Oligosaccharide Analysis Services
Studies focus on glycobiology is increasing, as well as the demand for carbohydrates detection. As a leading global company, Creative Biolabs has long been committed to glycosylation analysis. We have established a comprehensive and advanced platform for glycosylation analysis. Besides, our platform also offers a variety of advanced technologies in oligosaccharides analysis.
Background of Oligosaccharide Analysis
As the most abundant biological compounds on earth, carbohydrates
play crucial roles in many biological processes, such as immune responses, molecular recognition, signaling, and cellular communication. The oligosaccharide refers to a compound obtained by polymerizing 2-10 glycosidic bonds, which are formed by dehydration condensation of a monosaccharide hydroxy group with a hydroxyl group of another monosaccharide. The main types of covalent bonds linking them are N-glycan linkage and O-glycoside. N-linked oligosaccharides are always pentasaccharides attached to asparagine via a beta linkage to the amine nitrogen of the side chain. Alternately, O-linked oligosaccharides are generally attached to threonine or serine on the alcohol group of the side chain. It is important to determine the structure of the carbohydrates present in glycoproteins. Currently, oligosaccharide analysis has been widely applied in studying the structure of the carbohydrates.
Oligosaccharides Analysis Service at Creative Biolabs
Based on advanced platforms, we provide various oligosaccharide analysis services, including Xylooligosaccharide, Mannoligosaccharide, Fructooligosaccharide, and Soluble Sugar Content Analysis services.. Our analysis methods include high-performance anion-exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection (HPAE-PAD), capillary electrophoresis (CE), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and fluorophore-assisted carbohydrate electrophoresis (FACE).
-
HPAE-PAD has been proven to be a powerful technique to follow the progress of glycosidase and glycosyltransferase reactions. Because HPAE-PAD does not rely on a fluorescent or absorbent label for detection, the fate of the substrate(s) and the product(s) can be followed, allowing the analyst to judge the success of the reaction. These methods typically determine oligosaccharides in single sample analysis. Oligosaccharides will be first released from the protein by PNGase-F for asparagine (N-linked) oligosaccharides or by reductive β-elimination for serine/threonine oligosaccharides, and then injected into the HPAE-PAD system. Creative Biolabs has accumulated extensive experience in employing HPAE-PAD for carbohydrate analysis. We provide high-quality service to facilitate our customers' research and project development.
-
CE
CE is one of the most powerful techniques in terms of resolving power and is applied to the analysis of various carbohydrates from glycoconjugates. Capillary electrophoresis separation is based on the migration of analytes in fused-silica capillaries filled with an electrolyte. Separation is usually performed using a capillary of 50-100 μm internal diameter, under an electric field of several hundred voltages per centimeter capillary. Under such high voltage, carbohydrates are migrated based on their charge to mass ratios, and directly detected by an on-column detector. A combination of CE and laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) detection enables to detect even fmol (10-15 mol) to amol (10-18 mol) of carbohydrates. Creative Biolabs owns a team of technical experts to deal with any problem you may meet in CE.
-
Neutral oligosaccharides bind to amine-bonded HPLC columns because of hydrogen bonding via hydroxyl groups, which is promoted by acetonitrile and disrupted by water. The sample is loaded in a high concentration of acetonitrile and the column is developed with a gradient of increasing water. Neutral oligosaccharides are initially retained by the column and elute in order of increasing size (increasing numbers of hydroxyl groups). Oligosaccharides are detected based on their radioactivity (if previously radiolabeled) or by physical or chemical means (if unlabeled). Information about the number and size of oligosaccharide species in a mixture is thus obtained. Creative Biolabs has years of experience for HPLC, thus you can trustingly hand over any problem to us.
-
FACE
FACE is a straightforward, sensitive method for determining the presence and relative abundance of individual oligosaccharides in an oligosaccharide mixture. The single terminal aldehydes of oligoglucoside residues released by acid hydrolysis of β-1, 3-D-glucan from yeast were tagged with the charged fluorophore 8-aminonaphthalene-1,3,6-trisulfonate (ANTS) and separated with high resolution based on size by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. ANTS fluorescence labeling was not biased by oligoglucoside length; therefore, band fluorescence intensity was directly related to the relative abundance of individual oligoglucoside moieties in the heterogeneous sample. Currently, FACE has been treated as an accessible, sensitive, and quantitative analytical tool for the analysis of oligosaccharides derived from different sources. In terms of the extensive experience in FACE technology, Creative Biolabs is proud to offer our clients high-quality services with the best quality and most competitive price.
Advantages of Our Service
-
Multiple technologies for choice
-
Targeted customized service plan
-
Accurate, efficient and cost-effective
-
Perfect after-sale service
Creative Biolabs is a forward-looking company that has established platforms to offer the best oligosaccharides analysis services for global customers. Strong technical support makes us confident in providing the best service to any requirements. Please feel free to contact us for more information.
Published data
Oligosaccharides play a variety of important roles in biological systems, from energy supply to intercellular signaling, and they play an indispensable role in the normal physiological processes of organisms. Despite the obvious importance of oligosaccharides, the analysis of oligosaccharides faces major challenges due to their complex structure and heterogeneity. Commonly used analytical techniques, such as liquid chromatography (LC) and electrophoresis (CE), can separate the complex components of oligosaccharides, but it is difficult to determine their specific isomeric forms. To address this problem, the authors selected a commercially available nutritional supplement as the research object in this study. By combining LC with mass spectrometry (MS) and infrared spectroscopy (IR) technology, they successfully identified and recognized various human milk oligosaccharide components in the supplement, thereby providing a practical detection method for the structural analysis of oligosaccharides.
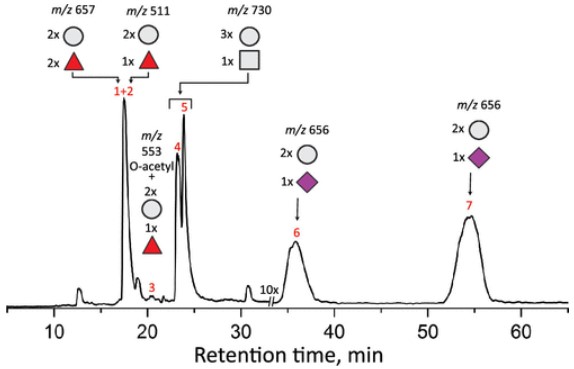 Fig.1 Glycan analysis results in nutritional supplements.1
Fig.1 Glycan analysis results in nutritional supplements.1
FAQs
Q1: What unique technology platforms does your company have for oligosaccharide analysis?
A1: Creative Biolabs has a comprehensive set of advanced platforms, including HPAE-PAD, CE, HPLC, and FACE technologies, which can meet the specific needs of clients around the world. We provide a variety of technology options, and clients can choose the most appropriate analysis method according to their specific needs.
Q2: How is oligosaccharide released from glycoproteins for analysis?
A2: To release oligosaccharides from glycoproteins, different enzymes, and chemical reactions are used depending on the linkage type. For N-linked oligosaccharides, PNGase-F enzyme is used to cleave the glycosidic bond at asparagine residues. For O-linked oligosaccharides, reductive β-elimination is utilized to release oligosaccharides at serine or threonine residues. These released oligosaccharides are then ready for further analysis using the proper techniques.
Q3: Can Creative Biolabs provide fully customized oligosaccharide analysis services for specific research needs?
A3: Yes, Creative Biolabs offers tailor-made analysis services to meet specific research requirements. Our team collaborates closely with clients to understand their study objectives and designs a custom analysis strategy leveraging our diverse platform technologies. Whether the need is for a specific type of glycosylation analysis or a combination of different methods, we ensure the approach is tailored to achieve precise and reliable results.
Customer Review
High Accuracy of Analysis Service
“The oligosaccharide analysis service provided by Creative Biolabs was able to accurately detect all the important oligosaccharide structures in my samples, making our research results more reliable and reproducible. They not only completed the analysis efficiently and accurately but also delivered all the results within the scheduled time.”
Comprehensive Glycosylation Analysis
“The comprehensive glycosylation analysis provided by Creative Biolabs covered all aspects of our needs, from initial oligosaccharide release to detailed post-analysis support. This made the entire process seamless and efficient. I highly recommend their oligosaccharide analysis service.”
Reference
-
Abikhodr, Ali H., et al. "Combining Liquid Chromatography and Cryogenic IR Spectroscopy in Real Time for the Analysis of Oligosaccharides." Analytical Chemistry 96.4 (2024): 1462-1467. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Glycan analysis results in nutritional supplements.1
Fig.1 Glycan analysis results in nutritional supplements.1

