Creative Biolabs is a world-leading service provider of application-specific antibody development. Here, we introduce our in vitro diagnostic (IVD) antibody development and immunoassay development services targeting Fas receptor. Our state-of-the-art technologies ensure that our clients receive high-quality, stable, flexible, and cost-effective products and services.
Introduction of Fas Receptor
The first apoptosis signal receptor (Fas), also named as apoptosis antigen 1 (APO-1), is a protein in humans encoded by the FAS gene. It is also known as cluster of differentiation 95 (CD95) or tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6. The mature Fas protein has 319 amino acids, which is divided into 3 cysteine-rich domains in their extracellular region at the N-terminus: an extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic domain. All of the three domains are responsible for different ligand bindings. Fas is originally discovered as the target of two monoclonal antibodies that trigger apoptotic cell death in certain human tumor-derived cell lines in culture or as xeno-transplants in immuno-deficient mice. Fas receptor is also a type I cell surface glycoprotein which belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily of membrane receptors and has a broad distribution on various. Abundant expression can be found in the thymus, liver, heart, and kidney, and Fas receptor is highly expressed in activated lymphocytes and in a variety of lymphoid or non-lymphoid origin, as well as in neoplastic tissues and tumor cell lines. Another effect is that Fas receptor bond to a death receptor on the surface of cells leading to programmed cell death.
 Fig.1 Structure of the FAS protein.1
Fig.1 Structure of the FAS protein.1
Fas Receptor Marker of Sepsis
Intensive pathophysiology studies of sepsis revealed that apoptosis is an important mechanism of cell death in animal models of sepsis. Sepsis induces extensive apoptosis of lymphocytes, which has been suggested to contribute to immunosuppression and mortality. Fas receptor is the main molecule involved in apoptosis during the sepsis. It was reported that apoptosis was increased in different cells and organs in patients with fatal sepsis, and the levels of circulating (soluble) Fas molecule in sepsis patients were higher than that in healthy individuals. Fas protein was up-regulated in the liver and the spleen after sepsis, particularly in hepatocytes and lymphocytes, respectively. Besides, whilst Fas ligand expressed in CD8+ T cells contribute to apoptosis and pro-inflammation in the liver but not the spleen after sepsis. It was suggested that inhibition of Fas/Fas-Ligand pathway might represent a novel and potential therapeutic modality for maintaining organ perfusion and preventing liver injury during human sepsis.
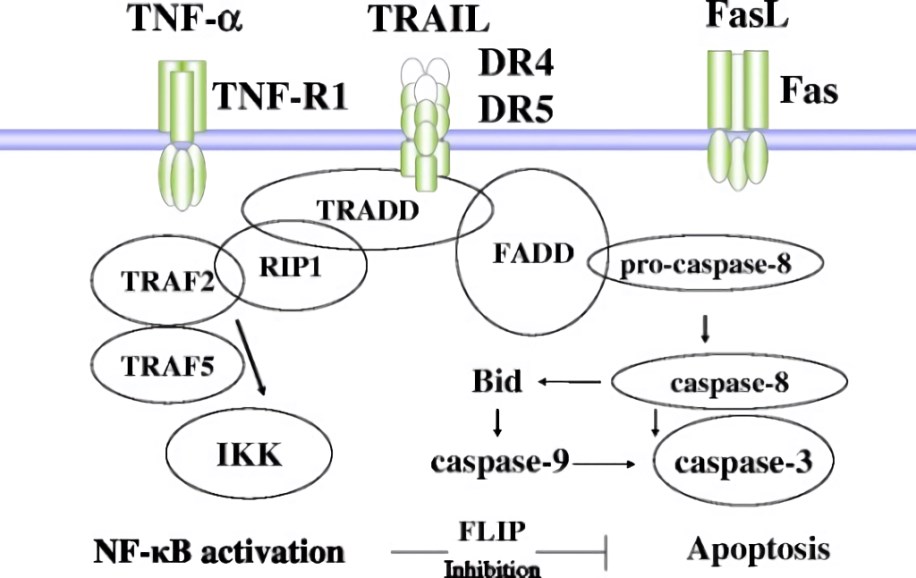 Fig. 2 The death receptor signaling in sepsis-induced vasculitis. (Matsuda, 2016)
Fig. 2 The death receptor signaling in sepsis-induced vasculitis. (Matsuda, 2016)
Features
To aid in the prognosis and diagnosis of sepsis, Creative Biolabs offers an extensive range of IVD antibody development services against Fas receptor antigens to measure its levels clinically. The features of our services include:
- Expertise: expert in the development of antibodies for different immunoassays (e.g., ELISA, immunohistochemistry, Western blot, immunochromatography assay).
- Experience: years of experience in the IVD field with the completion of numerous IVD-related projects.
- Efficiency: fast turnaround time and competitive pricing.
- Facility: fully equipped facility to perform antigen & antibody conjugation, protein characterization and purification.
Creative Biolabs provides IVD antibody development services against an extensive range of sepsis biomarkers in addition to Fas Receptor. During antibody development, we work hand in hand with you and your team to ensure project goals and timelines are being met. Contact us to discuss your projects and experience the great value of our expert services.
References
- From Wikimedia: By Emw - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, without modification, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Protein_FAS_PDB_1ddf.png.
- Matsuda, Naoyuki. "Alert cell strategy in SIRS-induced vasculitis: sepsis and endothelial cells." Journal of Intensive Care 4 (2016): 1-10. under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.