All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
Creative Biolabs has generated chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) specific for a variety of target antigens, many of which are overexpressed on tumor cells. Based on experience in CAR-T, we are pioneering the development of chimeric antigen receptor macrophage (CAR-MA). Moreover, we offer high-quality custom fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) assay.
FRET allows the detection of the approach between two molecules within several nanometers. The mechanism of FRET involves a donor fluorophore in an excited electronic state, which may transfer its excitation energy to a nearby acceptor chromophore in a non-radiative fashion through long-range dipole-dipole interactions. FRET can be used to measure the distance between the donor and the acceptor or the dynamical activities between two sites on this macromolecule, such as protein interactions. This technique is widely applied in many fields such as single-molecule experiments, molecular motors, biosensors, and DNA mechanical movements. FRET is extremely useful for biomedical research for three major reasons:
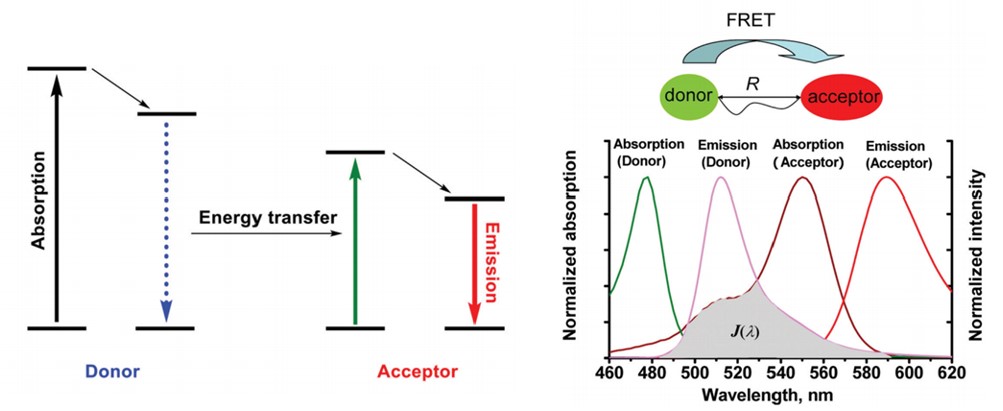 Fig.1 The mechanism of FRET. (Wu, 2020)
Fig.1 The mechanism of FRET. (Wu, 2020)
In fluorescence microscopy, fluorescence confocal laser scanning microscopy, as well as in molecular biology, is a useful tool to quantify molecular dynamics in biophysics and biochemistry, such as protein-protein interactions, protein-DNA interactions, and protein conformational changes. FRET can also be used in techniques such as flow cytometry, immunocytochemistry, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA, to identify potential molecular interactions.
Creative Biolabs provides custom FRET analysis for function research such as protein-protein interaction. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us.
Reference
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION