With vast experience in antibody discovery and development, Creative Biolabs has launched a full range of biomarker-specific in vitro diagnostic (IVD) antibody development services to aid in the development of high-quality diagnostic immunoassays. Particularly, we introduce our IVD antibody development services targeting thrombomodulin marker.
Thrombomodulin
Thrombomodulin (TM), also known as CD141 or BDCA-3, is an integral membrane protein which is expressed on the surface of endothelial cells, as well as human mesothelial cell, monocyte and a dendritic cell subset. It is encoded by the THBD gene in humans. TM is composed of a single chain with six tandemly repeated EGF-like domains, a transmembrane domain and a Serine/Threonine-rich spacer. It functions as a cofactor for thrombin and decreases blood coagulation by means of converting thrombin to an anticoagulant enzyme from a procoagulant enzyme. In the anticoagulant pathway, TM serves as a cofactor in the thrombin-induced activation of protein C by forming a 1:1 stoichiometric complex with thrombin, and thus increases the speed of protein C activation thousandfold. Meanwhile, TM-bound thrombin has procoagulant activity by inhibiting fibrinolysis through cleaving thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI, aka carboxypeptidase B2) into an active form.
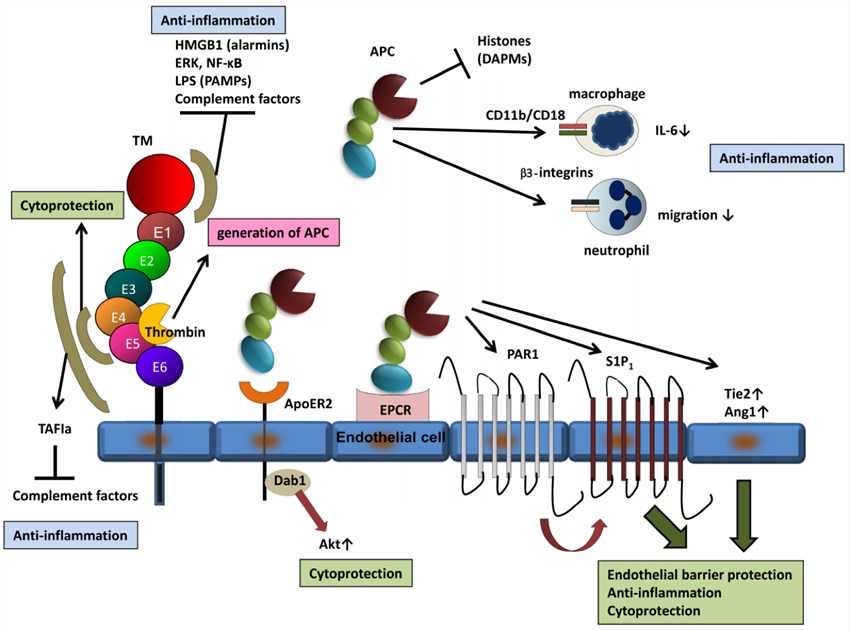 Fig. 1 Anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective functions of thrombomodulin.1, 2
Fig. 1 Anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective functions of thrombomodulin.1, 2
The role of Thrombomodulin in Sepsis
Thrombomodulin (TM) plays an essential role in the protein C system which is central to the pathogenesis of sepsis. During sepsis, the expression of thrombomodulin on the endothelial cell is strongly downregulated, leading to a diminished activation of protein C which is important in the modulation of coagulation activation and inflammatory processes. Additionally, thrombomodulin also has noticeable immunomodulatory effects, targeting neutrophil adhesion, cytokine generation, and complement activation. Thrombomodulin expressed on vascular endothelium binds to thrombin, and then forms a 1:1 complex which serves as an anticoagulant. Meanwhile, the thrombin-TM complex activates protein C to produce activated protein C (APC), which deactivates factors VIIIa and Va in the presence of protein S, therefore inhibiting further thrombin formation. And the soluble form of thrombomodulin is released from the surface of endothelial cells into the serum by proteolytic degradation. As been reported, the serum thrombomodulin is increased in diseases related to endothelial injuries, such as acute disseminated intravascular coagulation, respiratory distress syndrome and organ dysfunction induced by sepsis.
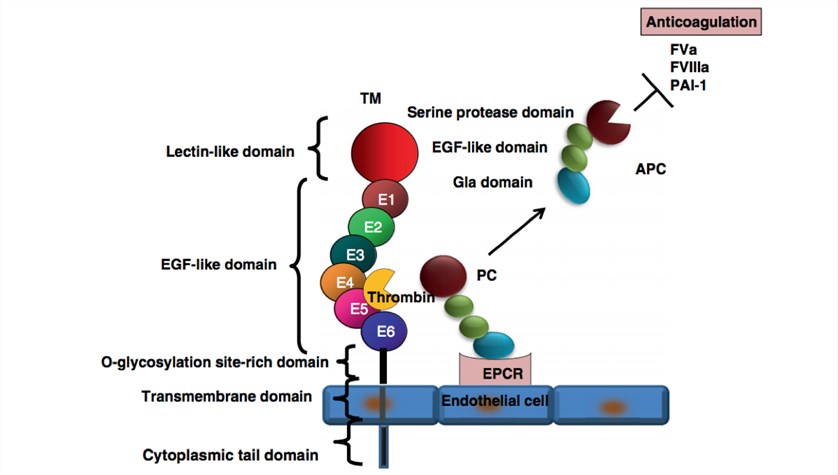 Fig. 2 Anticoagulant function of thrombomodulin.1, 2
Fig. 2 Anticoagulant function of thrombomodulin.1, 2
Anti-Thrombomodulin Antibody Development Services
According to the significant role of endothelial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of sepsis, serum thrombomodulin level has been regarded as a potent predictor of the severity of sepsis and mortality. Through our role as a leading antibody service provider, Creative Biolabs is well-positioned to develop high-quality CD20-specific antibodies. Besides antibody generation, Creative Biolabs also offers diagnostic immunoassay development services, including feasibility analysis, assay design, assay protocol establishment, assay optimization, and kit production.
If you are interested in our IVD antibody development services, please feel free to contact us for more details.
References
- Ikezoe, Takayuki. "Thrombomodulin/activated protein C system in septic disseminated intravascular coagulation." Journal of intensive care 3 (2015): 1-8
- under Open Access license cc BY 4.0. without modification.
For Research Use Only.