All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
Creative Biolabs offers a wide range of CLL1 CAR-related products to assist in CART development. Here is a brief list of some CLL1 CAR products. You can also search for the products you are interested in by searching for the corresponding keywords.
CLL-1, known as CD371, is a type II transmembrane glycoprotein with receptor inhibitory function. CLL-1 protein is restricted expressed in myeloid cells as well as in most AML cells. More importantly, CLL-1 is selectively expressed in leukemia stem cells (LSCs) in AML, but not in normal HSCs, making it an excellent therapeutic target for AML.
Associated Diseases
Designing the appropriate CAR format is a critical step in CART development. Creative Biolabs has successfully launched a user-friendly online CAR design tool to synthesize customer-preferred CAR formats, including many classical CAR constructions, and special armored CAR constructions.
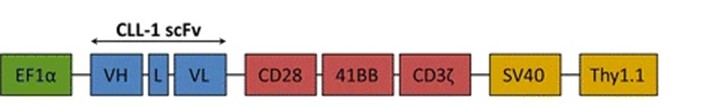
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the CLL1 CAR construction.1
Phenotype Analysis of Anti-CLL1 CAR-T
In order to better detect the performance of CART cells when interacting with tumor cells, we have developed a variety of phenotypic detection services via various approaches, including but not limited to proliferation test, activation test, and exhaustion detection.
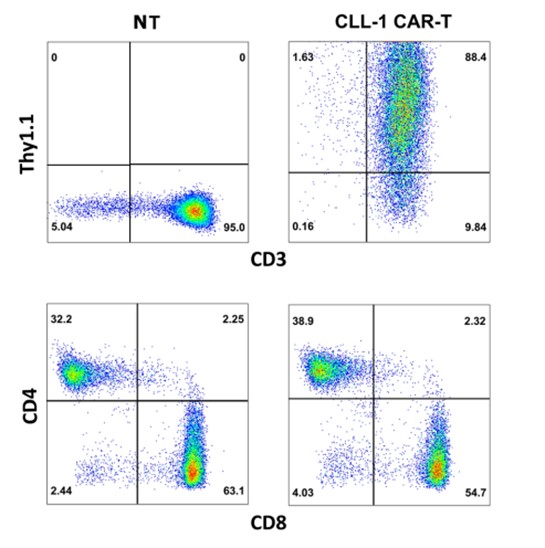
Fig.2 Representative phenotype of CLL-CART cells by flow cytometry.1
Anti-CLL1 CAR-T Cytokine Release Test
Multiple cytokine detection provides a convenient detection method for CART studies, which can detect various kinds of cytokines simultaneously when the volume of cell culture supernatant is limited. In addition to multiplex cytokine testing, we also offer other testing methods to meet the different needs of global customers, such as intracellular cytokine flow detection.
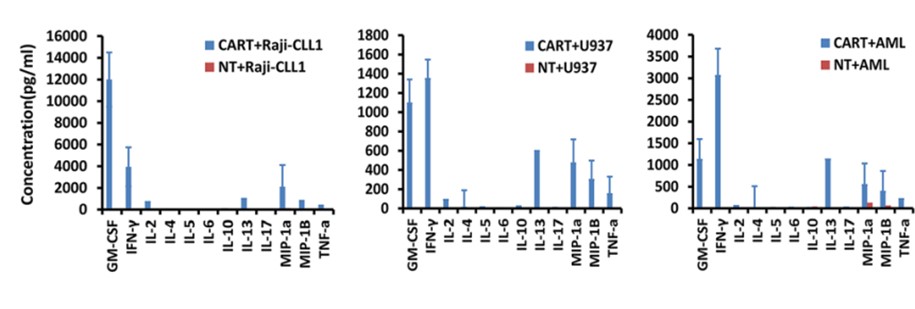
Fig.3 Cytokine detection of CLL-1 CAR-T co-cultured with various target cells by multiple cytokine profiling.1
Anti-CLL1 CAR-T In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
In vitro tumor killing assay is a crucial test to verify the target specificity and effectiveness of CART cells against target cells, which provides relevant reference for subsequent in vivo experiments. Creative Biolabs offers a variety of testing services for toxicity verification, such as CSFE- staining test, real-time dynamic cytotoxicity test, etc.
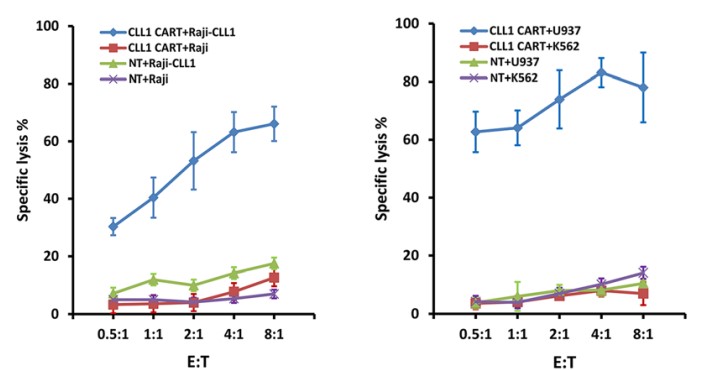
Fig.4 In vitro cytotoxicity test of anti-CLL1 CAR-T cells against different tumor cells.1
In Vivo Animal Models for CLL1 CAR-T
With years of experience in the CART field, Creative Biolabs offers one-stop services for CLL1 CART development. For CART in vivo verification, we offer a wide range of suitable animal models and customized in vivo experimental designs for specific target research.
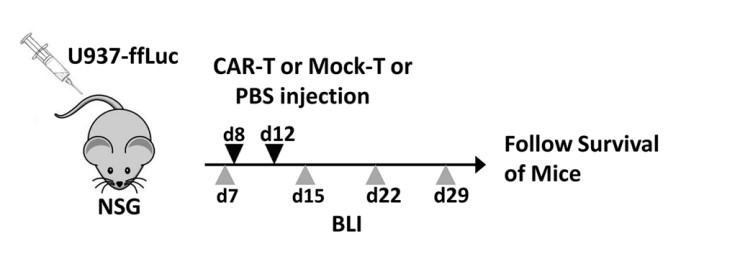
Fig.5 Schematic diagram of the in vivo experimental design of anti-CLL1 CAR-T.1
Efficacy Test of Anti-CLL1 CAR-T
Our efficacy testing services focus on evaluating the effectiveness and persistence of CAR-T treatment in killing tumor cells and inhibiting tumor growth in animal models. We test the cytotoxicity of CAR T cells against target tumor cells by various kinds of in vivo assays.
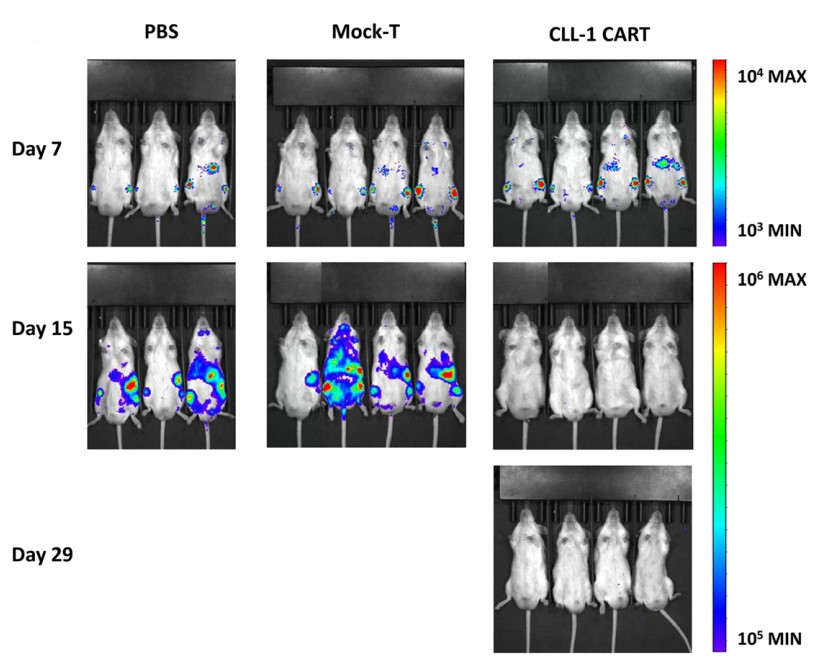
Fig.6 Efficacy assessment of CLL-1 CAR-T cells in U937 xenograft model detected by bioluminescent imaging.1
Toxicity Evaluation of CLL1 CAR-T
CAR-T toxicity evaluation is designed to assess the safety and potential toxicities associated with the use of CAR-T cells. Creative Biolabs offers a series of CAR-T toxicity testing services, such as off-target study, and phenotype analysis of animal model tissues.
Reference
 Loading...
Loading...
| CAT | Product Name | Target Species | Antibody Clone | Antibody Host | Receptor Construction | Vector Type | Targeting Cell Type | CAR Vector Type | Inquiry & Datasheet |
| CAR-SB-LX0183 | Anti-CLL1 (6E7.L4Hle) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pSBCAR1 | Human | 6E7.L4Hle | Human | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposon | T cell | ||
| CAR-SB-LX0184 | Anti-CLL1 (21C9.L2H3) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pSBCAR1 | Human | 21C9.L2H3 | Human | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposon | T cell | ||
| CAR-SB-LX0185 | Anti-CLL1 (3H10) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pSBCAR1 | Human | 3H10 | Human | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposon | T cell | ||
| XS-0622-ZP3171 | Anti-CLL1 h(VHH1-VHH2-CD28-CD3ζ) Biepitopic CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | VHH1-VHH2-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||||
| XS-0622-ZP3343 | Anti-CLL1 h(VHH1-VHH2-4-1BB-CD3ζ) Biepitopic CAR, pCDCAR1 | VHH1-VHH2-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | |||||
| XS-0822-YF1213 | Anti-Human CLL1 (XW-293) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR IVT Plasmid, pCARIVT | Human | XW-293 | Human | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | In Vitro Transcription (IVT) Vector | |||
| XS-0922-ZP1417 | Anti-CLL1 (XP9) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | XP9 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF4893 | Anti-CLL1 TCR-ABR (scFv-CD3ε, XW-293) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-293 | Human | scFv-CD3ε | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF4894 | Anti-CLL1 TCR-ABR (scFv-CD3ε, XW-294) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-294 | Human | scFv-CD3ε | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF4895 | Anti-CLL1 TCR-ABR (scFv-CD3ε, XW-295) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-295 | Human | scFv-CD3ε | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF4896 | Anti-CLL1 TCR-ABR (scFv-CD3ε, XW-296) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Mouse | XW-296 | Rat | scFv-CD3ε | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF4897 | Anti-CLL1 TCR-ABR (scFv-CD3ε, XW-297) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-297 | Mouse | scFv-CD3ε | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF4898 | Anti-CLL1 TCR-ABR (scFv-CD3ε, XW-298) CAR Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | XW-298 | Mouse | scFv-CD3ε | Lentiviral vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF5813 | Anti-CLL1 (XW-293) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pAAV | Human | XW-293 | Human | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF5814 | Anti-CLL1 (XW-294) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pAAV | Human | XW-294 | Human | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF5815 | Anti-CLL1 (XW-295) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pAAV | Human | XW-295 | Human | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-1122-YF5816 | Anti-CLL1 (XW-296) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pAAV | Mouse | XW-296 | Rat | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector | T Cell | ||
| XS-0823-LX30 | Anti-hCLL-1 (Ab) ICD(CD28-OX40-CD3ζ) CAR-MA, pAd5f35 Vector | Human | Ab | Adenoviral vectors |
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION