronic inflammation and tissue damage, contributing to a wide range of diseases, including autoimmune disorders and neurodegenerative conditions. Soluble complement regulators (SCRs) are natural or engineered proteins that can inhibit or modulate this cascade. They represent a highly promising class of therapeutics due to their high specificity and potential for reduced off-target effects. Published data highlights that specific complement components, such as C3 and C5, play a central role in amplifying the cascade, making them key targets for therapeutic intervention.
Our services in soluble complement regulator development are meticulously tailored to your unique project needs, delivering efficient, high-quality, and cost-effective solutions. We offer a specialized suite of services, including:
sCR1 (TP10) is a well-established therapeutic candidate that modulates the complement system. It was developed to treat conditions like ischemia-reperfusion injury and is used specifically for coronary artery bypass graft surgery.
C4BP is a key regulatory protein in the classical and lectin complement pathways. Its function as a cofactor in Factor I-mediated cleavage makes it an important therapeutic target for regulating complement activation.
Factor H (FH) is a crucial deactivator of the alternative pathway. Its deficiency can lead to severe autoimmune diseases, establishing it as a promising and effective target for therapeutic development.
Factor I (FI), a serine protease, regulates complement by degrading C4b and C3b. Its deficiency is linked to various diseases, making it a potential therapeutic target.
The human body's intrinsic complement-inhibiting proteins primarily target convertases or the terminal complement complex (TCC), offering a valuable foundation for therapeutic development. Among these, soluble complement receptor 1 (sCR1), also known as TP10 or Avant, has seen the most widespread development. Its robust inhibitory action across both the classical (CP) and alternative (AP) pathways makes it suitable for diverse disease models. Furthermore, recombinant Factor H (FH) has been investigated for conditions like age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and certain kidney disorders, which are often influenced by FH gene variations. Initial examples in clinical trials include creating a fusion inhibitor from the brief four-domain regulators MCP and DAF, or shortening the CR1 molecule into smaller, active fragments.
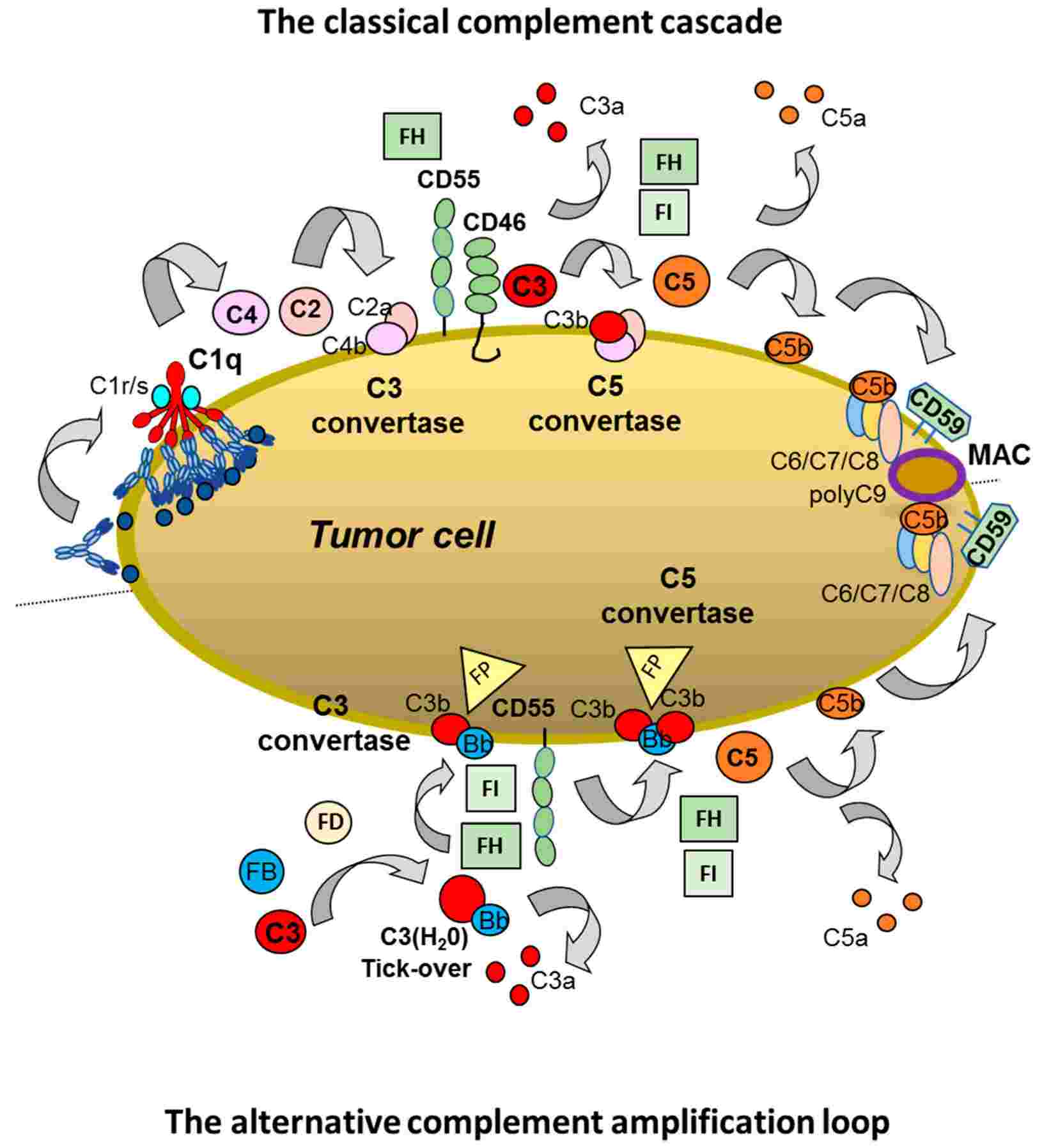 Fig.1 The soluble complement regulator in the complement system.1,3
Fig.1 The soluble complement regulator in the complement system.1,3
Application
Soluble complement regulators are versatile therapeutic agents with broad applications across various disease areas where complement dysregulation is a central pathological mechanism. These applications include:
-
Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases: Targeting uncontrolled complement activation in conditions like systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome.
-
Neurological Disorders: Inhibiting complement-mediated inflammation in diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and multiple sclerosis.
-
Viral Infections: Modulating the complement system to combat viral infections, as complement dysregulation has been implicated in the pathology of severe diseases like COVID-19.
-
Transplantation: Preventing complement-mediated rejection of transplanted organs.
Published Data
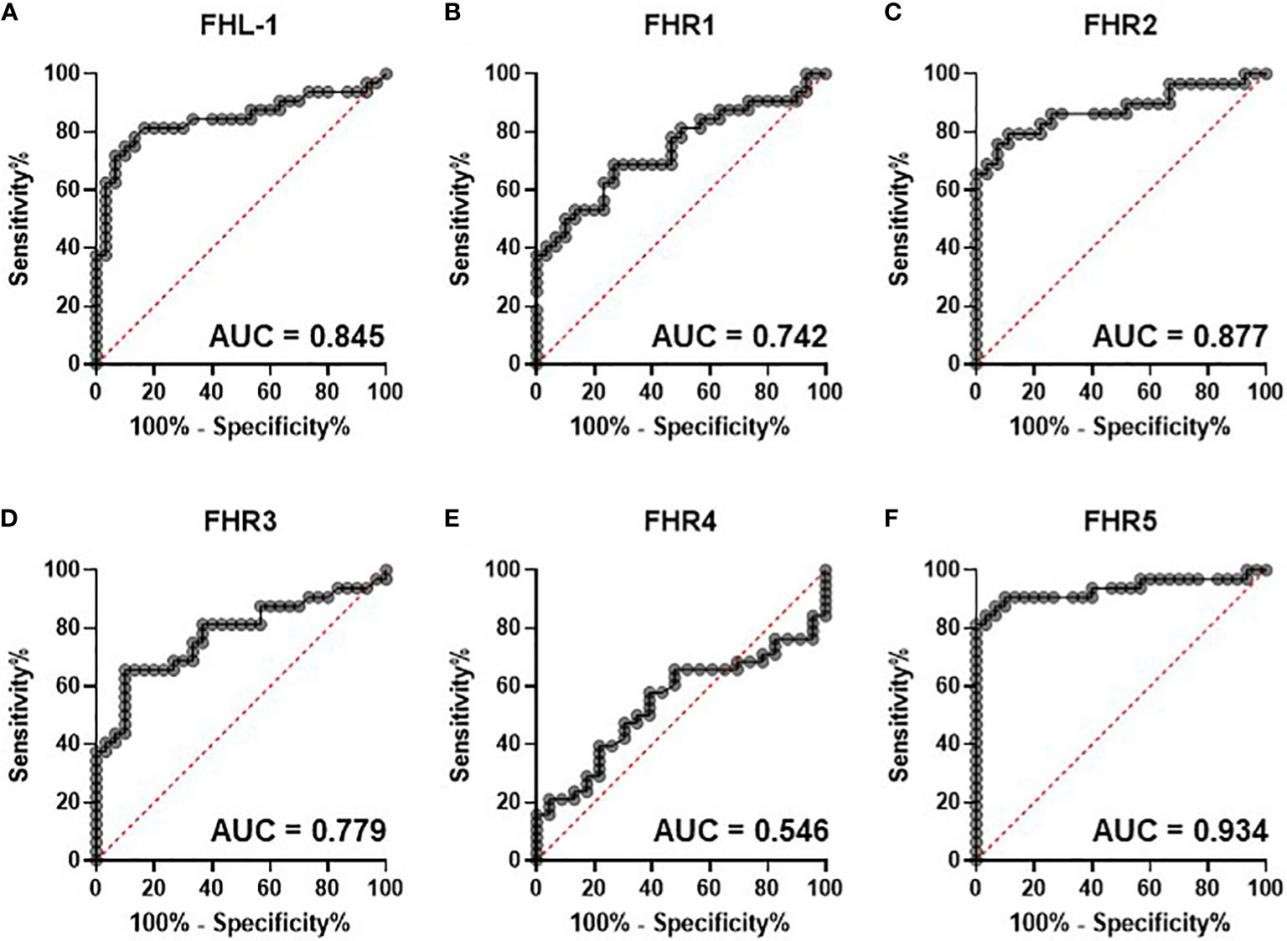 Fig.2 Circulating complement cofactors predict disease severity.2,3
Fig.2 Circulating complement cofactors predict disease severity.2,3
Recently published research highlights a strong link between the levels of soluble complement regulators and disease severity in patients with COVID-19. In a study, researchers used a shotgun proteomic approach to analyze the circulating levels of Factor H (FH), its variant Factor H like 1 (FHL-1), and five Factor H related proteins (FHR1-5). The experiment revealed a significant elevation in FHR proteins, particularly FHR2 and FHR5, in patients with more severe disease compared to those with mild symptoms. This data supports the hypothesis that the elevation of FHR family proteins can predict disease severity. The study concludes that early, uncontrolled activation of the complement system, amplified through the alternative pathway, is a key feature of severe COVID-19, offering a crucial insight for targeted therapeutic strategies.
What We Can Offer?
Beyond our core development service, we provide a suite of related products and services designed to support your research and drug discovery efforts.
-
Custom Soluble Complement Regulator Design: Tailored design and engineering of novel soluble regulators based on your specific needs.
-
Recombinant Protein Expression & Purification: High-quality production of complement proteins and regulators for research or therapeutic purposes.
-
Functional & Binding Assays: A full range of in-house assays to evaluate the activity of your molecules.
-
Antibody Development Services: We offer services for developing highly specific antibodies targeting complement components, which can serve as alternative therapeutic agents.
Workflow
01
Initial Consultation & Strategy Design: We collaborate to define project goals, select targets, and design a strategic development plan.
02
Gene Synthesis & Vector Construction: We synthesize the target gene and clone it into a high-yield expression vector.
03
Protein Expression & Purification: The protein is expressed using our platforms and purified for high yield and purity.
04
Functional & Binding Assays: The purified protein is tested for binding and complement regulation to validate its therapeutic potential.
05
Biophysical Characterization & Optimization: We analyze protein stability and properties, then optimize lead candidates for enhanced efficacy.
Why Choose Us?
Choosing a partner for developing soluble complement regulators is a critical decision. Creative Biolabs offers a unique combination of deep scientific knowledge and cutting-edge technology to ensure the success of your project. Our key advantages include:
-
Specialized Expertise: Our team consists of seasoned experts with extensive experience in complement biology and protein engineering.
