Introduction of Complement System
Complement system is a tightly regulated network of proteins which are either present as soluble proteins in the blood or are present as membrane-associated proteins and have an important influence in host defense and inflammation. Activation of complement leads to a sequential cascade of enzymatic reactions, also termed as the complement activation pathways. Complement activation is known via three main different pathways: alternative, classical and lectin (Fig. 1) involving proteins that mostly exist as inactive zymogens that are then sequentially cleaved and activated, and factors that can stop pathways indicated in boxes. Complement activation activates opsonization of pathogens and their removal by phagocytes, and cell lysis.
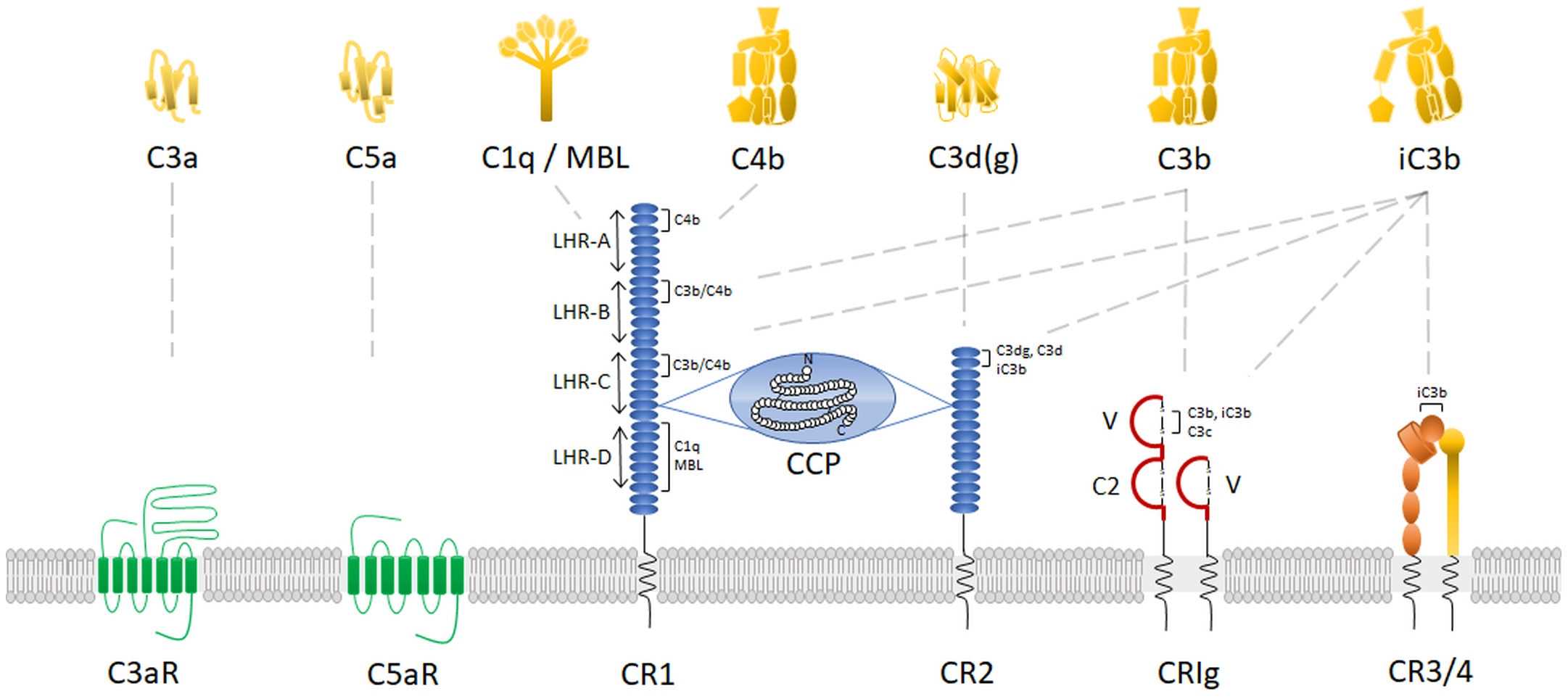
Fig. 3 Complement receptors.3, 4
Complement Membrane Attack Complex/MAC Structure
The membrane attack complex is a crucial innate immune effector of the complement terminal pathway that forms cytotoxic pores on the surface of microbes. MAC contains a complex of four complement proteins (C5b, C6, C7, and C8) that targets the outer surface of the plasma membrane, and many copies of C9 that hook up to one another, combining together to form a ring in the membrane, shown in Fig.2.
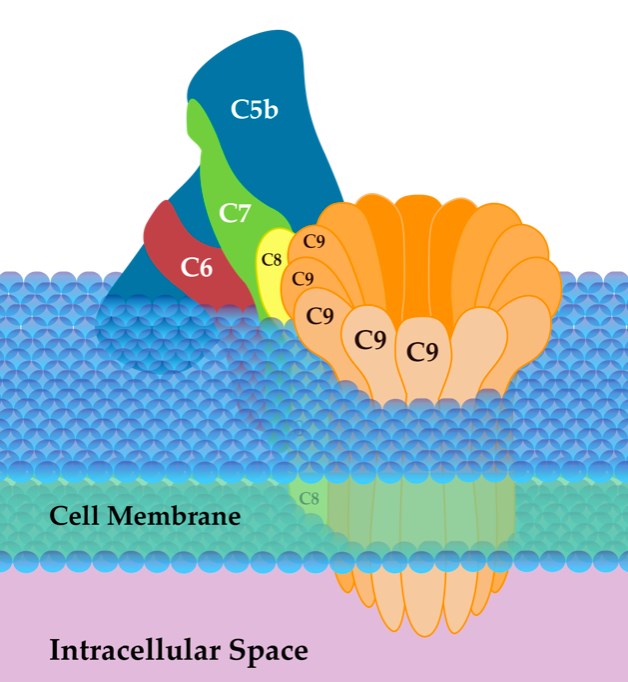
Fig. 2 Structure of MAC.2
Complement Component / Protein Structure
The complement system contains 12 component proteins among the enzymatic activation cascades, including C1, C4, C2, Factor B, Factor D, Factor P, C3, C5, C6, C7, C8, C9. Most of the proteins are normally inactive. When in response to the recognition of molecular components of microorganisms, these complement component proteins become sequentially activated.
Table.1 The component proteins of the complement system.
|
Component proteins
|
Structure
|
|
C1
|
Composed of 3 subunits, C1q (460 kDa), C1r (80 kDa), C1s (80 kDa)
|
|
C4
|
Three chains (α, 97 kDa; β, 75 kDa, γ, 33 kDa)
|
|
C2
|
A single chain, 102 kDa
|
|
fB (Factor B)
|
A single chain, 93 kDa
|
|
fD (Factor D)
|
A single chain, 24 kDa
|
|
fP (Factor Properdin, Factor P)
|
Oligomers of identical 53 kDa chains
|
|
C3
|
Two chains: α, 110 kDa; β, 75 kDa
|
|
C5
|
Two chains: 115 kDa, 75 kDa
|
|
C6
|
A single chain, 120 kDa
|
|
C7
|
A single chain, 110 kDa
|
|
C8
|
Three chains: α, 65 kDa, β, 65 kDa γ, 22 kDa
|
|
C9
|
A single chain, 69kDa
|
Complement Regulator Structure
Complement regulators control the spontaneously activated complement cascade. Meanwhile, any disturbances in this delicate balance can result in damage to tissues and autoimmune disease. Complement regulators include CD55 drug (also called DAF- decay accelerating factor), Factor H, CD46 (also called MCP-membrane cofactor protein), C1INH (C1 inhibitor), CD59 (Protectin), Vitronectin (S-protein), Clusterin (apolipoprotein J).
Table.2 Structure of complement regulators.
|
Complement Regulators
|
Structure
|
|
CD55 (DAF)
|
A 70 kDa glycoprotein
|
|
Factor H
|
Twenty tandemly arranged SCR units
|
|
CD46 (MCP)
|
A 51–68 kDa integral membrane glycoprotein
|
|
C1 INH (C1 inhibitor)
|
A single chain and 105 kDa plasma glycoprotein
|
|
CD59 (Protectin)
|
A 18–25 kDa glycoprotein
|
|
Vitronectin (S-protein)
|
A single chain glycoprotein
|
|
Clusterin (apolipoprotein J)
|
A 70–80 kDa amphiphilic molecule
|
Complement Receptor Structure
The complement receptors are receptors of the complement system, part of the innate immune system. Complement receptors target proteins of the complement system, and are able to detect pathogens without mediation via antibodies. Complement receptors are membrane proteins that expressed on the surface of immune cells. They interact specifically with complement factors and initiate the removal of antigen from the circulation. There are six main types of complement receptors, including CR1, CR2, CR3 (ITGAM), CR4(ITGAX), C1q receptors, anaphylatoxin receptors. The structure of CR1 and CR2 is shown in Fig.3.
Table.3 Structure of CR3, CR4, C1q, anaphylatoxin receptors.
|
Complement Regulators
|
Structure
|
|
CR3 (ITGAM)
|
A protein subunit that forms heterodimeric integrin alpha-M beta-2 (αMβ2) molecule
|
|
CR4(ITGAX)
|
An integrin alpha X chain protein that composed of an alpha chain and a beta chain
|
|
C1q
|
A 400 kDa protein and composed of three polypeptide chains, A, B and C
|
|
Anaphylatoxin receptors
|
A group of G-protein coupled receptors which bind anaphylatoxins
|
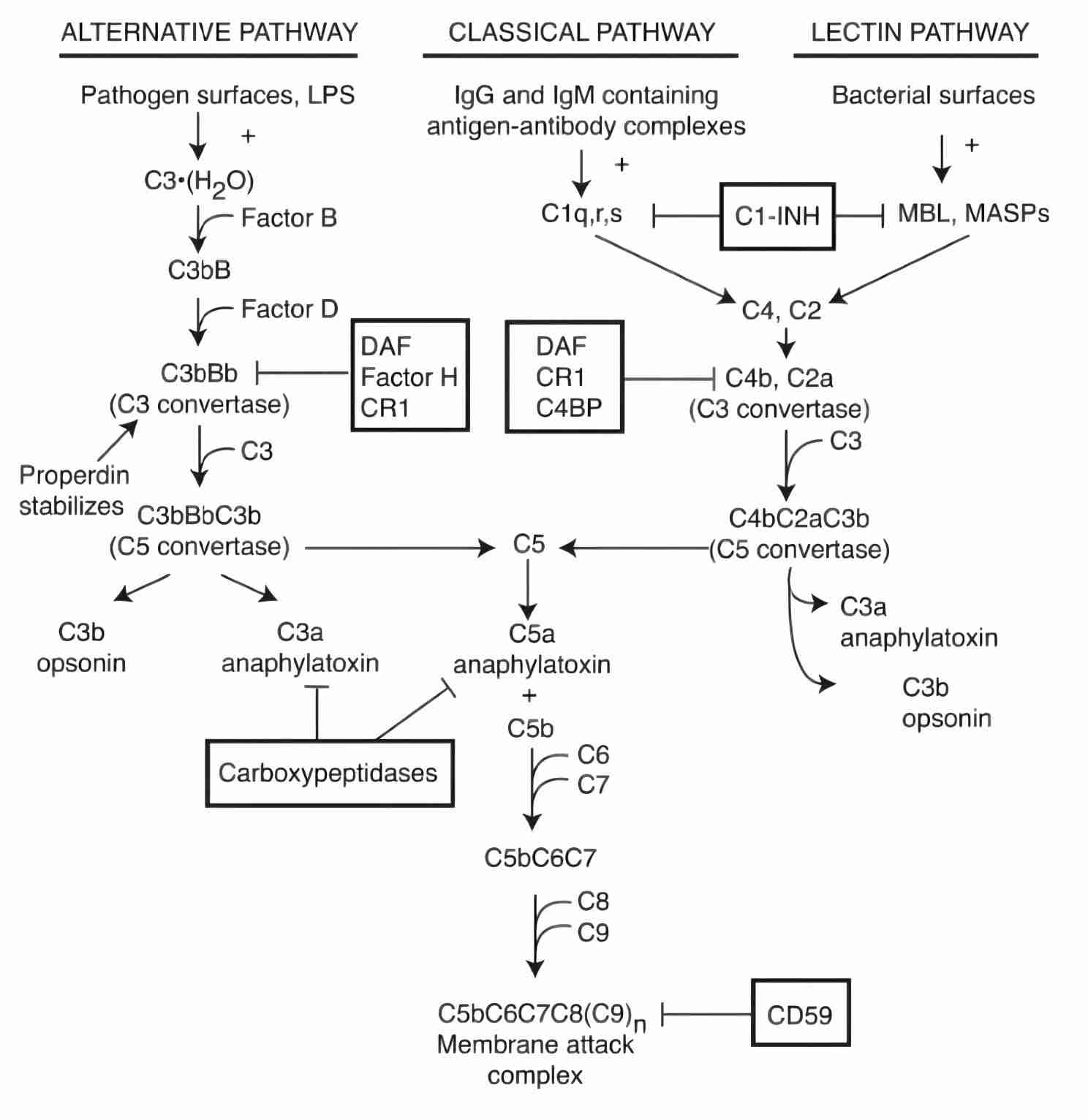
Fig. 3 Complement receptors.3
Collectins and Ficolins: Humoral Lectins of the Innate Immune System
Collectins and ficolins are humoral molecules of the innate immune systems and can recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns.
Collections are collagen-like lectins. They are collagen containing C-type lectins of which nine have been discovered:
-
Mannose-binding lectin (MBL)
-
Surfactant proteins A (SP-A)
-
Surfactant proteins D (SP-D)
-
Collectin-10, also as collectin liver 1 (CL-10 or CL-L1)
-
Collectin placenta 1 (CL-12 or CL-P1)
-
Conglutinin
-
Collectins of 43kDa (CL-43)
-
Collectins of 46 kDa (CL-46)
-
Collectin-11 (CL-11 or CL-K1)
Ficolins contain both a collagen-like domain and a fibrinogen-like domain that has a specific binding affinity for N- acetylglucosamine. Three types of human ficolin have been known so far:
-
L-ficolin (ficolin-2)
-
H- ficolin (ficolin-3)
Creative Biolabs provides comprehensive complement-related products and complement testing services, including but not limited to:
If you have any questions about our services or products, please feel free to contact us.
References
-
Sarma, J. Vidya, and Peter A. Ward. "The complement system." Cell and tissue research 343.1 (2011): 227-235.
-
From Wikipedia: By SLiva2016 - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Membrane_Attack_Complex_(Terminal_Complement_Complex_C5b-9).png
-
Vandendriessche, Sofie, et al. "Complement receptors and their role in leukocyte recruitment and phagocytosis." Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 9 (2021): 624025.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification
Related Product
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:



