Therapeutic Antibody Glycoengineering Services
Glycoengineering through biosynthetic pathway has enabled the production of certain pure or enriched monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) glycoforms for functional studies and therapeutic development. Nevertheless, the quality and diversity of glycoforms that can be modified through genetic manipulations are quite limited, owing to the complexity and restriction of biosynthetic pathways. In contrast to in vivo genetic approaches, in vitro chemoenzymatic glycan remodeling of mAbs using glycosidases and glycosyltransferases has been employed to extend the glycan chains in an intact antibody. With Ph.D. level scientists and extensive experience in the research of glycoengineering, Creative Biolabs is proficient in employing chemoenzymatic method for glycoengineering of mAbs. We are dedicated to serving every unique need of our clients by providing custom mAb glycoengineering service to meet our clients’ R&D timeline and budget.
The Fragment Crystallizable (Fc) Glycoforms of mAbs
As an important class of therapeutic glycoproteins, mAbs are widely used in the treatment of cancer, inflammation, and infectious diseases. Therapeutic mAbs possess several clinical actions including disruption of tumor cell signaling, activation of complement-dependent cytotoxicity (ADC), Ab-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), Ab-dependent cellular phagocytosis, and induction of adaptive immunity. The immunoglobulin G (IgG) type mAbs consist of two heavy and two light chains, which are covalently associated to form three domains, two identical Fab domains, and the Fc domain. IgG mediates its immune functions through complement and cellular IgG-Fc gamma receptors (FcγR). The Fc domain of IgG is recognized by FcγR on myeloid and natural killer cells, providing target recognition and activation of immune effector cells. A highly conserved glycan at position Asn297 in the Fc-domain infers structural changes to the Fc-region required for binding to FcγR. This glycan consists of variable levels of fucose, sialic acid, galactose, and bisecting N-acetylglucosamine. Subtle differences in this glycan can affect the effector functions of antibodies and may also change the interaction with FcγR. However, mAbs are usually generated as mixtures of Fc glycoforms, and the control of glycosylation in the homogeneous status in different host expression systems is still a challenge.
Approaches of Glycoengineering of mAbs
The significant impact of fine structures of Fc N-glycans on the biological functions of antibodies has stimulated more and more interest in exploring methods to control the Fc glycosylation of antibodies. Great efforts have been taken in mammalian cells, yeast cells, and plant cells aiming to control the glycosylation of mAbs in these expression systems. Those in vivo methods have resulted in the production of low-fucose or non-fucosylated monoclonal antibodies with improved therapeutic efficacy. However, complete control of the Fc glycosylation to a given specific homogeneous glycoform is still a challenge. In vitro chemoenzymatic method is another promising strategy for glycan remodeling via chemoenzymatic synthesis, which could lead to highly homogeneous antibody glycoforms. Scientists have used chemoenzymatic method to generate a panel of enriched Fc glycoforms, including G0F, G2F, and bisecting GlcNAc G2F of an intact antibody.
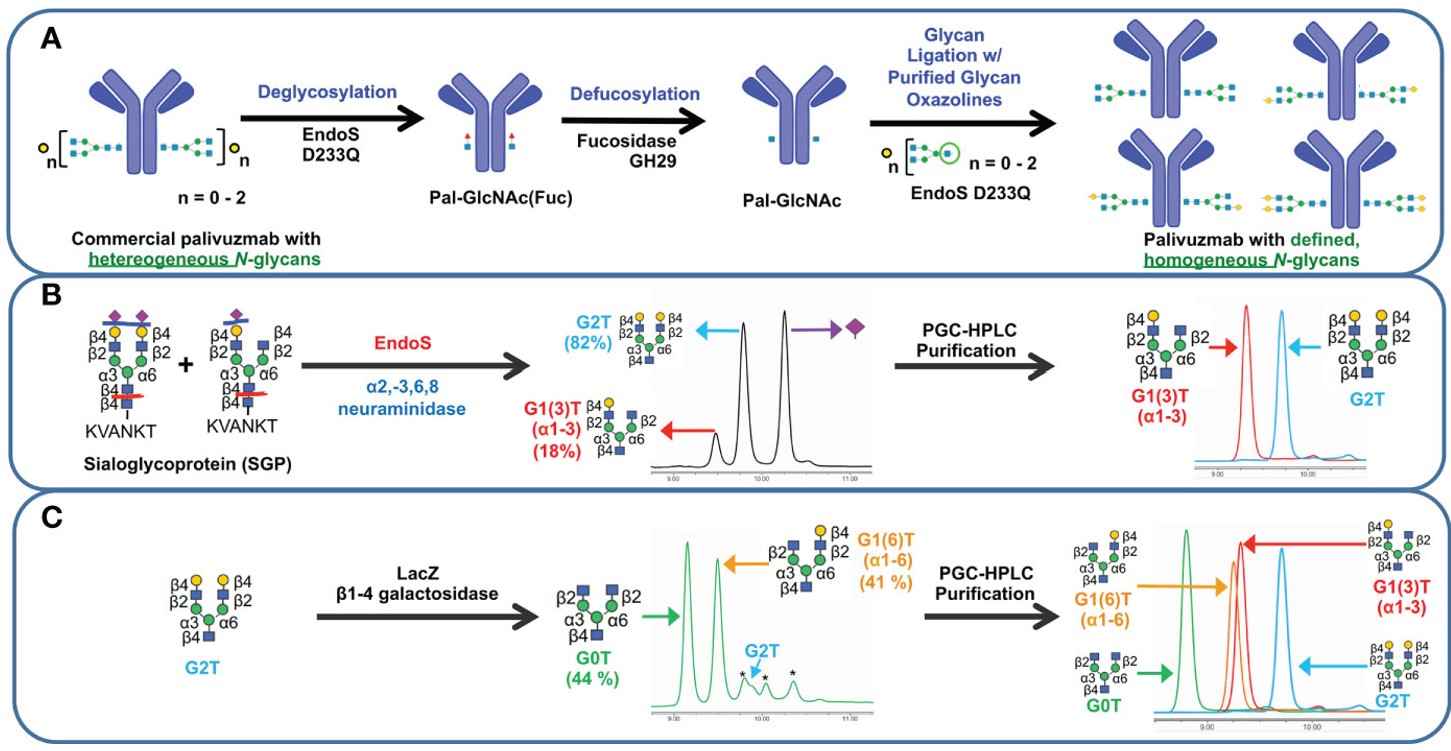 Fig.1 Schematic representation of transglycosylation of palivizumab.1, 3
Fig.1 Schematic representation of transglycosylation of palivizumab.1, 3
Glycoengineering of Antibody at Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs has proven experience in glycoscience, and we utilize in vitro chemical enzymatic strategies to provide our clients with excellent antibody glycoengineering service. In vitro glycoengineering of antibodies can adjust the glycosyl structure of the antibody and optimize its pharmacokinetic properties and immunogenicity, thereby improving the targeting, activity, and safety of the drugs. We use specific glycosidases and glycosyltransferases to quickly and efficiently obtain mAbs with better homogeneity in vitro to achieve the Glycan Remodeling process. For example, we galactosylate IgG through β-1,4-galactosyltransferase, obtain stable G2F glycans in a short time, and achieve glycan remodeling of antibodies. Our chemoenzymatic glycoengineering strategy provides a versatile platform to optimize therapeutic efficacy and improve mAb effector functions.
In addition, we also provide a variety of high-quality products to accelerate the glycan remodeling process of antibodies, such as glycosylases, sugar nucleotides, oligosaccharides, activated glycosyl donors, custom glycosyl donors, antibody Fc glycans remodeling kits, and more. Moreover, we also provide Custom Glycosyl Linker Synthesis Services for the unique compound structures you design.
Highlights
-
Chemoenzymatic glycoengineering approach
-
Highly specific for the Fc N-glycans without affecting other glycan traits
-
Highly professional Ph.D. level scientists
-
Reliability and information security
-
Tailored research & services
This chemoenzymatic glycoengineering method can be used for the Fc glycosylation remodeling of various mAbs to provide homogeneous Fc glycoforms for different applications. Creative Biolabs is fully competent and dedicated to serving as your one-stop-shop for custom mAb glycoengineering and characterization. For more detailed information, please feel free to contact us or directly send us an inquiry.
Published data
N-glycosylation has a major impact on the functionality and biological stability of therapeutic antibodies. In vitro, chemoenzymatic glycan remodeling has been used to produce antibodies with homogeneous glycoforms to avoid glycosylation inconsistency and heterogeneity. This study describes an effective chemoenzymatic glycan remodeling technique that combines in vitro chemoenzymatic glycosylation with in vivo deglycosylation to produce antibodies with homogeneous glycoforms. Using a plant expression system with the monoclonal antibody rituximab as a model antibody, the researchers ultimately produced a homogeneous glycosylated form without plant-specific α-1,3-fucose and others through in vivo and in vitro remodeling. The antibodies were found to have similar binding affinities by assay but were significantly more cytotoxic in vitro. This study provides an effective guide for in vitro glycoengineering of therapeutic antibodies.