-
State-of-the-Art Platform: We leverage a robust, validated platform for gene synthesis, protein expression, and purification, ensuring high yield and quality.
-
Comprehensive Service: We provide an end-to-end solution, from initial design and cloning to final functional characterization and lead optimization, saving you time and resources.
-
Published Data: Our methodologies are supported by and align with published data demonstrating the efficacy of our approach in developing functional biologics.
Obtain the Creative Biolabs Advantage – Seek a Quote Today
FAQs
Q: How do the distinct mechanisms of action and pharmacokinetics of soluble complement regulators compare to those of small molecule inhibitors for therapeutic applications?
A: Soluble complement regulators (SCRs) are large protein-based therapeutics. Their large size means they typically exhibit high specificity and can bind to multiple sites on a target protein, leading to potent and precise inhibitory effects. This typically yields enhanced safety characteristics with reduced off-target effects. Nevertheless, their larger dimensions may restrict tissue permeation, necessitating parenteral delivery (e.g., injection or infusion). Conversely, small molecule inhibitors exhibit substantially reduced size and enable oral administration. They can more easily penetrate tissues and cells, but may have a higher risk of off-target effects. The choice between an SCR and a small molecule depends on the specific target, disease indication, and required therapeutic profile.
Q: What is your approach for developing regulators that target complex or multimeric complement proteins?
A: Complex protein targets, such as C3 or the C3 convertase, require a sophisticated approach. Our team uses advanced in silico modeling and protein engineering techniques to design regulators that can precisely interact with these complex structures. Our specialized expression and purification platforms are optimized for producing these challenging proteins in a functional state, ensuring they are correctly folded and post-translationally modified. This expertise allows us to tackle even the most difficult targets in the complement cascade.
Q: Could you explain the elements affecting a project's schedule, specifically throughout the refinement and analysis stages?
A: The total duration is typically between 8 to 14 weeks. The timeline can be affected by the need for extensive sequence optimization to improve expression or stability. The characterization phase, which involves multiple functional assays and biophysical analyses (e.g., SPR, DLS, mass spectrometry), can be extended if the lead candidate requires further refinement. Our goal is to provide a comprehensive solution without compromising on the quality of the final product.
Q: What is your strategy for scaling up the production of a soluble complement regulator from the initial development phase to large-scale manufacturing?
A: Our development process is designed with scalability in mind. We use stable cell lines and high-titer expression systems that can be seamlessly transitioned to larger bioreactors. Our team can also assist with process development and purification protocol optimization to ensure consistency, yield, and quality are maintained as production volume increases. We can assist you at any stage of the project and ensure that your project can move to the next stage seamlessly.
Q: What specific quality control measures and functional validation assays do you use to guarantee the purity, integrity, and activity of the final product?
A: We perform rigorous quality control at every stage. The final product undergoes extensive characterization, including purity analysis via SDS-PAGE and SEC-HPLC for assessing purity and aggregation, respectively. For functional validation, we perform a variety of assays, such as hemolytic assays (e.g., CH50 or AP50), ELISA-based binding assays, and complement deposition assays to confirm the molecule's specific inhibitory activity and potency. This multi-faceted approach ensures the final product meets the highest standards for use in subsequent research or preclinical studies.
Creative Biolabs is your trusted partner in Soluble Complement Regulators Development. Our end-to-end service, backed by our specialized expertise and robust platform, is designed to accelerate your project from concept to a lead candidate. We offer comprehensive solutions that address the specific challenges of protein-based drug discovery, helping you advance your therapeutic goals with confidence.
Featured Services
Feature Products
References
-
Golay, Josée, and Ronald P Taylor. "The Role of Complement in the Mechanism of Action of Therapeutic Anti-Cancer mAbs." Antibodies (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 9,4 58. 28 Oct. 2020, https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9040058
-
Tierney, Anna L et al. "Levels of soluble complement regulators predict severity of COVID-19 symptoms." Frontiers in Immunology vol. 13 1032331. 18 Oct. 2022, https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.1032331
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig.1 The soluble complement regulator in the complement system.1,3
Fig.1 The soluble complement regulator in the complement system.1,3
 Fig.2 Circulating complement cofactors predict disease severity.2,3
Fig.2 Circulating complement cofactors predict disease severity.2,3