Glycobiology and Proteomics
Overview of Glycobiology and Proteomics
Glycosylation is one of the most common post-translational modifications, and glycoproteins play crucial roles in important biological processes like cell signaling, host-pathogen interaction, immune response, and diseases, including cancer, and even the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
The systems-level analysis of all proteins expressed by cells, tissues, or organisms is known as “proteomics”. Glycoproteomics aims to determine the positions and identities of the complete repertoire of glycans and glycosylated proteins in a given cell or tissue.
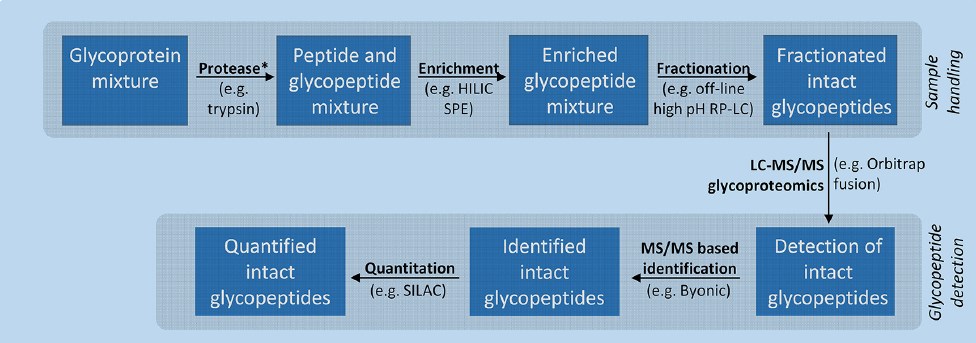 Fig.1 Generic workflow illustrating important components of a glycoproteomics experiment.1, 2
Fig.1 Generic workflow illustrating important components of a glycoproteomics experiment.1, 2
From Glycomics to Target-Driven Glycoproteomics
A key question that often follows the identification of important glycosylation features by glycomics is, which proteins carry the implicated glycan structures and at which sites?
-
Determination of De-N-Glycosylated Protein Sites
Glycosylation site analysis by MS of de-N-glycosylated peptides is at present the prevalent mode of glycoproteomic analysis of a complex protein sample, but this approach does not give information on what glycan structure(s) are present on these defined glycosylation sites. These previously glycosylated proteins can then be subjected to trypsin digestion and LC-MS/MS analysis, and the MS/MS data searched against proteomic databases for rapid identification of the glycosylation sites on the tryptic peptide. This approach can be coupled to initial affinity or chemical capture of the glycoproteome subset, by use of lectins at the glycoprotein and/or digested glycopeptide level, or by hydrazine capture of the oxidized glycans on the glycopeptide, followed by PNGase F release of the captured peptide. In this manner, hundreds of N-glycosylation sites can now be routinely identified and their relative abundance quantified.
-
Glycoproteomics: Determining the Heterogeneous Site Glycosylation
Glycoproteomics needs ideally to be able to identify all glycoproteins in a sample down to the level of which sites are occupied and to quantify and characterize their respective glycoforms at that site. The ultimate aim is to dynamically take snapshots of the distribution of disparate glycans on each glycoprotein in a cell to infer how site-specific glycosylation may promote or interfere with interactions, signaling, and any close encounter.
Advances in Glycoproteomics
Glycoproteomics usually involves glycoprotein enrichment of the samples of healthy and/or disease states that can be compared to find differentially expressed glycoproteins potentially playing important roles in certain diseases or disease states. Such an approach requires sophisticated comparative proteomics methods, advanced MS techniques, and powerful bioinformatics tools to identify biomarkers for the early prediction of diseases that can eventually be used for disease prognosis. Label-free quantification, stable isotope labeling, isobaric tag for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ), and tandem mass tags (TMT) are some of the methods used to interpret the differentially expressed proteins between samples for biomarker and target discovery.
Hydrazide chemistry and solid-phase extraction of glycosylated peptides provide means to identify and quantify N-linked glycoproteins. Using this technique, scientists evaluated the differences in glycoproteomic profiles of dyssynchronous heart failure and cardiac resynchronization therapy. Relative changes in the level of glycoproteins were determined by iTRAQ and verified by label-free LC-MS. Using sialoglycoprotein enrichment and isotope labeling methods, differentially expressed proteins in breast cancer were identified. Further Western blot and lectin analyses confirmed that versican is one of the most highly differentially expressed sialoglycoproteins in breast cancer. Hydrazide chemistry, lectins, multilectin affinity chromatography, and metabolic incorporation of sugar analogs for glycoprotein isolation are all commonly used methods for biomarker and target discovery aimed at early detection and therapy of different cancer types.
Glycobiology and Proteomics Includes These Areas of Focus
Technologies for Glycobiology and Proteomics Research
As a comprehensive and leading biology company, Creative Biolabs possesses abundant technology platforms for glycobiology and proteomics research, as follows:
With a strong technology platform, effective project management, and relevant scale-up capacity, Creative Biolabs’ high-quality contract research services enable our clients to develop and improve a wide variety of glycobiology projects. If you are interested in our services and technology, please contact us for more.
References
-
Thaysen-Andersen, Morten, Nicolle H. Packer, and Benjamin L. Schulz. "Maturing glycoproteomics technologies provide unique structural insights into the N-glycoproteome and its regulation in health and disease." Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 15.6 (2016): 1773-1790.
-
Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Resources

 Fig.1 Generic workflow illustrating important components of a glycoproteomics experiment.1, 2
Fig.1 Generic workflow illustrating important components of a glycoproteomics experiment.1, 2