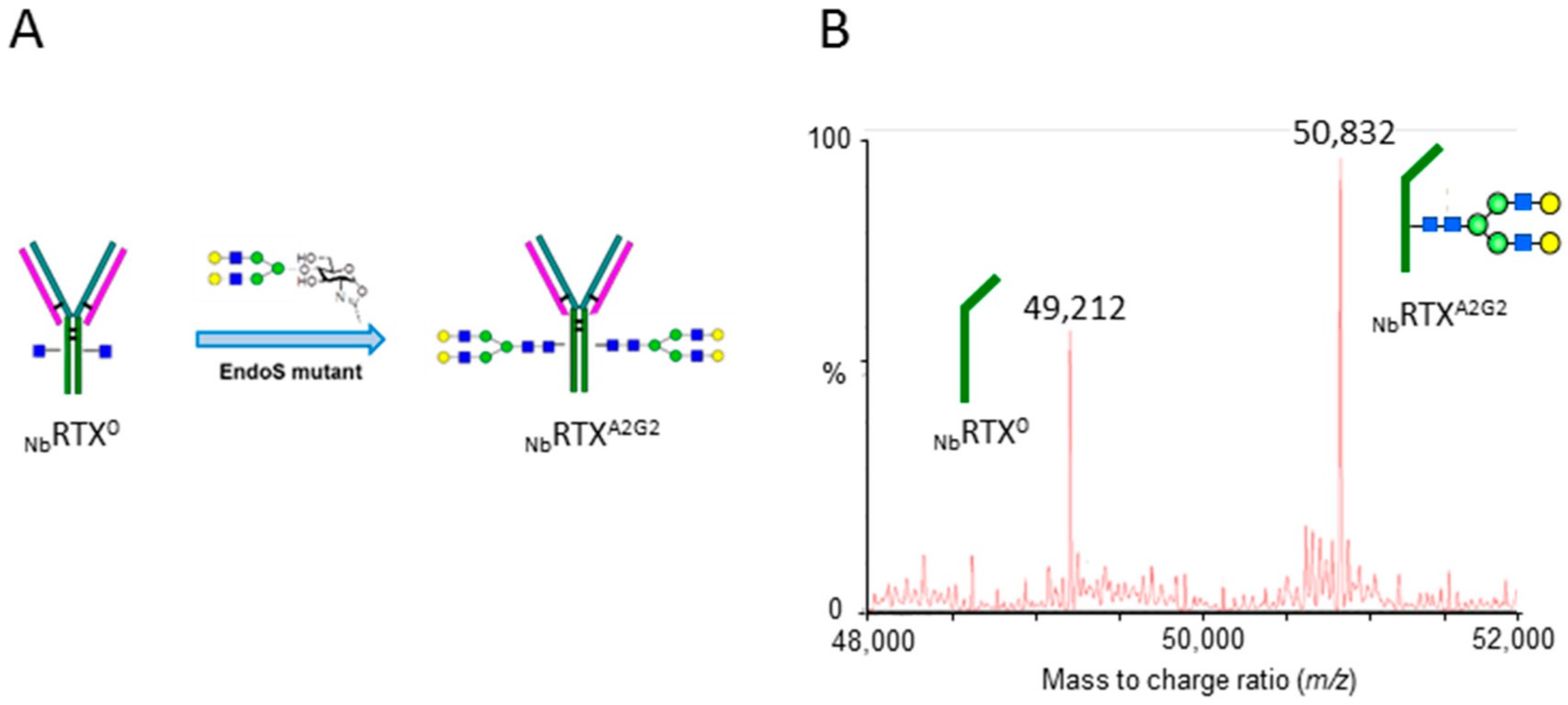 Fig.2 Chemoenzymatic transglycosylation.2, 3
Fig.2 Chemoenzymatic transglycosylation.2, 3
FAQs
Q1: How does glycoengineering affect the development of antibody therapeutics?
A1: Glycoengineering expands the possibility of designing novel antibodies with enhanced properties, including improved stability, functional and binding affinity, and reduced immunogenicity. Along with the development of new antibodies, more effective treatments for a wide range of diseases, including cancer, autoimmune diseases, and infectious diseases, will be developed over time.
Q2: What are the advantages of in vitro glycoengineering of therapeutic antibodies?
A2: Glycosylation patterns affect the functions, binding, and stability of therapeutic antibodies. Therapeutic antibody in vitro glycoengineering offers significant advantages in controlling homogenized glycosylation by adding custom oligosaccharides to the mAb via in vitro glycan remodeling technology to produce a single homogeneous glycan pattern.
Customer Review
Efficient in Vitro Glycoengineering Strategies
"We turned to Creative Biolabs to help us solve the key problems we encountered in antibody glycan remodeling. They demonstrated a high level of expertise in therapeutic antibody glycoengineering. After understanding our specific requirements and goals, they developed a tailored strategy. Ultimately, they succeeded in improving antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) through glycan remodeling and accelerating our antibody research. We recommend this service to anyone interested in antibody research."
First Choice for Therapeutic Antibody Glycoengineering
"Creative Biolabs' professionalism, expertise, and project experience made them the first choice for therapeutic antibody glycoengineering. They used advanced technology to achieve glycan remodeling of antibodies to optimize their efficacy, which had a nice boost to our project. Their commitment to quality and attention to every detail was commendable."
References
-
Hatfield, Grayson, et al. "Specific location of galactosylation in an afucosylated antiviral monoclonal antibody affects its FcγRIIIA binding affinity." Frontiers in Immunology 13 (2022): 972168.
-
Bennett, Lindsay D., et al. "Implementation of glycan remodeling to plant-made therapeutic antibodies." International Journal of molecular sciences 19.2 (2018): 421.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Schematic representation of transglycosylation of palivizumab.1, 3
Fig.1 Schematic representation of transglycosylation of palivizumab.1, 3
 Fig.2 Chemoenzymatic transglycosylation.2, 3
Fig.2 Chemoenzymatic transglycosylation.2, 3

