Post-translational Modification Research
In recent years, the research of glycoproteins has been receiving extensive attention. As a leader in this field, Creative Biolabs has been committed to the research of glycoproteins. Based on our precise knowledge and skilled technology, we are confident to help customer solve problems related to glycoprotein projects.
Introduction of Post-translational Modifications (PTMs)
The precursor proteins are inactive and often require a series of post-translational modifications (PTMs) to become mature protein products. PTM means the usual enzymatic modification after proteins biosynthesis. PTM can appear in the amino acid side chain, or at the C-terminus or N-terminus of the protein. PTM can modify the existing functional groups of amino acids, and the result of the modification makes amino acids have other functional groups. Therefore, the limited chemical library of amino acids can be significantly expanded through the PTM process.
Modifications Involving the Peptide Bonds
Proteolytic cleavage is the most conventional covalent modification of all proteins. Specific enzymes can remove amino acids from the N-terminus of proteins, or cut peptide chains in the middle. Insulin is a typical example of this type of modification. Insulin is cleaved twice after the disulfide bond is established, and the peptide precursor is removed in the middle of the chain. The resulting protein contains two peptide chains connected by disulfide bonds.
PTMs Involving Addition of Functional Groups
PTM also includes covalent additions of protein functional groups, and this type of PTM plays an important role in biological processes. It is worth noting that there are many common PTMs with added functional groups, including methylation, acetylation, sulfation, phosphorylation, glycosylation, propionylation. Among a variety of PTMs, phosphorylation is the most significant PTM and also a crucial mechanism for regulating enzyme activity. Furthermore, glycosylation is the most extensive PTM. Glycosylation is a reaction that requires enzyme catalysis, in which a glycosyl donor is attached to another molecule to form a glycoconjugate. Most proteins in organisms are glycosylated. The glycosylation modification of protein can significantly affect the processes of cell adhesion, clearance, molecular transport, and signal transduction.
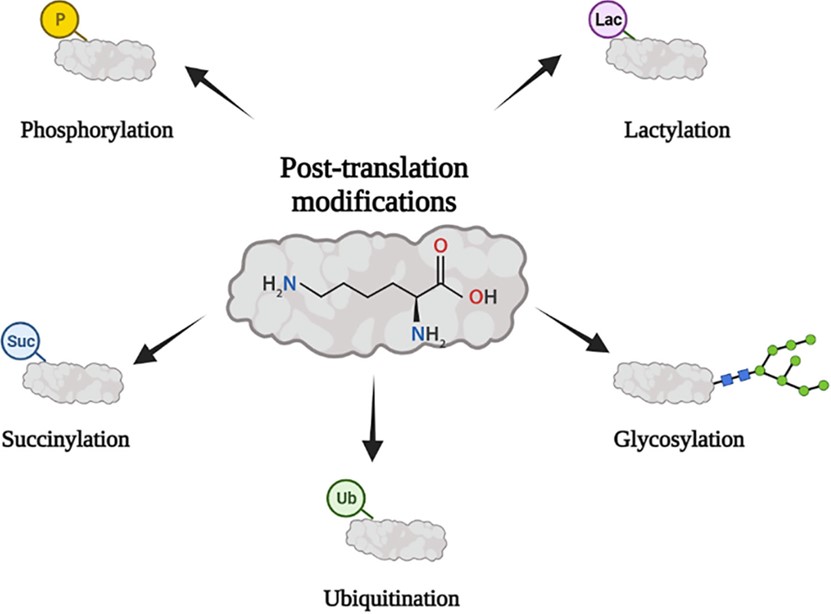 Fig.1 Main forms of PTM.1
Fig.1 Main forms of PTM.1
Other Proteins or Peptides
PTM also involves other proteins or peptides, ubiquitination and SUMOylation are the most common ones.
Ubiquitin is a small protein in eukaryotes. Ubiquitination is the modification of the substrate protein with ubiquitin, which has an important impact on the function of its substrate. In addition, ubiquitination also has a great impact on protein interactions.
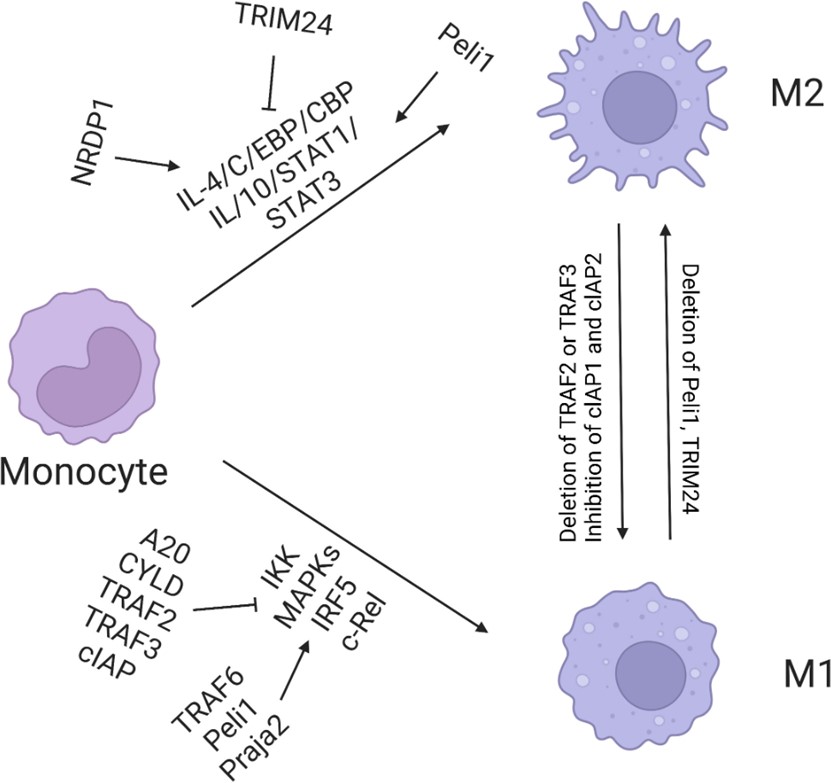 Fig.2 Regulation of macrophage polarization by ubiquitination.1
Fig.2 Regulation of macrophage polarization by ubiquitination.1
Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier (SUMO) proteins are a family of small proteins that can change the function of target substrates by covalently connecting and separating from other proteins in the cell. This process is called SUMOylation. SUMOylation is a kind of PTM that involves multicellular processes, such as transcriptional regulation, protein stability, apoptosis, nuclear cytoplasmic transport, stress response, and progression throughout the cell cycle.
Chemical Modification of Amino Acids
Another common type of PTM is the chemical modification of amino acids. Typical examples are deamidation and deimination. Deamidation is a chemical reaction in which the amide functional group in the side chain of the amino acid asparagine or glutamine is changed. Deimination is the conversion of the amino acid arginine in protein to the amino acid citrulline. These reactions are important in proteins or peptides, because they may change the structure and function of the protein or peptides, and may also lead to protein degradation.
With the development of research on PTM, the detection of PTM has gradually become a hot spot. The most frequently used detection methods are western blot analysis, Mass spectrometry (MS), and High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). As a leading biotechnology company in the world, Creative Biolabs provides customized PTM services to promote the development of protein-related research.
For more details, please feel free to contact us for more information.
Reference
-
Li, Yanqing, Runfang Zhang, and Hu Hei. "Advances in post-translational modifications of proteins and cancer immunotherapy." Frontiers in Immunology 14 (2023): 1229397. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Resources

 Fig.1 Main forms of PTM.1
Fig.1 Main forms of PTM.1
 Fig.2 Regulation of macrophage polarization by ubiquitination.1
Fig.2 Regulation of macrophage polarization by ubiquitination.1

