Identity Service of Viral Vector
Creative Biolabs leverages its expertise as a biomedical R&D partner to offer a comprehensive suite of advanced viral vector identification and characterization services. We are committed to providing the highest level of analytical rigor for investigational drug development.
Introduction to Viral Vectors
Viral vectors are a cornerstone technology in the rapidly developing field of advanced therapy, particularly gene and cell therapy. These biological vectors are derived from natural viruses, such as adeno-associated virus (AAV), lentivirus, adenovirus, and herpes simplex virus. After genetic modification, they lose their ability to replicate but retain the key mechanisms for efficiently delivering therapeutic payloads to target cells. The power of this technology lies in its ability to permanently or temporarily correct genetic defects, alter cell behavior, or serve as in vivo vaccines.
Why Need Viral Vector Identity?
In the context of drug development and regulatory compliance, "identity" is a critical quality attribute (CQA) that explicitly confirms that a viral vector conforms to its claimed identity. This is not a single measurement but a comprehensive assessment designed to verify that the vector's genetic structure, physical properties, and functional characteristics are fully consistent with its intended design.
Identifying the identity is crucial, serving the following purposes:
- Patient Safety - Ensuring that the drug delivery product contains the correct therapeutic gene and vector backbone, preventing the delivery of incorrect or harmful genetic material.
- Product Efficacy - Confirming that the vector has the correct serotype and genomic integrity, effectively transducing target cells and driving adequate expression of the therapeutic payload.
- Manufacturing Consistency - As a release criterion, ensuring batch-to-batch consistency and detecting any potential cross-contamination or labeling errors during manufacturing.
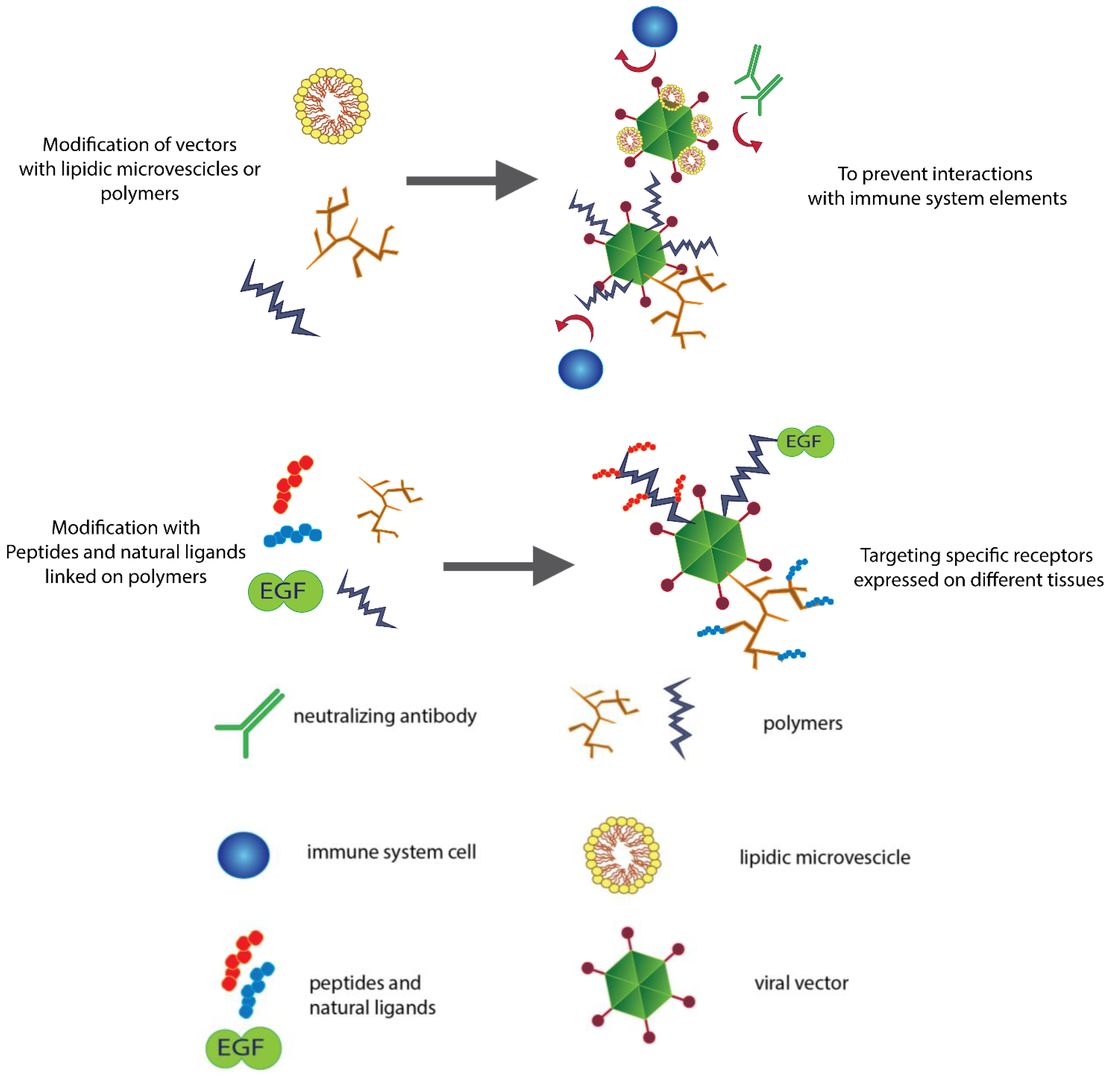 Figure 1. Modifying the surfaces of viral vectors for different purposes. Shielding viral vectors with polymers and lipidic vesicles typically results in the reduced immunogenicity and increased persistence of the vectors in the blood stream.1
Figure 1. Modifying the surfaces of viral vectors for different purposes. Shielding viral vectors with polymers and lipidic vesicles typically results in the reduced immunogenicity and increased persistence of the vectors in the blood stream.1
Physical Characteristics of Viral Vectors
Major physical characteristics of viral vectors encompass pH, osmolality, and aggregate formation. pH and osmolality are assessed via potentiometry and osmometry, respectively. Aggregate formation is evaluated utilizing dynamic light scattering (DLS). Aggregate formation refers to the propensity of viral particles to clump together, serving as a survival mechanism to resist environmental stress and endure degradation by disinfectants. Viral aggregation can impact the stability of viral vectors in various ways, including:
- Decrease the infectivity of viral vectors: Larger aggregates may hinder effective cell membrane penetration, reducing the vectors' ability to infect cells efficiently.
- Enhance the clearance of viral vectors in vivo: Larger aggregates are more prone to immune system recognition and clearance, potentially limiting gene expression and the duration of therapeutic effects.
- Impact on the safety of viral vectors: Large aggregates pose risks of adverse effects, including toxicity, inflammation, or organ damage.
Viral Genome Sequencing
The vector genome can be assessed using PCR or high-throughput next-generation genome sequencing (NGS) to verify its positive identity. NGS is employed to sequence all DNA encapsulated within viral particles. Firstly, packaged DNA is extracted from purified, DNase-treated AAV and subjected to NGS. The raw sequencing data is then analysed to determine the identity, as shown in the Figure.
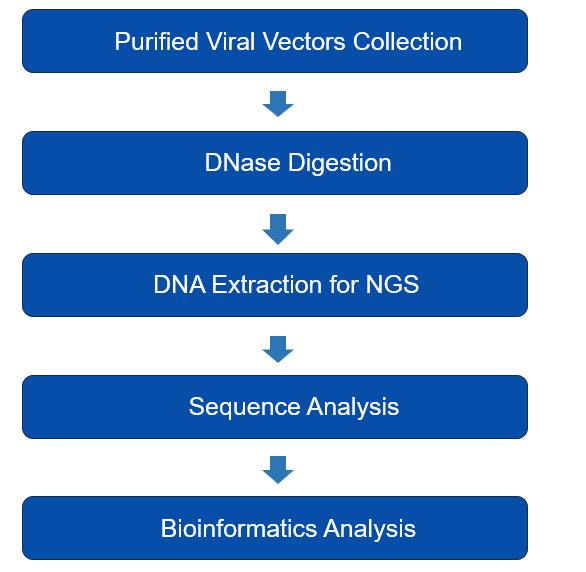 Figure.2 Simplified workflow for viral genome sequencing.
Figure.2 Simplified workflow for viral genome sequencing.
Viral Genome Sequencing Technologies
Technology of Viral Genome Sequencing
Significant progress has been made in viral vector sequencing, evolving from traditional Sanger sequencing to more powerful and higher-resolution technologies.
-
Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
NGS platforms enable deep, massively parallel sequencing of the entire vector preparation. This comprehensively reveals the genetic heterogeneity of viral populations, enabling highly sensitive detection of low-frequency variants, recombinant viral strains, and exogenous pathogens. -
Long-Read Sequencing
Long-read sequencing technologies are crucial for resolving complex genomic regions (e.g., highly repetitive ITRs) and providing haplotype-level information (identifying variations present on the same DNA molecule). -
Digital PCR (dPCR)
While primarily a quantitative tool, dPCR can also provide absolute, sequence-specific confirmation without the need for standard curves by using specific probes targeting unique junctions within the vector genome (e.g., promoter-transfer boundaries).
Applications of Viral Vector Identity Analysis
Comprehensive vector identification is not only a regulatory hurdle but also a prerequisite for the translation and commercialization of numerous therapeutic approaches.
- Preclinical Studies: In animal models, using incorrectly identified vectors can lead to erroneous conclusions about tropism, efficacy, and toxicity, wasting valuable time and resources.
- Vaccine Development: In viral vector-based vaccine platforms, identification analysis ensures the presence and stability of the correct expression cassette for the target antigen, directly impacting immunogenicity.
- Cell and Gene Therapy Products: For in vitro therapies (i.e., transducing and reinfusing patient cells), the identity of the vector used is a direct component of the final drug product's identity.
- Biomanufacturing Optimization: Identifying partial or rearranged genomes early in the process helps manufacturers identify issues with bioreactor conditions, culture medium composition, or harvesting protocols, significantly saving time and costs.
Confirming the Identity of Serotypes
For many viral vectors, especially adeno-associated viruses (AAVs), the serotype of the viral capsid determines the vector's tropism—its preference for infecting specific cell types or tissues.
Serotype Confirmation Methods:
- Molecular Genotyping: The most straightforward method is sequencing the genes encoding capsid proteins (e.g., the vp1, vp2, and vp3 genes for AAVs). The resulting amino acid sequences are then compared to a database of known serotypes. This method can confirm the expected genotype of the capsid component used in production.
- Serological Assay (Neutralization and Binding): Functional confirmation can be achieved by detecting the binding of the produced vector to a set of neutralizing antibodies against known serotypes. If the vector is neutralized only by antibodies corresponding to the target serotype, its identity is functionally confirmed.
- Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics: This powerful analytical technique can definitively confirm the identity and quantity of proteins. By digesting the capsid protein and analyzing the resulting peptides, mass spectrometry can verify the amino acid sequence of the VP protein, ensure the correct serotype assembly and rule out contamination from other serotypes.
Core Services at Creative Biolabs
At Creative Biolabs, we offer comprehensive analytical services designed to provide you with a complete perspective on viral vector characteristics.
-
Whole Genome Sequencing
Using NGS and Sanger sequencing technologies, we map and confirm every nucleotide of your vector genome. -
Residual Plasmid DNA Analysis
Quantifying and identifying any residual backbone plasmids used in the manufacturing process. -
Physical Titer and Empty/Filled Capsid Ratio Analysis
Using analytical ultracentrifugation (AUC) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). -
Stability and Comparability Studies
Monitoring changes in viral characteristics and other critical quality attributes (CQAs) over time and through the manufacturing process.
Why Choose Our Service?
