Evaluation of ASO-BBB-Penetrating Peptide Conjugates
Introduction
Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) hold promises for central nervous system (CNS) disorders due to their ability to selectively modulate gene expression. However, the blood-brain barrier (BBB) poses a significant challenge, limiting ASO delivery to the CNS. While methods like intrathecal injections exist, they present limitations such as adverse side effects. This study explores non-invasive CNS delivery systems, with a focus on cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs). Specifically, scientists designed and synthesized BBB-penetrating peptides (BPPs) derived from apolipoprotein E (ApoE) and transferrin receptor-binding peptide (THR), conjugated to phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PMO, a safe and systemically deliverable ASO chemistry. Its resistance to nuclease degradation, coupled with the uncharged and hydrophobic nature of its backbone, facilitates penetration across biological barriers.). The BPP-PMO conjugates were assessed for their ability to restore SMN2 mRNA transcript levels. In vivo studies were conducted to examine CNS uptake and biodistribution in SMA mice.
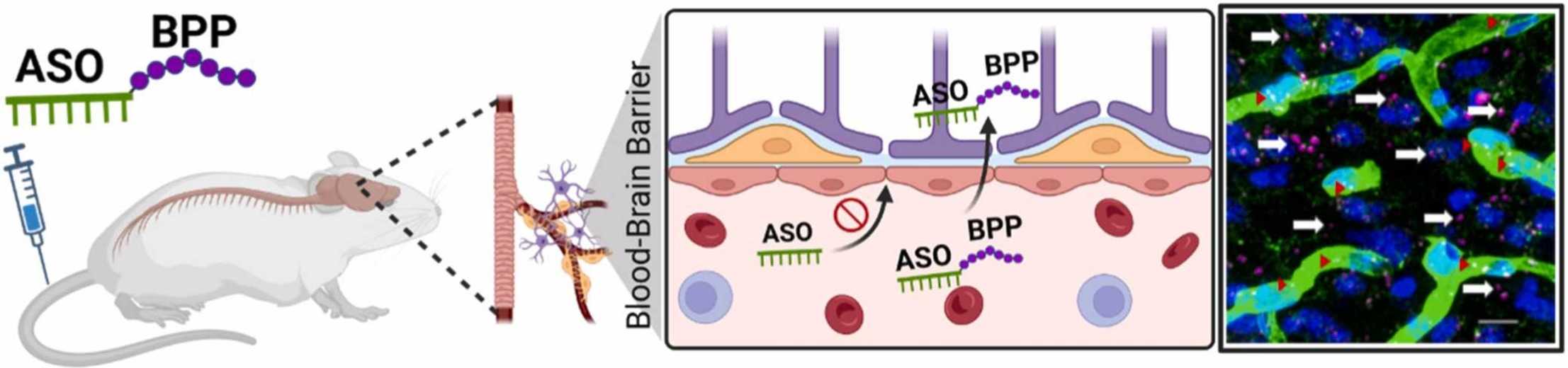 Fig.1 A novel BPP delivers its conjugated ASO into the brain following intravenous administration.1
Fig.1 A novel BPP delivers its conjugated ASO into the brain following intravenous administration.1
Design and Synthesis of BPP-PMO Conjugates
PMO was functionalized with 3-maleimidopropanoic acid, and BPPs were conjugated to PMO via a thiol-maleimide bond. The resulting BPP-PMO conjugates were then purified by RP-HPLC and characterized using UV-Vis absorbance. A series of BPPs containing ApoE or THR were designed, with or without the hemagglutinin-2 (HA2) endosomal escape peptide. To enhance proteolytic stability, D-amino acids were incorporated into some BPPs.
In Vitro Cellular Uptake Efficiency and Antisense Activity of BPP-PMO Conjugates
The in vitro cellular uptake efficiency and antisense activity of the BPP-PMO conjugates were evaluated using RT-qPCR in SMA patient-derived fibroblasts. The fibroblasts were treated with the conjugates, and SMN2 exon-7 inclusion was analyzed. All BPP-PMO conjugates increased full-length functional SMN2 expression in a concentration-dependent manner. Notably, ApoE BPPs exhibited superior cell-penetrating properties compared to THR BPPs, and the inclusion of the HA2 endosomal escape peptide enhanced cellular uptake and antisense activity.
