The complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) crossmatch (CDC-XM) is a technology that can be applied to both T cells and B cells. The former reflects the presence of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I antibodies, while the latter reflects both HLA class I and II antibodies. Since B cells express higher amounts of class I antigens, a positive B cell CDC-XM associated with a negative T cell CDC-XM may indicate low levels of class I antibodies. Creative Biolabs offers CDC-XM test to provide direct evidence for the presence of potentially pathologic (cytotoxic) alloantibodies.
CDC was the first technique routinely used for HLA antibody detection and the crossmatch test. The mechanism of CDC is antibody-coated target cells recruit and activate components of the complement cascade, leading to the formation of a membrane attack complex (MAC) on the cell surface and subsequent cell lysis.
Firstly, good quality T- and B-lymphocytes are isolated from the donor's blood and incubated separately with the serum of potential recipients. Rabbit complement is subsequently added and after an appropriate incubation period, eosin is added together with formalin to fix the cells. Longer incubation periods and additional wash steps have been introduced to eliminate unbound antibodies before the addition of complement. If donor-specific antibodies are present in recipient serum, these will bind to HLA antigens on donor cells resulting in complement activation via the classical pathway. This finally generates the MAC, which inserts into the lipid bilayer causing cell rupture and uptake of vital dye. These dead cells will be visualized as red when seen under the microscope (shown as Fig.1).
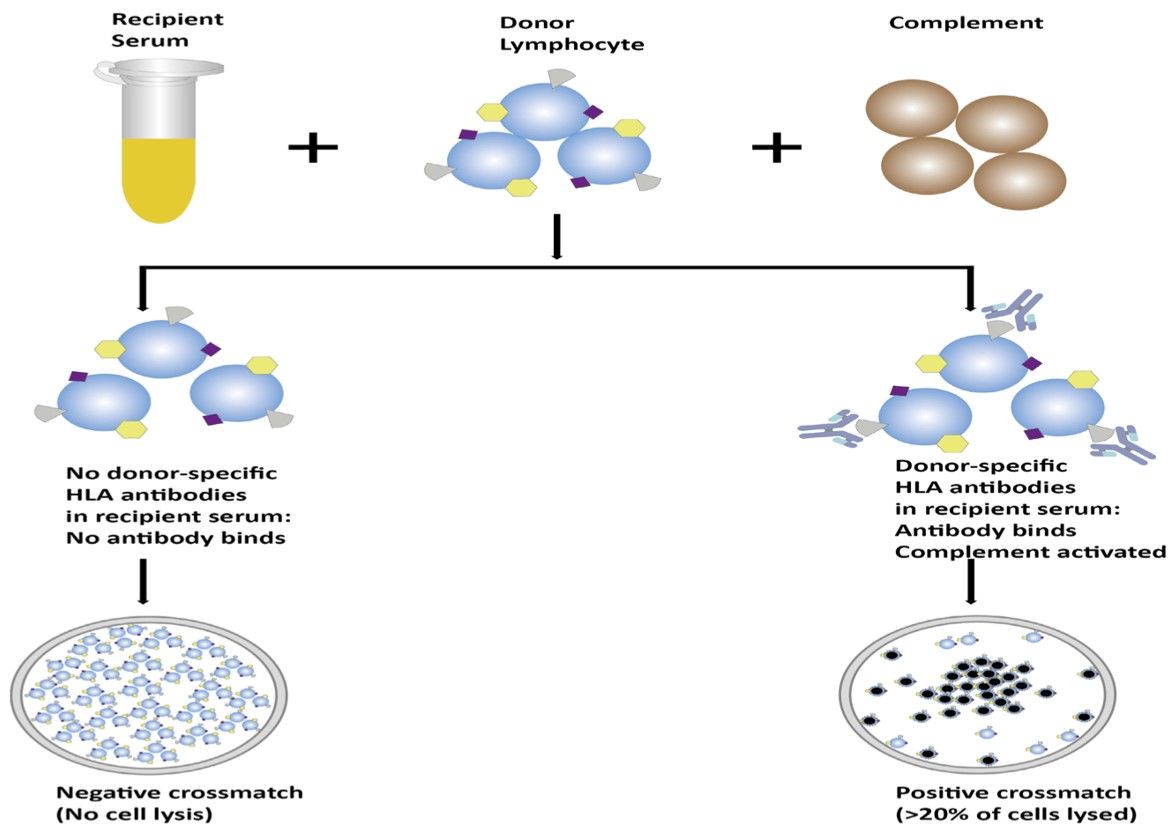 Fig.1 Schematic representation of the process of CDCXM.1
Fig.1 Schematic representation of the process of CDCXM.1
Another way to determine the strength of the crossmatch is serial doubling dilutions of the recipient serum. More dilutions are necessary for the test to become negative, indicating a higher level of donor-specific antibodies. The antibodies have to be present in enough quantity to link complement to the Fc-receptor and activate complement-mediated cytotoxicity. The sensitivity of the CDC-XM will be enhanced if anti-human globulin is added before the complement factors. This promotes complement fixation by binding to HLA antibody on donor cells and increases the number of Fc-receptors available for complement binding.
Except for classical CDC-XM assay, Creative Biolabs also provides further modified CDC-XM assays such as AHG-enhanced CDC-XM. If you are interested in our CDC-XM assays, please feel free to contact us directly.
Reference
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION