CFP Structure CFP Functions CFP Test CFP Deficiency Therapeutic Target
One of the lesser-discussed, yet critically important components of the immune response is complement component factor Properdin (CFP). Properdin plays a pivotal role in the regulation and activation of the complement system, particularly in the alternative pathway, which is crucial for recognizing and neutralizing pathogens, as well as maintaining immune homeostasis.
Structure of Complement Factor P
CFP is a glycoprotein that is composed of multiple subunits that form a dimeric or oligomeric structure. The native form of Properdin consists of five homologous units, arranged in a head-to-tail configuration. Each unit has a unique functional domain that contributes to the protein's ability to interact with other complement components and cell surfaces.
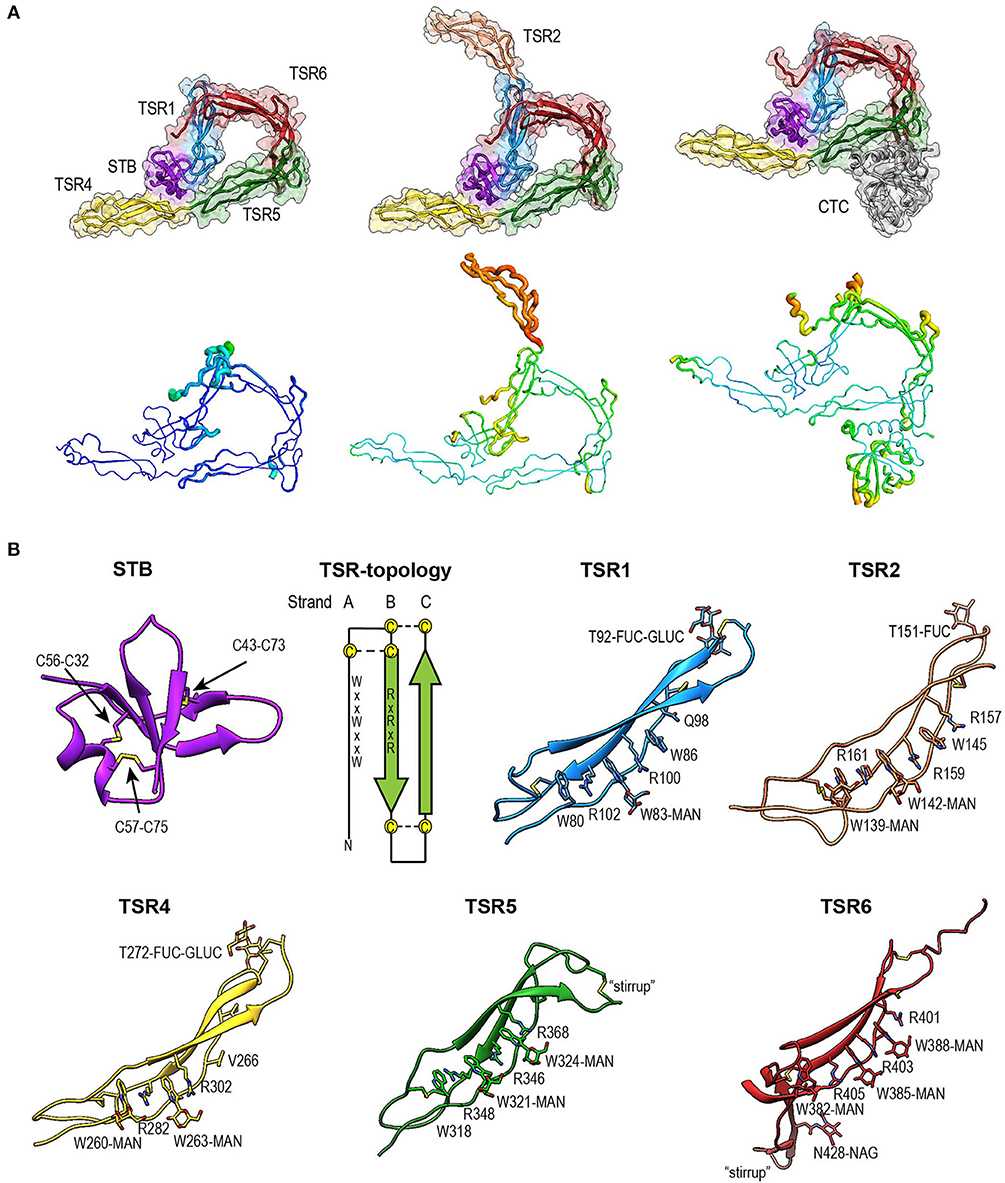 Fig. 1 Overview of Properdin structures.1,3
Fig. 1 Overview of Properdin structures.1,3
Key Structural Features of CFP
-
Molecular weight: Approximately 53-57 kDa (depending on isoform and post-translational modifications).
-
Amino acid composition: The protein is rich in proline, glycine, and serine residues, with several key cysteine residues involved in the formation of disulfide bonds that stabilize its oligomeric form.
-
Glycosylation sites: Properdin contains several glycosylation sites that are important for its stability and function.
-
Oligomerization: Properdin monomers polymerize head-to-tail into cyclic dimers, trimers, and tetramers, existing in plasma at a fixed ratio of ~22:52:28. The tetramer is the most prevalent form. These oligomers form ring-shaped vertices connected by flexible edges, with each vertex binding to a C3bBb convertase complex.
Functional Implications of CFP
The central functional domain of Properdin consists of a scr domain (short consensus repeat), which allows Properdin to bind to C3b and C3 convertase complexes in the complement system. Through this interaction, Properdin stabilizes the C3 convertase, which is essential for the amplification of complement activation.
-
Stabilization of convertases: The TSR5 and TSR6 domains bind C3b and Bb, preventing dissociation.
-
Initiation of AP activation: The oligomeric structure allows simultaneous binding to microbial surfaces and convertases.
-
Regulation: The flexible, modular design enables dynamic interactions with complement components and pathogens.
Properdin's modular, oligomeric structure enables its dual roles as a stabilizer and initiator in the alternative pathway. The interplay between TSR domains, post-translational modifications, and polymerization dynamics underscores its critical regulatory function in complement activation.
Function of Complement Factor P
CFP is a positive regulator of the complement system, primarily acting on the alternative pathway. Its functional roles are multifaceted, balancing immune defense and tissue protection.
Role of CFP in the Complement System
Table 1 Functional roles of CFP in the complement system.
|
Function
|
Approaches and Mechanisms
|
|
Stabilization of Convertases
|
Properdin's primary role is to stabilize AP convertases, including C3 convertase and C5 convertase, by:
-
Physical bridging: TSR5 and TSR6 domains bind C3b and Bb, maintaining their association and preventing dissociation.
-
Inhibiting decay: Competes with negative regulators (e.g., factor I, factor H) for convertase binding, reducing susceptibility to inactivation.
This stabilization increases convertase half-life by 5-10-fold, enhancing C3b deposition and amplification.
|
|
Initiation of Alternative Pathway Activation
|
Properdin can directly bind to microbial surfaces or host tissues, serving as a platform for de novo convertase assembly. Two mechanisms are proposed:
-
Nonspecific initiation: Fluid-phase C3b binds surfaces and forms convertases.
-
Properdin-directed initiation: Target-bound Properdin recruits C3b and Bb, bypassing the need for pre-existing C3b.
|
|
Amplification and Propagation
|
Properdin drives AP amplification by:
-
Enhancing C3b deposition: Stabilized convertases cleave more C3, creating a positive feedback loop.
-
Switching substrate specificity: High C3b density on surfaces enables convertases to cleave C5, initiating the terminal pathway.
-
Forming C5 convertase: Properdin stabilizes the C5 convertase, which cleaves C5 into C5a and C5b.
|
|
Modulation of Complement-mediated Lysis
|
Properdin's activity culminates in membrane attack complex (MAC) formation:
-
C5b-9 complex assembly: C5b interacts with C6, C7, C8, and C9 to form pores in target membranes, causing lysis.
-
Anaphylatoxin release: C3a and C5a recruit immune cells and amplify inflammation.
|
Role in the Immune Regulation
In addition to its role in pathogen defense, Properdin is involved in the modulation of inflammatory responses. It has been shown that Properdin can influence the balance of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, which play a role in controlling the immune response and preventing autoimmune reactions.
-
Cytokine modulation: Properdin can influence the secretion of interleukins, particularly IL-6 and IL-8, both of which are key players in the inflammatory response.
-
Autoimmunity and tissue protection: Dysregulation of Properdin has been implicated in autoimmune diseases, where an inappropriate activation of the alternative pathway may result in tissue damage.
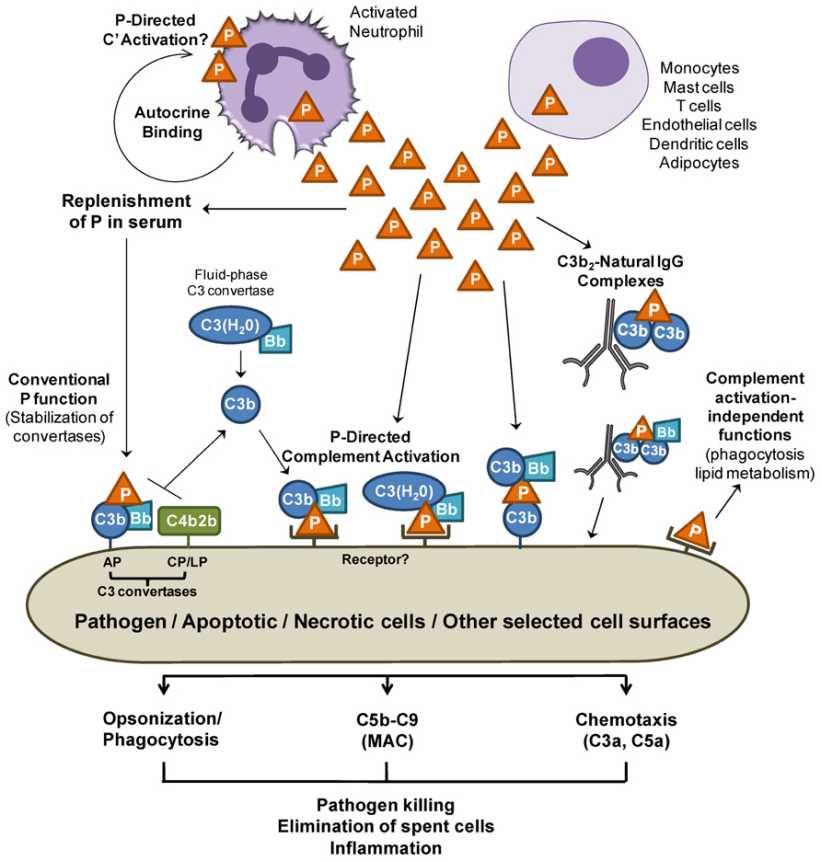 Fig. 2 Overview of Properdin functions.2,4
Fig. 2 Overview of Properdin functions.2,4
CFP is an important component of the complement pathway. CFP testing is an important tool for diagnosing defects and monitoring complement-driven diseases. Functional assays assess biological activity, while quantitative assays measure protein levels, each providing different insights into AP regulation.
The CFP test is available in two primary formats:
Functional Assays
-
Purpose: Measure the biological activity of CFP in stabilizing AP convertases (C3bBb and C5 convertase).
-
Methodology:
-
ELISA-based: Use labeled antibodies to detect complement proteins deposited during convertase activity. The amount of deposited proteins correlates with Factor P functionality.
-
Range: Typically 0–200% relative activity, with results compared to a calibrator set at 100% functionality.
-
Sample types: Serum or EDTA plasma.
Quantitative Assays
-
Purpose: Measure CFP protein concentration in serum/plasma.
-
Methodology:
-
Sandwich ELISA: Immobilized antibodies capture CFP, detected via HRP-labeled secondary antibodies and TMB substrate. Results are read at 450 nm.
-
Range: 0–200 ng/mL.
Table 2 Methodology and key features.
|
Feature
|
Functional Assay
|
Quantitative Assay
|
|
Detection Target
|
Convertase activity (C3bBb/C5 convertase)
|
Factor P protein concentration
|
|
Technology
|
ELISA with complement protein detection
|
Sandwich ELISA with HRP/TMB
|
|
Sample Size
|
50 µL
|
Varies
|
|
Incubation Time
|
~4 hours
|
~2–4 hours
|
|
Regulatory Status
|
Research Use Only
|
Research Use Only
|
Interpretation and Limitations
The results of the different tests are interpreted below:
-
Functional assays
-
Low activity: Suggests factor P deficiency or dysfunction, requiring correlation with clinical symptoms.
-
High activity: May indicate AP hyperactivation in diseases like C3 glomerulopathy.
-
Quantitative assays
-
Low concentration: Associated with deficiency states or consumption in autoimmune diseases.
-
Elevated levels: Observed in inflammatory conditions.
Limitations also exist for both tests.
-
Functional assays: Do not measure protein concentration directly; results depend on convertase stability.
-
Quantitative assays: May not reflect biological activity, as oligomerization state affects function.
Factor P Deficiency and Related Diseases
CFP deficiency is a rare X-linked recessive disorder that severely compromises the alternative pathway of complement activation, leading to heightened susceptibility to bacterial infections, particularly Neisseria meningitidis.
CFP deficiency may exhibit a number of clinical manifestations.
Type I
-
Characteristics: Complete absence of detectable Properdin in plasma.
-
Risk: 250-fold increased susceptibility to meningococcal sepsis
Type II
-
Characteristics: Low but detectable Properdin levels (<10% of normal).
-
Risk: Similar to Type I but less common
Type III
-
Characteristics: Normal protein levels but dysfunctional Properdin.
-
Risk: Rare and less well-characterized
Properdin deficiency can lead to inadequate complement activation and impaired pathogen clearance and has been associated with an increased susceptibility to bacterial infections. In excessive activation of the complement system, Properdin may be implicated in the exacerbation of tissue damage by enhancing the complement-mediated inflammatory cascade, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis, and glomerulonephritis.
Factor P as a Therapeutic Target
CFP acts as the sole positive regulator of the complement alternative pathway, driving the amplification response of the complement system by stabilizing C3 convertase and C5 convertase. Its therapeutic targeting is mainly in the regulation of complement-mediated diseases, balancing immune defense and tissue protection by targeting degradation or inhibition of preparasin.
-
Targeted protein degradation (TPD) technology: Selective degradation of preparins using the ubiquitin-proteasome system or the lysosomal system reduces their ability to stabilize converting enzymes.
-
Antibody interference: Neutralizing antibodies can block the binding of caveolin to C3bBb, reducing convertase stability.
-
Small molecule inhibitors : Target the TSR structural domains (e.g., TSR5/TSR6) of preparasins and interfere with their interaction with C3b.
Table 3 Prospects and challenges for clinical applications.
|
Application Areas
|
Potential Value
|
Technical Challenges
|
|
C3 nephropathy
|
Reducing complement-mediated glomerular injury
|
Requires balancing immune defense with tissue protection
|
|
aHUS/PNH
|
Mitigation of intravascular thrombosis
|
Prolactin deficiency may increase risk of infection
|
|
Autoimmune diseases
|
Control of complement-mediated inflammatory response
|
Specificity and stability of targeting technologies need to be validated
|
Currently, researchers are still investigating the precise mechanisms by which Properdin regulates the alternative pathway. Several important areas of exploration include:
-
The role of Properdin in neuroinflammation
-
Improved complement inhibition
-
Properdin as a cancer immunotherapy target
CFP is an important component of the immune system and plays a key role in regulating alternative pathways of complement activation. Its function is not limited to pathogen defense, but also influences immune responses and inflammatory processes. CFP dysregulation has been linked to a variety of diseases, including infections, autoimmune diseases, and cancer. Ongoing studies of the molecular mechanisms of CFP offer exciting possibilities for novel diagnostic and therapeutic strategies aimed at modulating the complement system.
Creative Biolabs offers a full range of complement-related services and products, including:
If you want more information, please feel free to contact us.
References
-
Van den Bos, Ramon M., et al. "Insights into enhanced complement activation by structures of properdin and its complex with the C-terminal domain of C3b." Frontiers in immunology 10 (2019): 2097. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02097
-
Cortes, Claudio, et al. "Local release of properdin in the cellular microenvironment: role in pattern recognition and amplification of the alternative pathway of complement." Frontiers in immunology 3 (2013): 412. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2012.00412
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 3.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig. 1 Overview of Properdin structures.1,3
Fig. 1 Overview of Properdin structures.1,3
 Fig. 2 Overview of Properdin functions.2,4
Fig. 2 Overview of Properdin functions.2,4