Tumor angiogenesis is a hallmark of solid tumors. As a fundamental process, angiogenesis help to supply tumors with oxygen and nutrition required for their growth and survival. As malignancy develops, cells progress from a prevascular stage (normal to early hyperplasia) to a vascular stage (late hyperplasia to dysplasia to invasive carcinoma). Unlike normal vessels in healthy tissues, the tumor vasculature possesses abnormal morphology, high permeability and compressive force. The hypoxic and acidic tumor microenvironment (TME) contributes to this pathological angiogenic process. The abnormal vascular structure and function in turn cause a hypoxic and acidic TME.
Immature, tortuous, and highly permeable vessels are the most common features of intratumoral vasculature. The regulation of angiogenesis is dependent on pro- and anti-angiogenic regulators. Targeting these regulators can improve TME. The vessel depletion/inhibition, tumor blood vessels regression and vessel normalization represent three attractive approaches to reverse abnormal tumor vessels. Current vascular targeting strategies are based on the inhibition of key angiogenic signaling pathways known to promote tumor angiogenesis. Several strategies have been developed to inhibit angiogenesis that is suitable for clinical trials.
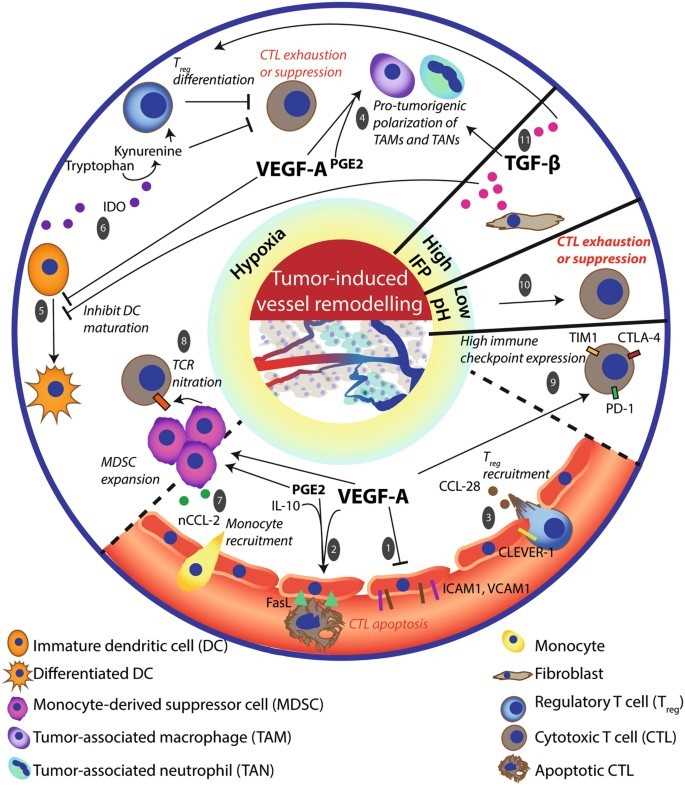 Fig.1 The nature of the TME influences immune cell composition and angiogenesis. (Schaaf, 2018)
Fig.1 The nature of the TME influences immune cell composition and angiogenesis. (Schaaf, 2018)
Some important growth factors are responsible for tumor-driven angiogenesis such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), etc. The most extensively clinically used direct anti-angiogenic strategy targets VEGF-A or its receptors.
Angiopoietins (ANGs) constitute another important class of angiogenic molecules that bind the endothelial-specific receptor tyrosine kinase (TIE) and act as a regulator of ANG-TIE signaling during angiogenesis. ANG1 stabilizes the tumor vasculature While ANG2 strongly promotes excessive angiogenic sprouting. Drugs that target the ANG-TIE pathway are in clinical development for oncological applications.
Several cytokines in the TME play an important role in tumor angiogenesis. Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) is a controversial pro-angiogenic cytokine because a few studies have revealed its inhibitory effect. Interferons (IFNs) are multifaceted in the regulation of tumor angiogenesis with enhancing or reducing angiogenesis. Interleukins play an important role in promoting tumor angiogenesis. In contrast, TNF-α is an anti-angiogenic and pro-angiogenic factor.
Hypoxia induces angiogenesis, a target of several immunotherapeutics. The key regulator, the transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF), can induce the expression of a large number of pro-angiogenic factors thus promoting angiogenesis. The newly formed vasculature is disorganized and leaky, which facilitates tumor cell invasion and metastasis, impairs drug delivery and further aggravates hypoxia in the tumor and the TME.
EPCs contribute to many processes, such as wound healing, myocardial ischemia, neovascularization, and tumor growth. Blocking EPC mobilization would inhibit the formation of new blood vessels and the metastatic niche.
Multifactorality and the complexity of interactions in TME might limit the success of therapeutic approaches targeting only single angiogenesis molecules. Combination therapies or agents with a multimodal mode of action could be more effective. Moreover, nanotechnologies approaches could improve the efficiency of drugs delivery and favor their selective accumulation in tumors.
Creative Biolabs is dedicated to assisting our clients to develop reshaping TME strategies. We provide you with various angiogenesis models and many assays such as tube formation assay that help assess the anti-angiogenic potential of new tumor therapeutic strategies.
Reference
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION