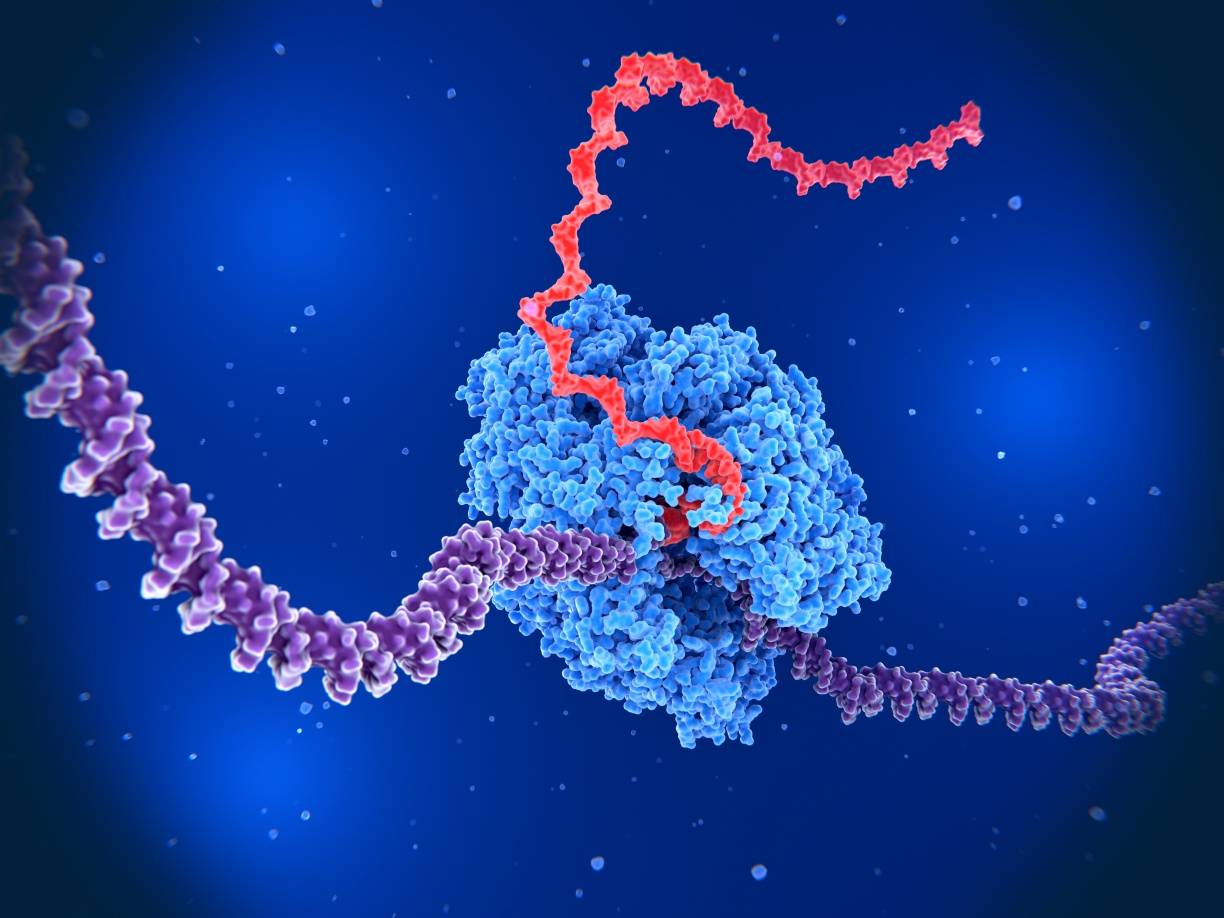
Polymer-Conjugated
ASO Development Service
Unlock the full potential of Antisense Oligonucleotides. We engineer advanced polymer conjugates to enhance stability, optimize pharmacokinetics, and ensure precise delivery.
Redefining ASO Therapeutics
While Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs) hold immense promise, challenges like rapid renal clearance and nuclease degradation persist. Polymer conjugation is the game-changer—altering physicochemical properties to extend circulation and shield your therapeutic payload.
Extended Half-Life
Increases hydrodynamic radius to bypass rapid renal filtration, significantly prolonging systemic circulation time.
Enhanced Stability
Forms a steric shield that protects the oligonucleotide backbone from serum nucleases and enzymatic degradation.
Precise Delivery
Modulates biodistribution profiles to facilitate cellular uptake and accumulation in target tissues over non-target organs.
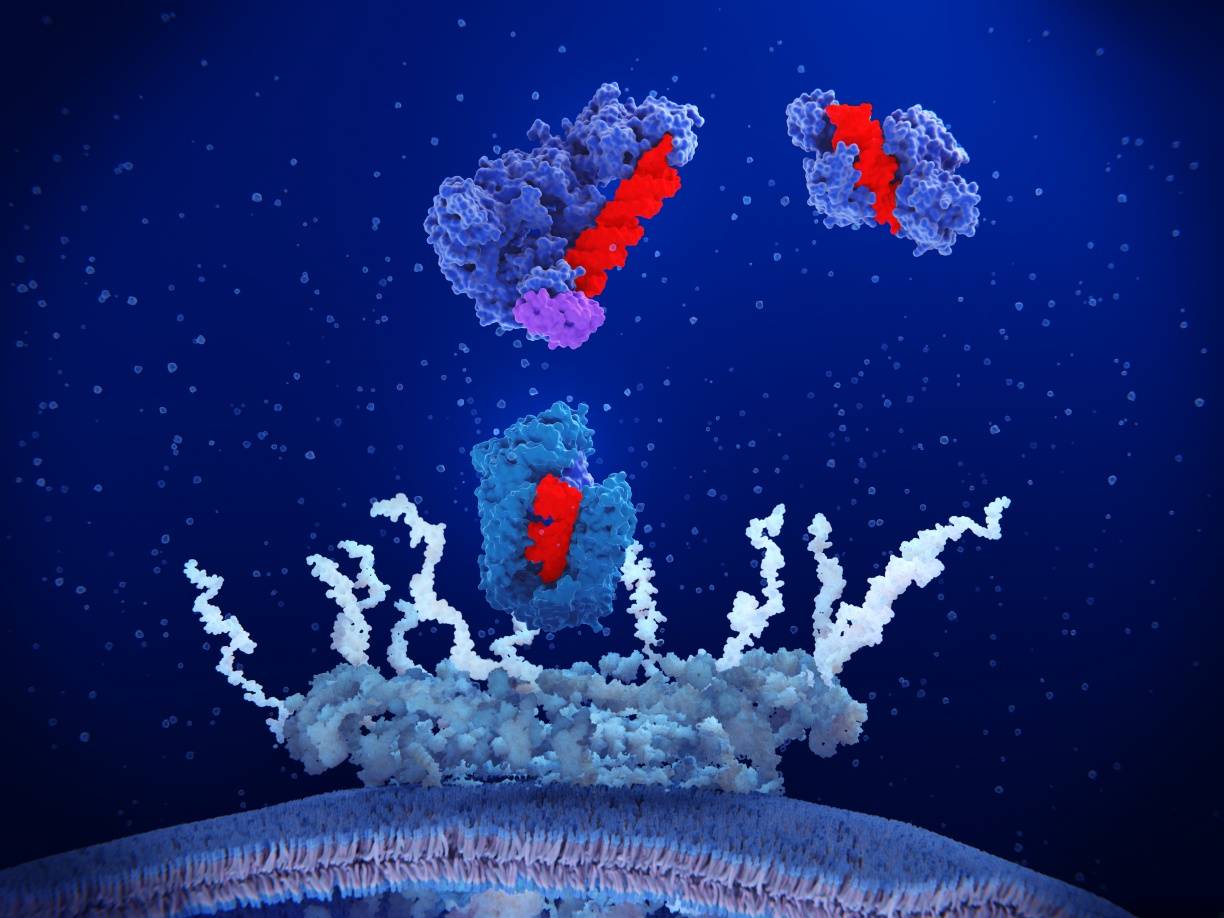
One-Stop Solution
From chemical synthesis to in vivo validation.
Comprehensive Development Ecosystem
Creative Biolabs offers a holistic platform for polymer-conjugated ASOs. We don't just perform reactions; we design therapeutics. Our tailored approach ensures optimization for your specific target, balancing efficacy with safety profile.
Custom Polymer Synthesis & Selection
Tailored polymer libraries including PEG, PEO, and biodegradable options.
Advanced Conjugation Chemistry
Utilizing Click Chemistry, Amide Bond formation, and Thiol-Maleimide coupling.
Rigorous Purification & Characterization
High-resolution HPLC purification and detailed QC analysis.
Core Capabilities
Engineered for precision and performance.
Smart Polymer Library
Access a diverse range of polymers including PEG, PEO, Polyglutamic Acid (PGA). We optimize molecular weight, charge density, and hydrophilicity.
Polymer SelectionPrecision Chemistry
Utilizing Click Chemistry, Thiol-Maleimide, and Amide coupling. Our strategies ensure high yield and site-specific modification.
Conjugation StrategyOptimized PK/PD
Designs focused on stability, solubility, and tissue targeting. We aim to enhance the half-life and promote cellular uptake while minimizing off-target toxicity.
Pharmacokinetics
Advanced Engineering
For Precise Delivery
Leveraging cutting-edge technologies to overcome delivery barriers. Our integrated ecosystem ensures precise control over conjugation sites, stability, and product homogeneity.
Smart Polymer Systems
Utilization of stimuli-responsive polymers that actively adapt to the physiological environment, ensuring cargo protection and timely release.
-
Stimuli-Responsive Reacts to pH & Temperature changes
-
Endosomal Escape Facilitates cytosolic delivery
Precision Conjugation Technology
Advanced bioconjugation technologies enabling site-specific attachment of polymers. We move beyond random conjugation to achieve defined drug-to-polymer ratios.
Biodegradable Linker Strategy
Intelligent design of cleavable linkers (e.g., disulfide, hydrazone) that balance systemic stability with efficient intracellular release.
Streamlined Development Process
Our comprehensive workflow ensures the highest standards of quality and efficiency from initial submission to final data delivery.
Step 01: Sample Submission & Feasibility
The process begins when the client submits viral vector samples along with detailed process information. Our technical team conducts a preliminary evaluation of the sample matrix and concentration levels to recommend the most suitable purity assays and experimental design.
Step 02: Method Optimization & Testing
For complex matrices, we perform rigorous method qualification or optimization strategies to ensure accuracy. Samples are then tested using selected high-precision technologies (e.g., AUC, ELISA, qPCR) alongside appropriate internal controls to validate the results.
Step 03: Data Analysis & Reporting
Raw data undergoes a strict analysis by our Quality Control (QC) team. We deliver a comprehensive report that includes detailed chromatograms, high-resolution images, impurity calculations, and a formal Certificate of Analysis (CoA) to support your downstream applications.
Therapeutic Applications
Targeted Disease Research
Polymer-conjugated ASOs are particularly useful in developing therapies for conditions that require sustained drug release or targeted delivery to specific organs.
Genetic Disorders
Enhancing delivery to muscle or CNS for diseases like Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) or SMA.
Cancer Therapy
Leveraging the EPR effect (Enhanced Permeability and Retention) of polymers to target tumor tissues.
Enhanced Delivery
Improved penetration into target tissues and cellular internalization efficiency compared to naked ASOs.
Biological Analysis
In biological studies, polymer-conjugated ASO can be used as probes or primers for DNA sequencing, gene cloning, and other experiments..
Molecular Diagnostics
The ability of ASO to bind to specific DNA or RNA sequences is used for early diagnosis and screening of diseases.
The Science Behind It
Understanding how polymer conjugation overcomes biological barriers is key to successful ASO therapeutic development. We tackle two main obstacles:
Stealth Effect
Polymer shielding significantly reduces protein adsorption (opsonization), preventing rapid clearance by the reticuloendothelial system.
Endosomal Escape
Specific polymer designs induce a proton-sponge effect or membrane disruption, facilitating the release of ASOs into the cytoplasm.

Unrivaled Expertise in
Polymer-ASO Engineering
-
Deep Domain Expertise Years of specialized experience in oligonucleotide chemistry and bioconjugation.
-
Tailored Development Customized roadmaps adapted to your specific drug properties and therapeutic goals.
-
End-to-End Solutions Seamless integration from synthesis to in vivo efficacy testing.
Accelerate Your Project
Ready to enhance your ASO delivery? Consult with our PhD-level experts today.
Trusted by Scientists
"The stability of our ASO was drastically improved using Creative Biolabs' PEGylation platform. Their team provided excellent communication and high-quality data throughout the project. We are moving forward to preclinical trials with confidence."
Dr. J. Smith
Director of R&D.
"We struggled with cellular uptake for months until we collaborated with Creative Biolabs. Their customized polymer conjugation strategy solved our delivery challenge efficiently. The final report was comprehensive and very professional."
Sarah L.
Senior Scientist
Expert Answers
Common questions regarding our conjugation services.
Start Your Project Today
Tell us about your project, and our experts will get back to you with a customized quote and proposal.