What is C2 C2 Function C2 Deficiency C2 Test Drug Discovery
Complement component C2 (C2) is a pivotal serine protease within the classical and lectin pathways of the complement system. Acting as a vital proteolytic component of the C3 convertase in both the classical and lectin pathways, C2 plays a pivotal role in microbial defense, immune complex clearance, and inflammatory signaling. As research into complement-driven disorders grows, understanding C2's structure and function has become a priority across immunology, infection biology, and drug development sectors.
Creative Biolabs provides comprehensive research services to explore complement proteins, including functional activity assays and C2-specific pathway analysis.
What is C2 Complement?
The content of C2 in human plasma is generally small, and it is mainly involved in the innate immune response to infection or injury through activation of the classical complement pathway. The activation of C2 involves the binding of C1 to the Fc portion of the antibody in the antigen-antibody complex. This binding forms C1 esterase, which cleaves C2 and C4.
C2 shares homology with complement factor B and belongs to the trypsin-like serine protease family. Upon cleavage by C1s or MASP-2, C2 yields two fragments:
-
Complement component C2a (active enzyme): Associates with C4b to form C3 convertase.
-
Complement component C2b (formerly called C2a in older nomenclature): Released and considered biologically inactive.
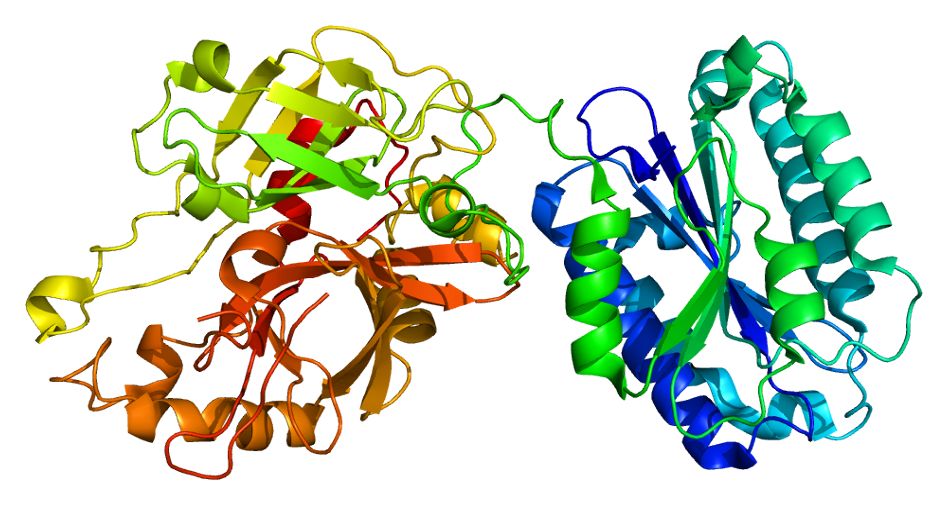 Fig. 1 Molecular structure of C2.1
Fig. 1 Molecular structure of C2.1
C2 is a single-chain glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 100–110 kDa. Its structure is characterized by:
-
Three-lobed architecture: Electron microscopy reveals a tripartite organization, with the N-terminal lobe comprising three complement control protein (CCP) modules, also known as sushi domains.
-
Glycosylation: C2 contains about 15.9% carbohydrate by weight, which influences its stability and interactions.
-
Serine protease domain: The C-terminal region harbors the catalytic serine protease activity essential for downstream complement activation.
C2 Protein Function
C2 serves as the catalytic core of the classical and lectin complement pathways, driving immune defense through its enzymatic activity in convertase complexes. Its functional role spans activation, amplification, and regulation of complement-mediated responses, making it indispensable for host protection and immune homeostasis.
Table 1 Functional role of C2 in complement activation.
|
Mechanistic Role
|
Description
|
|
Activation and Cleavage
|
C2 is activated through proteolytic cleavage by C1s (classical pathway) or MASP-2 (lectin pathway) when bound to surface-associated C4b in the presence of Mg2+.
|
This cleavage generates two fragments:
-
C2a: The larger fragment (509 residues) contains the serine protease domain and forms the catalytic subunit of C3/C5 convertases.
-
C2b: The smaller fragment (223 residues) is released into the fluid phase and may regulate inflammatory responses.
|
|
Convertase Formation
|
C2a binds to C4b to form two critical enzymatic complexes:
-
C3 Convertase (C4b2a): Cleaves C3 into C3a (anaphylatoxin) and C3b (opsonin), amplifying opsonization and inflammation.
-
C5 Convertase (C4b2a3b): Processes C5 into C5a (chemotactic factor) and C5b, initiating the membrane attack complex (MAC) for pathogen lysis.
|
|
These convertases are short-lived, ensuring localized activity to prevent systemic damage.
|
Enzymatic Activity and Substrate Specificity
-
Catalytic mechanism: C2a functions as a serine protease, with a catalytic triad (His-Asp-Ser) that hydrolyzes peptide bonds in C3 and C5.
-
pH sensitivity: C2 exhibits latent protease activity at alkaline pH (>7), independent of cofactors, enabling sustained C3 processing in inflammatory microenvironments.
-
Substrate recognition: The von Willebrand factor A domain in C2a enhances affinity for C4b, stabilizing the convertase complex.
C2 Protein Deficiency
C2 is the most commonly deficient component among classical pathway proteins. C2 deficiency is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern and results in impaired formation of C3 convertase. Clinical manifestations include:
Chronic complement activation via the C2-driven pathway is associated with the following processes.
-
SLE and RA: persistent immune complex deposition activates the classical pathway.
-
Glomerulonephritis: C2 mediated C3 converting enzyme leads to kidney damage.
Given its central role, C2 is an attractive target for therapeutic intervention. Selective modulation of the classical pathway by inhibition of C2 activity provides a means of inhibiting pathologic complement activation without compromising the function of the alternative pathway.
Complement C2 Test
Complement C2 testing is a specialized laboratory assessment used to evaluate the activity or concentration of the C2 in serum. Creative Biolabs has a robust standardized complement test platform and a variety of test technologies, such as nephelometry, ELISA, RID, and TRIFMA assays, to deliver fast, reliable & objective, easy to interpret results within 3 hours. We provide our customers with routine quantitative tests and functional activity test for individual components as well as a full range of complement components testing services.
Experimental Tools and Assays Involving C2
Table 2 Experimental tools and assays.
|
Tool
|
Application
|
|
ELISA kits
|
Quantification of C2 concentration in serum/plasma
|
|
Western blotting
|
Detection of full-length or cleaved C2 fragments
|
|
Hemolytic assays (CH50)
|
Assess classical pathway functionality
|
|
Recombinant C2 proteins
|
Functional studies, structural biology, and screening assays
|
|
Gene editing
|
Create C2 knockout cell or animal models
|
Interpretation of Results
Table 3 Interpretation of results
|
Result Type
|
Clinical Implication
|
|
Normal
|
Functional C2 present; classical pathway is intact
|
|
Low/Absent
|
Suggests C2 deficiency, increasing risk for recurrent infections and autoimmune disease (e.g., SLE)
|
|
Elevated
|
May be seen in acute phase response, but is less clinically significant
|
|
Equivocal
|
Partial deficiency or decreased activity, may require repeat or additional testing
|
C2 Research in Drug Discovery
Inhibiting C2 offers pathway-selective control, avoiding the systemic suppression seen with terminal complement inhibitors. This strategy is particularly beneficial for treating disorders where the classical pathway is overactivated while preserving the alternative pathway's microbial defense role.
-
SLE
-
Drives immune complex-mediated tissue injury
-
C2 inhibition may prevent complement-mediated flares
-
Immune complex glomerulonephritis
-
Contributes to renal inflammation
-
C2 blockade may reduce complement-driven renal damage
-
Antibody-mediated rejection (AMR)
-
Classical pathway activation by donor-specific antibodies
-
C2-targeted inhibition may reduce graft damage
-
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
-
Autoantibody binding activates complement
-
Suppressing C2 may prevent hemolysis
Small-molecule inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies, and RNAi-based therapeutics targeting C2 are currently being investigated in preclinical models. These approaches offer promising pharmacological profiles with high specificity.
As the field of complementology evolves, C2 emerges not only as a classical cascade component but also as a promising therapeutic target. Targeted inhibition, biomarker discovery, and structural-functional studies of C2 may unlock novel treatment strategies for complement-driven disorders.
Creative Biolabs continues to support global researchers with advanced solutions in complement component analysis. With a robust portfolio of reagents, assay systems, and expert consulting, we are committed to accelerating discoveries in innate immunity.
If you want more information, please feel free to contact us.
Reference
-
From Wikipedia: By Emw - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Protein_C2_PDB_2i6q.png
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig. 1 Molecular structure of C2.1
Fig. 1 Molecular structure of C2.1