The success of your advanced therapeutic protocols hinges on the reliability of your vector characterisation data. Choosing Creative Biolabs means partnering with experts who understand the science and regulatory landscape of gene therapy.
-
PhD-level Expertise
Our analytical team comprises experienced virologists, molecular biologists, and bioinformatics specialists.
-
Orthogonal Methodology Strategy
We utilise multiple independent analytical platforms (e.g., sequencing, mass spectrometry, chromatography) to validate critical parameters.
-
Rapid Turnaround and Data Integrity
Our streamlined workflow and dedicated high-throughput sequencing (HTS) infrastructure ensure rapid delivery of high-quality data.
-
Cutting-edge Technology
We invest in cutting-edge platforms (NGS, dPCR, HPLC, MS) to deliver data with the highest precision and sensitivity.
-
Regulatory Support
Our solutions are designed to comply with global regulatory standards and provide comprehensive documentation support for your applications.
-
Customized Solutions
We understand that every vector is unique. We will work closely with you to tailor an authentication strategy based on your specific structure and development stage.
Customer Review
"Creative Biolabs' whole-genome sequencing service detected a cryptic recombination event in our vector that our in-house methods had failed to detect. Their timely delivery of high-resolution data allowed us to halt production and modify the plasmid construct, saving costs and avoiding a major regulatory setback. Their scientific rigor is unparalleled."
— Dr. Evelyn V., Chief Scientific Officer
"We rely entirely on Creative Biolabs for empty/filled capsid ratio analysis using analytical ultracentrifugation. The consistency of their results, coupled with detailed analytical certificates, gives us complete confidence in our viral vector detection. Their team is knowledgeable and responds quickly to complex scientific questions."
— Mr. Ken F., VP of Quality Control
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How do you handle challenging repetitive sequences, such as AAV ITRs, in your whole-genome sequencing?
A: We primarily use advanced long-read sequencing technologies. These platforms generate reads much longer than the ITR region itself, allowing sequencers to precisely traverse and resolve the complete ITR structure and its flanking sequences, ensuring accurate identification of these critical regulatory elements.
Q: What is the typical turnaround time for empty/full ratio analysis using analytical ultracentrifugation (AUC)?
A: Depending on the vector complexity and the laboratory's current processing capabilities, our standard turnaround time for AUC-based empty/full ratio determinations is typically 2 to 3 weeks after receiving the sample. We also offer expedited analysis options to meet urgent IND application timelines.
Q: Can you help us develop acceptance criteria for critical quality attributes (CQAs) of viral vectors?
A: Absolutely. Our experienced scientific team works closely with clients to develop scientifically sound and product-stage-appropriate acceptance criteria based on industry best practices, regulatory guidelines, and preliminary non-clinical data, helping your product successfully enter clinical trials.
Q: What is the minimum sample size required for complete identification and purity testing?
A: Sample size requirements depend on the specific vector type (e.g., AAV vs. lentivirus) and the specific assays required. For standard comprehensive assays, we typically require at least 1 × 10¹² genome copies (GC), but we provide detailed customized consultation for each project to optimize sample usage.
Q: How much vector material is needed for analysis?
A: The required amount depends on the titer and the specific assays required. Typically, 1E10 to 1E11 vector genomes are sufficient for comprehensive analysis. We provide detailed sample preparation guidelines after project initiation.
Q: Can your services differentiate closely related serotypes, such as AAV1 and AAV6?
A: Absolutely. Our serotype confirmatory assays use highly specific detection methods, including discriminative qPCR and mass spectrometry analysis of specific capsid peptides, enabling accurate differentiation of closely related variants.
Connect with Us Anytime!
At Creative Biolabs, we are committed to being your strategic partner in this field. With advanced analytical services and deep scientific expertise, we are dedicated to ensuring your viral vectors are accurately characterized, thereby accelerating your research process from drug discovery to application.
Reference
- Capasso C, Hirvinen M, Cerullo V. Beyond gene delivery: Strategies to engineer the surfaces of viral vectors. Biomedicines, 2013, 1(1): 3-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines1010003 (Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.)
