Autophagy is a major lysosomal degradation pathway that supports intracellular components recycling to maintain cell homeostasis. Autophagic degradation serves as an important source of nutrients such as amino acids, nucleotides and fatty acids. Autophagy occurs with the formation of double-membrane vesicles known as autophagosomes. Autophagosomes sequester the material that is targeted for degradation, and ultimately fuse with the lysosome to form the autolysosome. The lysosome contains hydrolytic enzymes and a low pH that allows degradation of the materials sequestered by the autophagosome. Increasing evidence suggests that autophagy is employed by cancer cells as a highly plastic and dynamic mechanism to either repress initial steps in carcinogenesis or support the survival and growth of established tumors. In fact, autophagy can act both as a tumor suppressor or a tumor promoter depending on the stage of tumorigenesis, TME, and mutational and oncogenic background.
In the early stage of tumorigenesis, autophagy is a tumor suppressor via degradation of potentially oncogenic molecules. Autophagy acts as a tumor suppressor by restricting tumor cell necrosis, which is likely to favor tumor-promoting immunity. Because autophagy is deeply involved in the proper functioning of various immune cells, controlling the autophagy pathway may stimulate immune reactions against tumor cells. Moreover, autophagy also restricts cancer cell proliferation by favoring oncogene-induced senescence. Beclin 1 and LC3, crucial genes for autophagy, are altered in several types of human cancer. It is possible that loss of them blocks activation of autophagy, and may inhibit the development of cancers.
Once the tumors progress to late-stage, autophagy can promote tumor progression in response to intracellular and environmental stress. Multiple elements affect the emergence of autophagy, such as hypoxia, low glucose, AMP/ATP, amino acids, and growth factors. Many cancers benefit from and require functional autophagy for their growth and progression. During cancer maintenance, the activity of the autophagy pathway is often upregulated. This upregulation ensures sufficient energy supply and contributes to survival during stress, metastasis and drug resistance. Cancer cell-associated autophagy can affect both neighboring cancer cells as well as other cell types that make up the TME via cell-cell communication. Autophagy induced by environmental stress also promotes the escape to cytotoxic lymphocytes (CTL) or NK-mediated elimination of tumors cells.
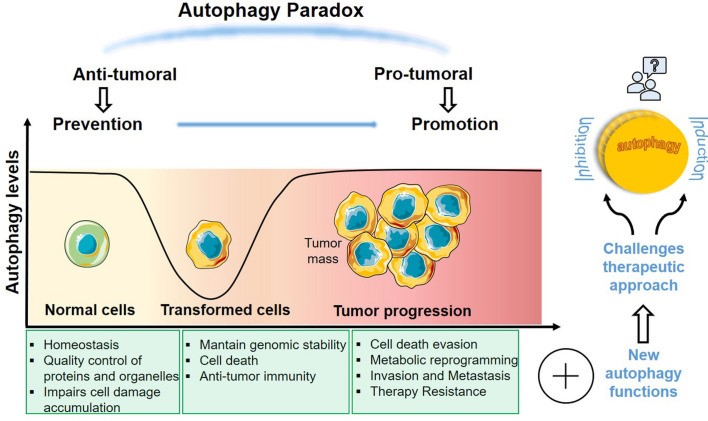 Fig.1 Dual role of autophagy in cancer.1,3
Fig.1 Dual role of autophagy in cancer.1,3
Abundant preclinical evidence indicates that stress-induced autophagy in tumor cells is predominantly cytoprotective and that inhibition of autophagy can enhance tumor cell death by diverse anticancer therapies. Each stage in autophagy has a subset of potential therapeutic targets for inhibiting autophagy in humans. As a therapeutic strategy in tumors, the pharmacodynamics of current autophagy inhibitory drugs, new target identification, and new inhibitor development are all important challenges facing the field of researchers investigating autophagy inhibition. Several preclinical and clinical studies have been undertaken to develop drugs able to inhibit autophagy. Pharmacological inhibitors of autophagy pathway include 3-methyladenine (3-MA), Chloroquine (CQ), hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), and Lys05 (a dimeric form of CQ) to inhibit the formation of autophagosome. Some of these signaling modulators are under clinical testing, including the inhibitors of mTOR, AMPK, and PI3K.
In addition, activators of autophagy may potentially contribute to the control of immunity and cancer. Several approved and/or experimental drugs, together with natural compounds, have been reported to induce autophagy in different cancer types. The development of new drugs that are designed to be more selective inducers of autophagy function in target organs is expected to maximize clinical benefits while minimizing toxicity. It is critical to characterize specific neoplasms for their actual dependency on autophagy before implementing the use of autophagy inhibitors/inducers in the clinical routine. From a therapeutic and translational perspective, further knowledge on the impact of autophagy on the TME and antitumor immunity will support the design of optimal clinical protocols that incorporate the use of autophagy modulators in combination with anticancer treatments.
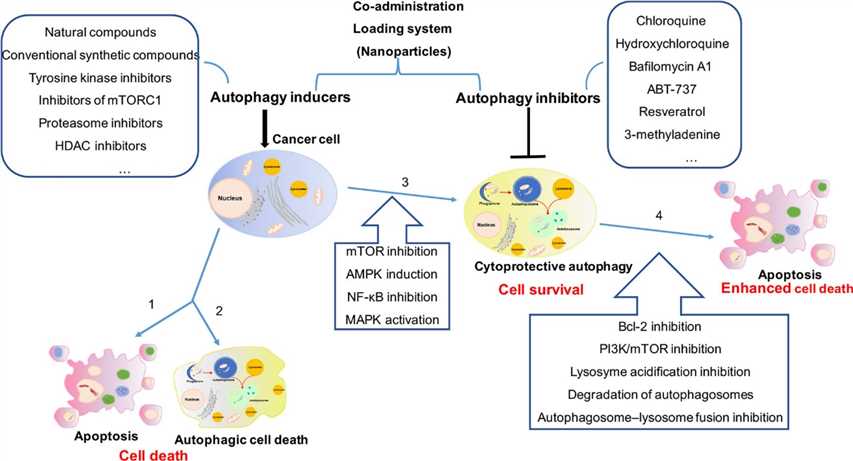 Fig.2 The comprehensive mechanism of autophagy induction and inhibition in cancer therapy.2,3
Fig.2 The comprehensive mechanism of autophagy induction and inhibition in cancer therapy.2,3
With a deep understanding in the impact of autophagy on the TME, Creative Biolabs offers autophagy related services for reshaping TME. Our scientists can assist you to meet your specific demands and tailor the most appropriate solution that contributes to the success of your projects. Please feel free to contact us.
References
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION