All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
Creative Biolabs has developed various anti-CD37-related products to support the development of CAR-T therapy. Do not hesitate to contact us for further information or to discuss how our CD37 CAR related products and services can benefit you.
CD37 is a highly glycosylated protein and belongs to the tetraspanins family that participates in several important cellular processes, such as cell membrane organization, cell proliferation, cell adhesion, and motility. The expression of CD37 is almost restricted to the immune system cells, particularly to mature B cells. Several studies showed that CD37 is associated with various diseases, including B-cell lymphoma, T-cell lymphoma, autoimmune diseases, and so on. Regarding these features, targeting CD37-related immunotherapy serves as a promising approach for clinical research.
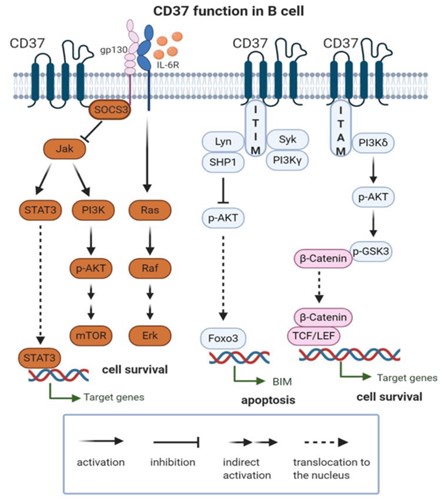 Fig.1 The main function of CD37 in B cell.1
Fig.1 The main function of CD37 in B cell.1
Anti-CD37 CAR-T Expression Test
Creative Biolabs has successfully developed various CAR detection reagents (target-specific types, G4S linker-specific types) to evaluate CAR expression. Meanwhile, we offer several appropriate approaches to help clients speed up CART development, including but not limited to flow cytometry, qPCR, and WB.
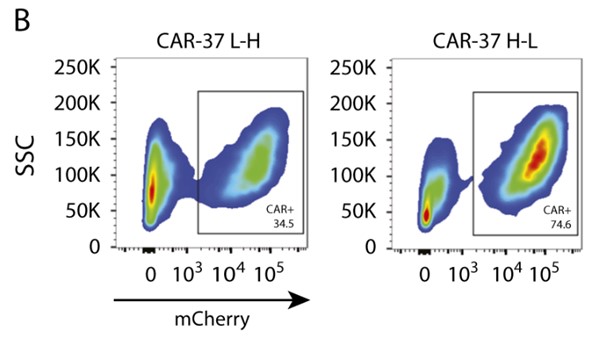 Fig.2 Flow cytometry analysis of CD37 CAR expression on activated CD37 CAR-T cells after lentivirus transduction. The figure shows that CD37 CAR scFv VH-to-VL orientation construct with a higher CD37 CAR expression (see CAR-37 H-L).2
Fig.2 Flow cytometry analysis of CD37 CAR expression on activated CD37 CAR-T cells after lentivirus transduction. The figure shows that CD37 CAR scFv VH-to-VL orientation construct with a higher CD37 CAR expression (see CAR-37 H-L).2
Anti-CD37 CAR-T Expansion Test
Proliferation capacity is a reflection index of cell vitality, state, and so on. Creative Biolabs provides comprehensive expansion capacity assessment services for CAR-T development, including proliferation tests with or without special target stimulation. Regarding the special targets and project needs of different clients, we are dedicated to providing customized and appropriate service to get the desired results.
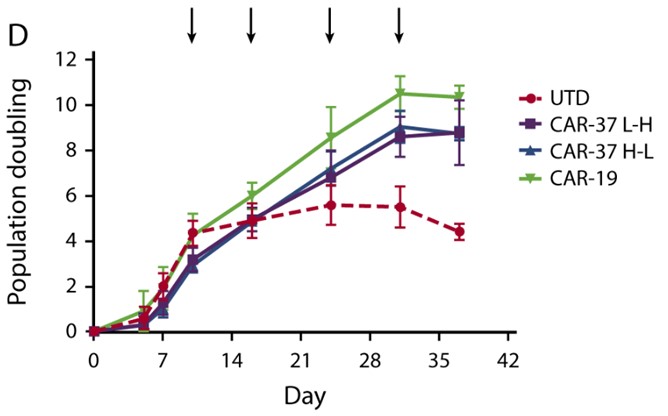 Fig.3 Ex vivo expansion analysis of CD37 CAR-T cells with CD3/CD28 bead and target cell stimulation. Each arrow showed the CD37+&CD19+ expressed K562 cell stimulation.2
Fig.3 Ex vivo expansion analysis of CD37 CAR-T cells with CD3/CD28 bead and target cell stimulation. Each arrow showed the CD37+&CD19+ expressed K562 cell stimulation.2
Anti-CD37 CAR-T Cytokine Release Test
In the process of co-incubation of CART cells and tumor cells, cytokine production is often associated. For the anti-CD37 CAR-T cytokine release test, Creative Biolabs provides various approaches to measure the effect. For a few cytokine types, we recommend economical single cytokine testing by ELISA. For customers who want to carry out various types of testing, we also provide robust multiplex cytokine tests.
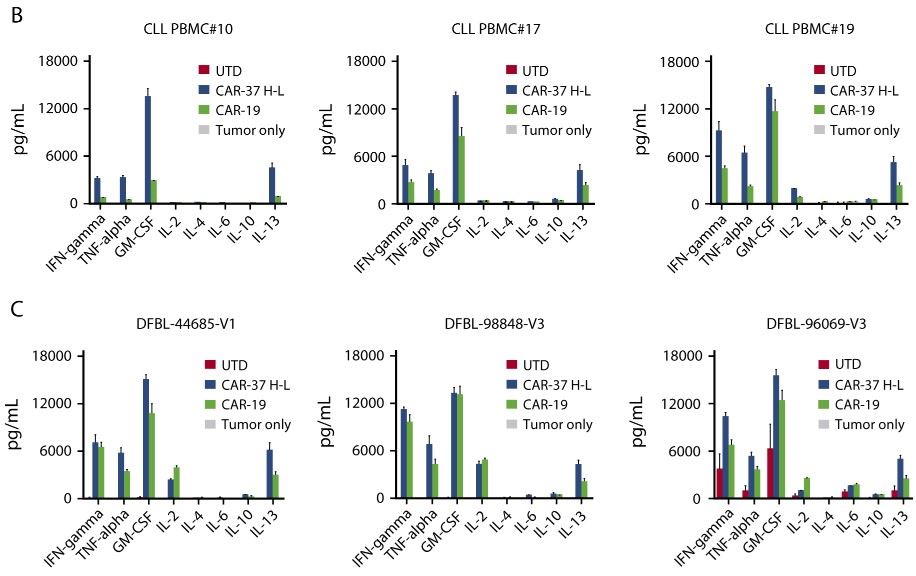 Fig.4 Cytokine array analysis of CD37 CAR-T cells co-cultured with CLL (B) or MCL (C) tumor cells at a 1:1 E:T ratio.2
Fig.4 Cytokine array analysis of CD37 CAR-T cells co-cultured with CLL (B) or MCL (C) tumor cells at a 1:1 E:T ratio.2
Anti-CD37 CAR-T In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
For the in vitro cytotoxicity test, we provide several highly sensitive approaches and multiple types of tumor target cell lines to evaluate the killing efficacy of anti-CD37 CART.
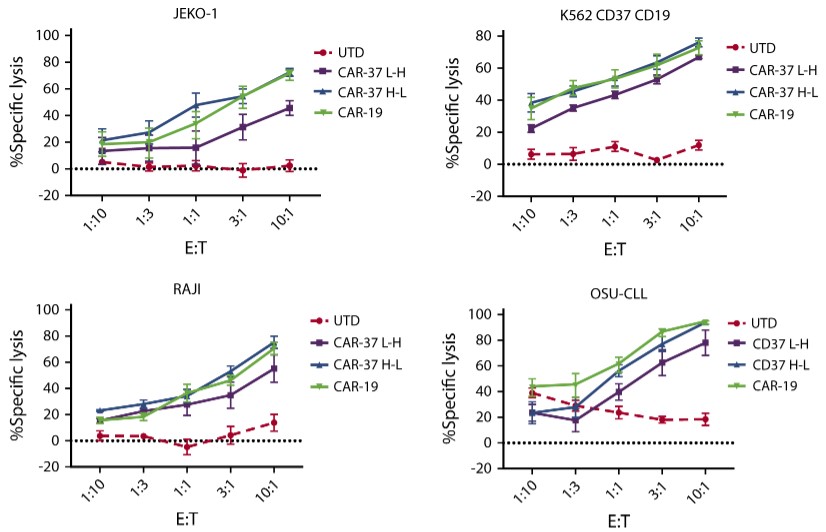 Fig.5 In vitro cytotoxicity analysis of CD37 CAR-T against different target cells with indicated E:T ratios.1
Fig.5 In vitro cytotoxicity analysis of CD37 CAR-T against different target cells with indicated E:T ratios.1
Anti-CD37 CAR-T Cell Therapy Animal Models
To evaluate the in vivo efficacy of CAR-T cells, it is crucial to choose an appropriate animal model and establish a suitable experiment design according to the project's needs. Creative Biolabs has established extensive efficient models for in vivo evaluation, including cell line-derived xenografted (CDX) models, and patient-derived xenografted (PDX) models, patient-derived organoid models for CAR-T development.
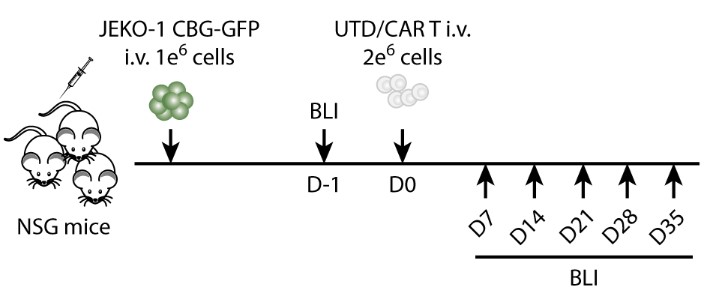 Fig.6 Experiment design of in vivo efficacy evaluation for CD37 CART.2
Fig.6 Experiment design of in vivo efficacy evaluation for CD37 CART.2
Efficacy Test of Anti-CD37 CAR-T
For in vivo efficacy assessment for CART, we offer a variety of detection approaches to validate the efficacy based on multiple metrics, including but not limited to in vivo bioluminescence imaging, and tumor volume detection.
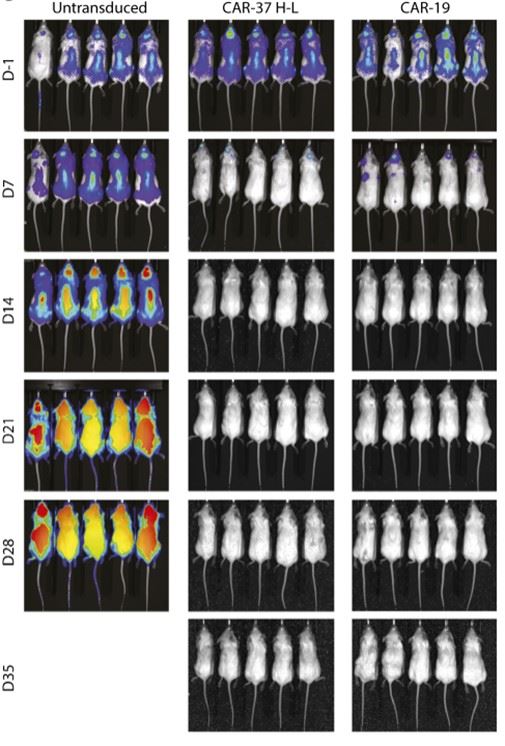 Fig.7 In vivo tumor clearance evaluation of CD37 CAR-T in a xenograft model of MCL.2
Fig.7 In vivo tumor clearance evaluation of CD37 CAR-T in a xenograft model of MCL.2
Toxicity Evaluation Anti-CD37 CAR-T
In addition, we also provide in vivo toxicity evaluation services for CAR-T cell therapy, such as tumorigenicity study, and off-target toxicity study.
References
 Loading...
Loading...
| CAT | Product Name | Target Species | Antibody Clone | Antibody Host | Receptor Construction | Vector Type | Targeting Cell Type | CAR Vector Type | Inquiry & Datasheet |
| CAR-YF054 | Anti-CD37 (CBL-YF012) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBL-YF012 | Humanized | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-YF055 | Anti-CD37 (CBL-YF012) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBL-YF012 | Humanized | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP070 | Anti-CD37 (ECD) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | ECD | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP071 | Anti-CD37 (ECD) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | ECD | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP2434 | Anti-CD37 (HH1) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | HH1 | Humanized | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP2435 | Anti-CD37 (HH1) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | HH1 | Humanized | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP2436 | Anti-CD37 (Otlertuzumab) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | Otlertuzumab | Human | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP2437 | Anti-CD37 (Otlertuzumab) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | Otlertuzumab | Human | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP2438 | Anti-CD37 (K7153A) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | K7153A | Human | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP2439 | Anti-CD37 (K7153A) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | K7153A | Human | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP2440 | Anti-CD37 (chHH1.1) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | chHH1.1 | Human | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP2452 | Anti-CD37 (M-B371) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | M-B371 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP2453 | Anti-CD37 (M-B371) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | M-B371 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP2454 | Anti-CD37 (1.BB.349) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 1.BB.349 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP2455 | Anti-CD37 (1.BB.349) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 1.BB.349 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP2456 | Anti-CD37 (IPO-24) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | IPO-24 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP2457 | Anti-CD37 (IPO-24) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | IPO-24 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP2458 | Anti-CD37 (8H186) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 8H186 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP2459 | Anti-CD37 (8H186) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 8H186 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| CAR-ZP2460 | Anti-CD37 (7H197) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 7H197 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell |
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION