All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
Creative Biolabs offers a wide range of products and services in the field of CD72 CAR-T cell therapy development. Furthermore, we understand that each client may have unique needs and requirements. Therefore, we also specialize in offering customizable services tailored to specific client preferences.
CD72, an ITIM-bearing inhibitor of B-cell receptor signaling, is highly expressed in MLL1-rearranged (MLLr) B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Further investigation has demonstrated the consistent CD72 expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. It is a promising immunotherapy target for the immunotherapy development of MLLr B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Our CD72 CAR-T expression test service provides a comprehensive analysis of the expression and functionality of CAR-T cells targeting CD72. Our team of experts, who have undergone rigorous training and have extensive experience, employ state-of-the-art methods to evaluate the effectiveness and quality of CAR-T cells.
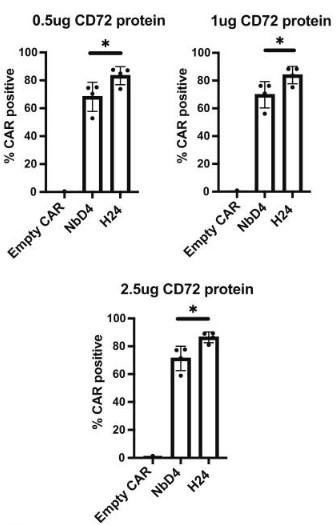 Fig.1 Flow cytometry with recombinant biotinylated CD72 to assess the expression of CD72 CAR.1
Fig.1 Flow cytometry with recombinant biotinylated CD72 to assess the expression of CD72 CAR.1
CD72 CAR-T Cytokine Release Test
Cytokine release syndrome is a potentially severe and life-threatening immune response that can occur after CAR-T cell infusion. We offer CD72 CAR-T cytokine release tests, which is a valuable tool used in immunotherapy to assess the safety and efficacy of chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cell therapy targeting CD72.
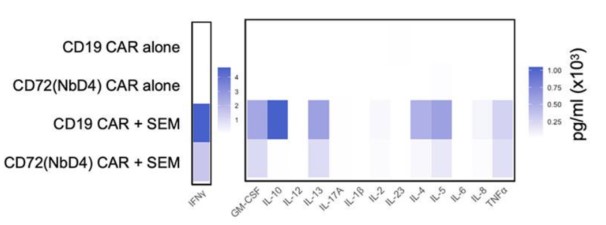 Fig.2 Cytokine profiling of CD72(NbD4) CAR T showed comparable patterns of cytokine release to CD19 CAR-T.2
Fig.2 Cytokine profiling of CD72(NbD4) CAR T showed comparable patterns of cytokine release to CD19 CAR-T.2
CD72 CAR-T In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
We are delighted to offer our CD72 CAR-T cytotoxicity assay service, utilizing cutting-edge technology and expertise to address your specific needs. This service is designed to assess the effectiveness and potency of CD72 CAR-T therapy in targeting and eliminating CD72-expressing cancer cells. Additionally, our CD72 CAR-T cytotoxicity assay service can be customized to meet your specific research goals.
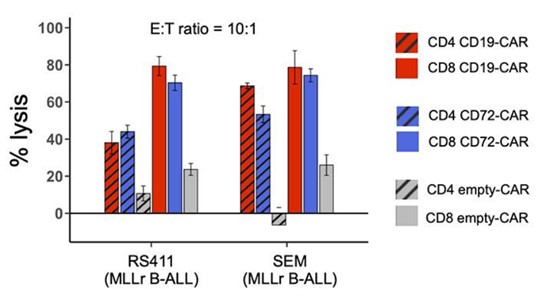 Fig.3 In vitro cytotoxicity of either CD72, CD19, or CD8and CD4CAR T's against two B-ALL cell lines.2
Fig.3 In vitro cytotoxicity of either CD72, CD19, or CD8and CD4CAR T's against two B-ALL cell lines.2
CD72 CAR-T Cell Proliferation Test
The CD72 CAR-T Cell Proliferation Test we offer is specifically developed to offer a thorough and precise understanding of the functional properties of CD72 CAR-T cells. Through a series of rigorous experiments and analysis, we evaluate the growth rate, viability, and potency of these engineered cells, ensuring their optimal functionality and therapeutic potential.
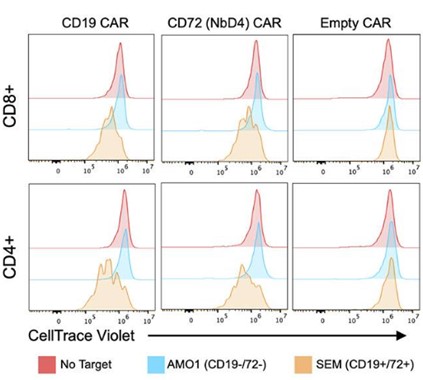 Fig.4 CD72 CAR-T's also demonstrated robust proliferation, equivalent to CD19 CAR-T.2
Fig.4 CD72 CAR-T's also demonstrated robust proliferation, equivalent to CD19 CAR-T.2
CD72 CAR-T Cell Therapy Animal Models
We have the expertise and resources to offer a range of services for the development of CD72 CAR-T Cell Therapy Animal Models. Our team of skilled scientists and researchers utilize advanced genetic engineering techniques to generate animal models that accurately recapitulate the human disease condition.
Our efficacy testing services focus on assessing the effectiveness of CD72 CAR-T therapy in killing cancer cells and suppressing tumor growth. Through a series of in vivo experiments, we evaluate the cytotoxicity of CD72 CAR-T cells against CD72-positive cancer cells.
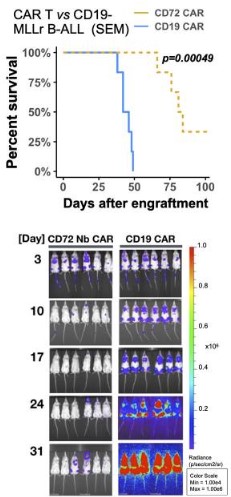 Fig.5 In both cell line and xenograft models of B-ALL, CD72 CAR T has demonstrated its ability to eradicate tumors and enhance survival rates.2
Fig.5 In both cell line and xenograft models of B-ALL, CD72 CAR T has demonstrated its ability to eradicate tumors and enhance survival rates.2
Toxicity Evaluation of CD72 CAR-T
We offer CD72 CAR-T Toxicity Evaluation services that are designed to assess the safety and potential toxicities associated with the use of CD72 CAR-T cells. Our CD72 CAR-T toxicity evaluation services include comprehensive in vivo tests, which involve the administration of CD72 CAR-T cells to animal models to evaluate their safety and potential toxicities.
References
 Loading...
Loading...
| CAT | Product Name | Target Species | Antibody Clone | Antibody Host | Receptor Construction | Vector Type | Targeting Cell Type | CAR Vector Type | Inquiry & Datasheet |
| CAR-0120ZP2713 | Anti-CD72 (4G4) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 4G4 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP2714 | Anti-CD72 (4G4) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 4G4 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP2715 | Anti-CD72 (II-2) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | II-2 | Human | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP2716 | Anti-CD72 (II-2) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | II-2 | Human | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP2717 | Anti-CD72 (sc02-025) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | sc02-025 | Human | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP2727 | Anti-CD72 (BL-A) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | BL-A | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP2728 | Anti-CD72 (BL-A) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | BL-A | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP2729 | Anti-CD72 (A11) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | A11 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP2730 | Anti-CD72 (A11) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | A11 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP2731 | Anti-CD72 (BU41) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | BU41 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP2732 | Anti-CD72 (BU41) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | BU41 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP2733 | Anti-CD72 (BU40) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | BU40 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP2734 | Anti-CD72 (BU40) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | BU40 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP2735 | Anti-CD72 (CBYY-C0427) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBYY-C0427 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP2736 | Anti-CD72 (CBYY-C0427) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBYY-C0427 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| CAR-0120ZP2737 | Anti-CD72 (CBYY-C0137) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBYY-C0137 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-0822-YF216 | Anti-Human CD72 (XW-216) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Human | XW-216 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF217 | Anti-Human CD72 (XW-217) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Human | XW-217 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF218 | Anti-Human CD72 (XW-218) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Human | XW-218 | Human | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-0822-YF219 | Anti-Mouse CD72 (XW-219) m(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Mouse | XW-219 | Rat | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector |
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION