What is Glycobiology?
Overview of Glycobiology
Glycobiology, also known as glycans, is the study of the structure, biosynthesis, and biology of saccharides (sugar chains or glycans) that are widely distributed in nature. Sugars or saccharides are essential components of all living things and aspects of the various roles they play in biology are researched in various medical, biochemical, and biotechnological fields. Glycobiology deals with the role of carbohydrates in biological events.
The field of glycobiology has evolved from the main structural characterization of naturally occurring carbohydrates (sugars or glycans) to functional studies of the biology and interaction of such compounds with both endogenous and exogenous proteins, lectins typically equipped with carbohydrate recognizing domains.
Glycoproteomics is a field that evaluates glycosylated proteins and their glycosylation sites. It usually involves glycoprotein enrichment of the samples of healthy and/or disease states that can be compared to find differentially expressed glycoproteins potentially playing important roles in certain diseases or disease states. Such an approach requires sophisticated comparative proteomics methods, advanced MS techniques, and powerful bioinformatics tools to identify biomarkers for the early prediction of diseases that can eventually be used for disease prognosis.
Glycoproteins are proteins containing glycans attached to amino acid side chains. Glycans are oligosaccharide chains, which are saccharide polymers, can attach to either lipid (glycolipids) or amino acids (glycoproteins). Typically, these bonds are formed through a process called glycosylation. Glycoproteins are fundamental to many important biological processes including fertilization, immune defense, viral replication, parasitic infection, cell growth, cell-cell adhesion, degradation of blood clots, and inflammation.
Glycosylation is a form of a co-translational and post-translational modification. The majority of proteins synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum undergo glycosylation. Glycosylation is also present in the cytoplasm and nucleus as the O-GlcNAc modification. Glycosylation is critical for a wide range of biological processes, including cell attachment to the extracellular matrix and protein-ligand interactions in the cell. Glycosylation increases the diversity of the proteome to a level unmatched by any other post-translational modification.
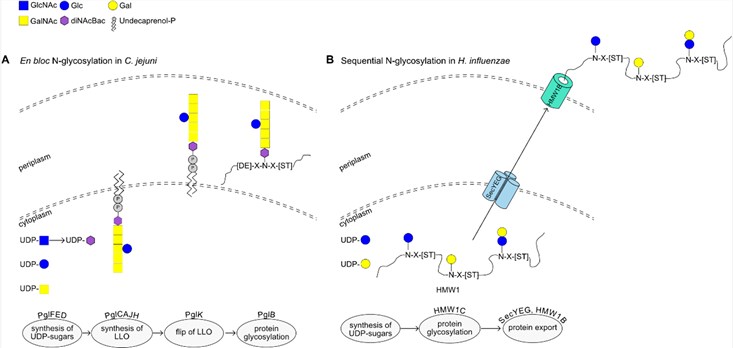 Fig.1 Examples of N-glycosylation mechanisms in bacteria.1, 2
Fig.1 Examples of N-glycosylation mechanisms in bacteria.1, 2
Glycosidases catalyze the hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds in complex sugars. They are found in essentially all domains of life. In prokaryotes, they are found both as intracellular and extracellular enzymes that are largely involved in nutrient acquisition. In higher organisms, glycoside hydrolases are found within the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus where they are involved in the processing of N-linked glycoproteins, and in the lysosome as enzymes involved in the degradation of carbohydrate structures.
Glycosylation is not coded by a template and therefore cannot be predicted from the genome. Furthermore, unlike proteins or DNA, glycans often do not have a linear structure. Monosaccharide components can have greatly different biological properties while having the same molecular composition and are therefore indistinguishable by most analytical methods. Glycan heterogeneity adds another level of complexity: a range of glycan variations can be found in the same protein giving rise to a group of related, but not identical, proteins (or glycoforms). The inherent complexity of glycosylation makes it necessary to employ orthogonal analytical techniques to elucidate the structure of each glycoconjugate and to understand its biological function.
Glycobiology-the study of the structure, function, and biology of carbohydrates. Glycomics-the systematic study of all glycan structures in a biological system. Carbohydrate-A generic term used interchangeably with sugar and glycan.
Services at Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs is a world-leading biotechnology company that has been at the forefront of glycobiology research for many years. As an innovative, experienced provider of glycobiology solutions, We use our state-of-the-art R&D expertise to provide custom services for our customers, including but not limited to:
Creative Biolabs provides you with the right support and expertise for each of the different stages of the development of the glycobiology project. You can count on our skilled and passionate workforce to find the most suitable path and to guide you through your research journey. We can make your glycobiology journey easier. If you are interested in any of our services, please contact us directly for details.
Referencess
-
Latousakis, Dimitrios, and Nathalie Juge. "How sweet are our gut beneficial bacteria? A focus on protein glycosylation in Lactobacillus." International journal of molecular sciences 19.1 (2018): 136.
-
Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Resources

 Fig.1 Examples of N-glycosylation mechanisms in bacteria.1, 2
Fig.1 Examples of N-glycosylation mechanisms in bacteria.1, 2