Safety of BPP-PMO Conjugates
- Cytotoxicity Assay: The cytotoxicity of the BPP-PMO conjugates was assessed using the MTS assay in HEK293 cells. The cells were treated with various concentrations of the conjugates, and cell viability was measured. The results showed that all BPP-PMO conjugates were non-toxic at concentrations where maximum SMN2 transcript levels were achieved. While toxicity was observed at higher concentrations for conjugates containing HA2, the BPP-PMO conjugates demonstrated a relatively large safe window of tolerability.
- In Vivo Toxicity Assay: To evaluate the in vivo toxicity and potential immunostimulatory properties of the BPP-PMO conjugates, serum ALT levels and IgG concentrations were measured in mice treated with BPP8-PMO. The results indicated that BPP8-PMO did not cause hepatotoxicity or induce an immune stimulatory effect, supporting the safety of BPPs as systemic CNS delivery vectors for PMO.
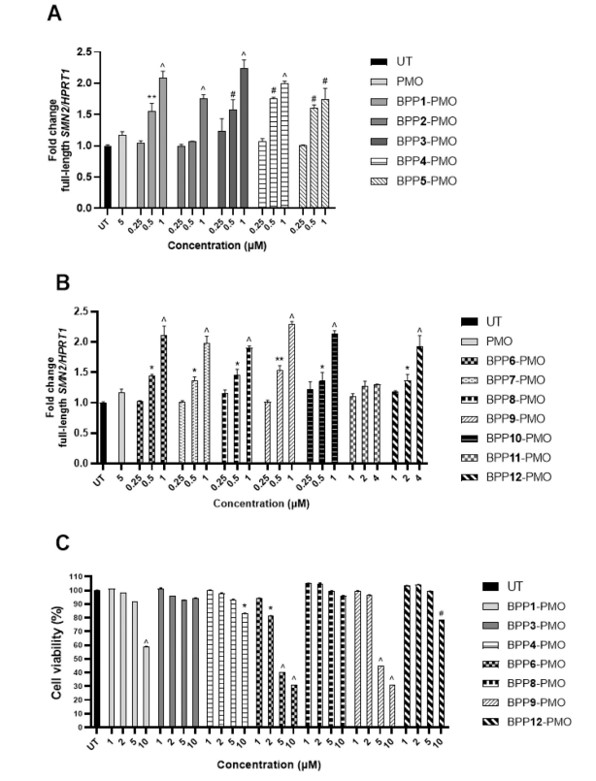 Fig.2 In vitro cellular uptake efficiency and cytotoxicity of the BPP-PMO conjugates.1
Fig.2 In vitro cellular uptake efficiency and cytotoxicity of the BPP-PMO conjugates.1
In Vivo BBB Permeability and Antisense Activity of BPP-PMO Conjugates
The in vivo BBB permeability and antisense activity of BPP-PMO conjugates were evaluated in SMN2 transgenic mice. The mice were treated with BPP8-PMO, BPP9-PMO, and BPP12-PMO, and SMN2 exon-7 inclusion was analyzed in brain and spinal cord tissues using qPCR. BPP8-PMO significantly increased SMN2 mRNA transcripts in both the brain and spinal cord, demonstrating its ability to deliver PMO into the CNS. In contrast, BPP9-PMO and BPP12-PMO showed no significant CNS activity.
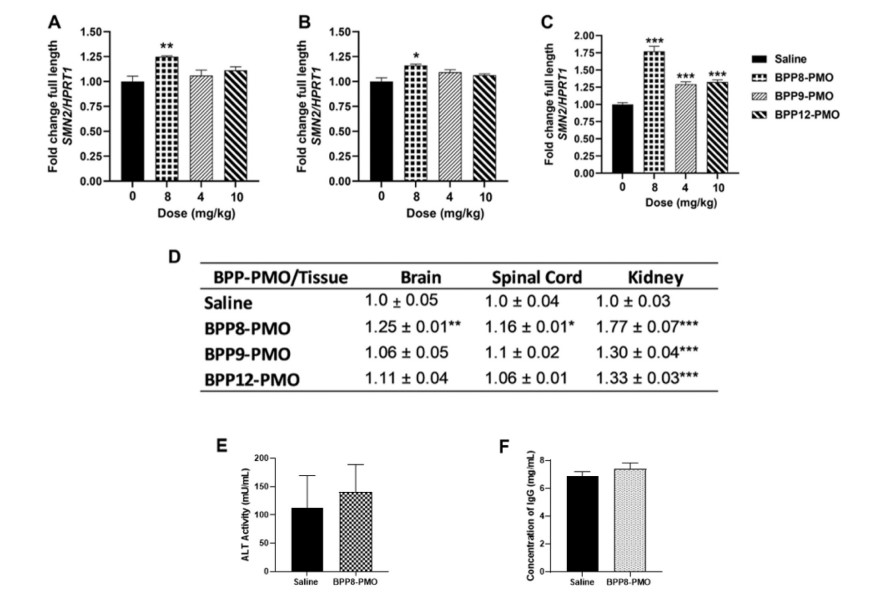 Fig.3 Analysis of the fold change in full-length SMN2 mRNA transcript levels and ALT activity of the BPP-PMO conjugates.1
Fig.3 Analysis of the fold change in full-length SMN2 mRNA transcript levels and ALT activity of the BPP-PMO conjugates.1
In Vivo Biodistribution Study of BPP-PMO Conjugates
The in vivo biodistribution of BPP8-PMO was investigated using fluorescence imaging. BPP8 and BPP8-PMO were labeled with Sulfo-Cyanine7, administered to SMN2 transgenic mice, and fluorescence emission was measured in harvested tissues. Both Cy7-BPP8 and Cy7-BPP8-PMO showed high fluorescence intensity in the brain and spinal cord, confirming CNS distribution. Notably, Cy7-BPP8-PMO exhibited higher localization in the brain parenchyma compared to Cy7-BPP8, demonstrating the peptide's ability to facilitate systemic delivery of PMO into the CNS.
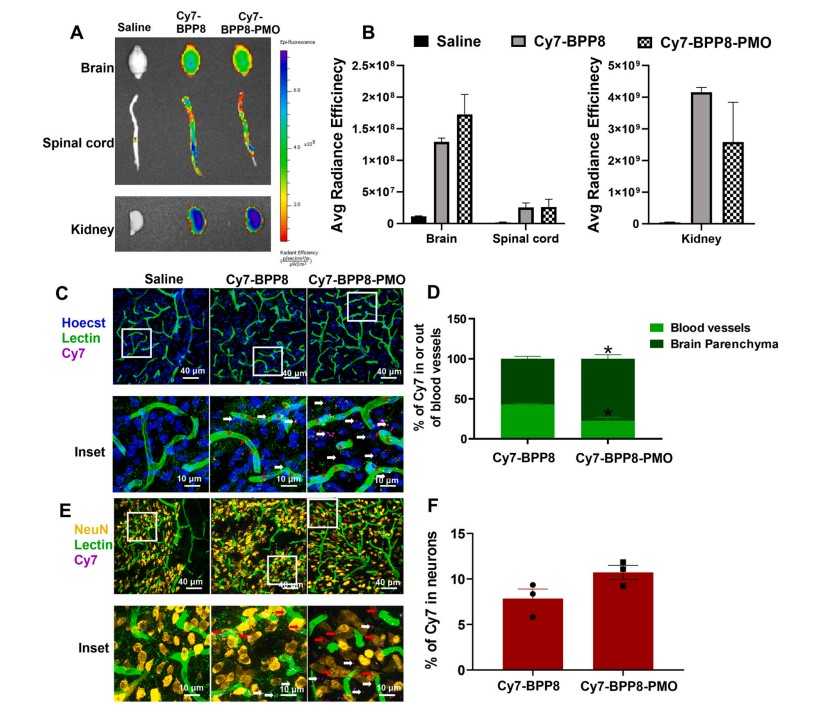 Fig.4 Analysis of uptake and quantification of Cy7-BPP8 and Cy7-BPP8-PMO biodistribution in the CNS.1
Fig.4 Analysis of uptake and quantification of Cy7-BPP8 and Cy7-BPP8-PMO biodistribution in the CNS.1
In summary, this study successfully designed and synthesized BPPs for the systemic delivery of PMO targeting SMN2 mRNA. The BPPs, particularly BPP8, demonstrated efficient CNS delivery of PMO in SMA mouse models, showing potential as a novel platform for systemically administered neurotherapeutics.
Leveraging extensive expertise in peptide synthesis and bioconjugation techniques, Creative Biolabs offers a one-stop service for custom oligonucleotide-peptide conjugate development. Contact us to explore your project needs.
Reference
- Yeoh, Yuan Qi, et al. "Efficient systemic CNS delivery of a therapeutic antisense oligonucleotide with a blood-brain barrier-penetrating ApoE-derived peptide." Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 175 (2024): 116737. Under open access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
