Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) offer a transformative platform for generating a wide range of cell types, including neural crest cells, which are pivotal in developmental biology and disease modeling. At Creative Biolabs, we provide a robust and customizable protocol for generating highly pure, functional neural crest cells from iPSCs, supporting cutting-edge research in neural development, regenerative medicine, and neural crest-derived pathologies.
Neural crest cells are a transient, multipotent, and migratory cell population that arise during vertebrate embryogenesis from the border region between the neural plate and non-neural ectoderm. They possess the remarkable ability to differentiate into a wide range of cell types, including peripheral neurons, glial cells, melanocytes, craniofacial cartilage, bone, and smooth muscle. Due to their extraordinary lineage potential and contribution to diverse tissues, neural crest cells are often referred to as the "fourth germ layer."
In vitro differentiation of neural crest cells from iPSCs closely mimics the in vivo developmental cues responsible for neural crest specification. This process involves a tightly regulated sequence of steps including:
By recapitulating these developmental signaling pathways using small molecules, neural crest cells can be efficiently and reproducibly derived from iPSCs in a chemically defined, feeder-free system. This eliminates the variability associated with embryoid body formation or serum-based differentiation protocols.
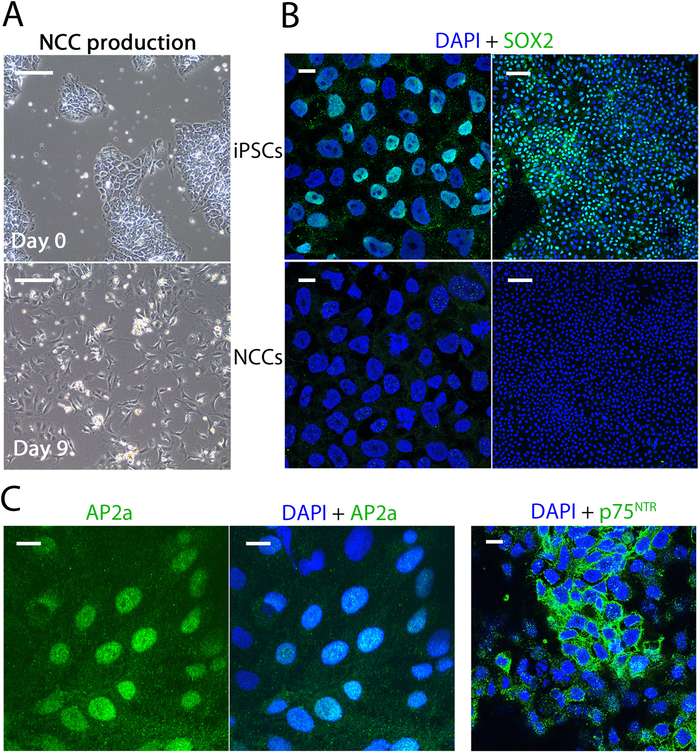 Fig.1 Generation of neural crest cells from hiPSCs.1,2
Fig.1 Generation of neural crest cells from hiPSCs.1,2
We provide a high-efficiency, customizable neural crest cell differentiation protocol tailored to both basic research and translational applications. Our platform ensures:
By unlocking the developmental blueprint of neural crest formation through iPSC technology, Creative Biolabs empowers researchers and developers to advance their scientific goals.
Below is a non-exhaustive list of essential reagents and media required for sensory neuron differentiation.
| Reagent/Material | Specification |
|---|---|
| iPSC line | Feeder-free, karyotypically normal |
| Matrigel | hESC-qualified |
| mTeSR1 medium | Feeder-free maintenance medium |
| N2 supplement | Neural differentiation support |
| B27 Supplement (minus vitamin A) | Neural induction support |
| SB431542 | TGF-β inhibitor |
| CHIR99021 | GSK-3β inhibitor (Wnt activator) |
| DMEM/F12 | Basal medium |
| Neurobasal medium | Neural support medium |
| Accutase | Cell dissociation |
| ROCK inhibitor | Enhances survival post-passage |
Coat plates with Matrigel in DMEM/F12 and incubate. Plate iPSCs in mTeSR1 medium, changing medium daily. Maintain cells at ~70–80% confluency to avoid spontaneous differentiation. Passage with Accutase every 4–5 days using ROCK inhibitor to promote survival.

Replace mTeSR1 with neural induction medium: DMEM/F12 + N2 supplement + SB431542 + CHIR99021. Incubate for 5 days, refreshing medium every 24 hours. Observe morphological changes: cells flatten, gain rosette-like morphology.

Promote neural crest cell lineage commitment from anterior neuroectoderm. On Day 5, switch to neural crest cell induction medium: Neurobasal medium + B27 (–Vit A) + N2 + CHIR99021 + SB431542. Continue culture for 5 additional days. Monitor for NCC morphology (elongated, migratory phenotype).

Detach cells using Accutase and re-plate on fibronectin-coated plates. Culture in neural crest cell expansion medium: DMEM/F12 + N2/B27 + bFGF + EGF. NCC markers (SOX10, HNK-1, p75NTR) typically peak during this phase.
| Parameter | Methodology |
|---|---|
| Morphological assessment |
|
| Marker expression |
|
| Functional assays |
|
Below is a comprehensive guide to resolving common issues and optimizing yield, purity, and functionality of neural crest cells.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low NCC induction efficiency |
|
|
| High cell death during neural induction |
|
|
| Spontaneous differentiation in iPSC culture |
|
|
| Heterogeneous cell populations post-induction |
|
|
| Inconsistent NCC marker expression |
|
|
| Poor migration behavior |
|
|
| Unwanted differentiation into neurons or glia |
|
|
With years of experience in iPSC differentiation services, Creative Biolabs recommends the following best practices to enhance consistency and scalability:
Creative Biolabs offers a full suite of services to support your iPSC-based neural crest research
Let Creative Biolabs be your trusted partner in iPSC-derived neural crest research. Whether you are modeling neural crest disorders or developing regenerative cell therapies, our team is here to deliver customized solutions with scientific rigor and commercial scalability.
Learn more or request a custom quote.
References
Created July 2025
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.