Before stem cells can be confidently employed in downstream applications, it is critical to verify their pluripotency markers. This ensures both research integrity and experimental reproducibility. Creative Biolabs' pluripotent cell marker expression analysis protocol is designed with precision, scalability, and customization in mind.
This protocol will guide you through the key principles, step-by-step workflow, optimization tips, and troubleshooting strategies that underlie successful pluripotent stem cell (PSC) marker expression analysis.
Pluripotency is defined by the ability of stem cells to self-renew indefinitely while maintaining the potential to differentiate into derivatives of all three germ layers. To ensure this defining trait, researchers rely on the detection of pluripotency-associated markers at the transcriptional and protein levels.
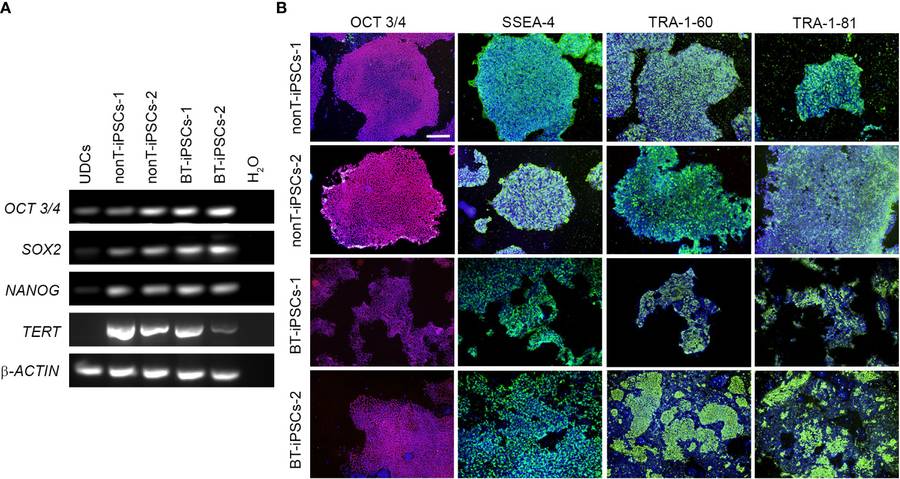 Fig.1 Analysis of the pluripotency markers in the generated iPSC lines.1,2
Fig.1 Analysis of the pluripotency markers in the generated iPSC lines.1,2
Transcription Factors:
Cell Surface Antigens:
Functional Indicators:
By employing qPCR, flow cytometry, immunocytochemistry (ICC), and Western blotting, Creative Biolabs integrates multiple readouts to confirm stem cell pluripotency robustly.
The underlying principle is straightforward:
| Category | Reagents |
|---|---|
| Stem Cell Samples |
Human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) |
| Key Reagents |
Primary antibodies: Anti-OCT4, Anti-SOX2, Anti-NANOG, Anti-SSEA-3, Anti-TRA-1-60 Secondary antibodies: Fluorescently labeled goat anti-mouse/anti-rabbit Fixatives: Paraformaldehyde Permeabilization buffers: Triton X-100 qPCR reagents: SYBR Green, primers for pluripotency genes Flow cytometry buffers: PBS + FBS |
Maintain PSCs under feeder-free or feeder-dependent conditions. Ensure colonies are compact, with high nucleus-to-cytoplasm ratios. Harvest cells at 70–80% confluency to avoid spontaneous differentiation.

Extract high-quality RNA using kits. Synthesize cDNA with reverse transcriptase. Perform qPCR using pluripotency-specific primers. Normalize results against housekeeping genes (GAPDH, ACTB). Interpret results: High OCT4, SOX2, and NANOG expression indicates pluripotency.

a. Western Blot: Lyse cells and extract proteins. Probe with primary antibodies against OCT4, SOX2, NANOG. Visualize bands using chemiluminescence. b. Immunocytochemistry (ICC): Fix and permeabilize cells. Incubate with primary antibodies (e.g., anti-SSEA-4, anti-TRA-1-81). c. Flow Cytometry: Stain live or fixed cells with fluorescently conjugated antibodies. Analyze marker expression profiles.

Cross-reference transcriptional and protein-level readouts. Validate pluripotency across at least two independent techniques. Generate comprehensive reports for research documentation.
Even with well-established protocols, pluripotent cell marker analysis can present challenges. Below are detailed troubleshooting and optimization tips that can help you achieve reliable and reproducible results.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low-quality RNA leading to poor qPCR amplification |
|
|
| Weak amplification signals or inconsistent Ct values |
|
|
| Weak staining or non-specific background |
|
|
| Non-specific staining obscures specific signal |
|
|
| Variable signal intensities or unexpected populations |
|
|
| PSCs appear negative for key markers despite proper culture |
|
|
To help clients move seamlessly from stemness validation to functional applications, we offer a wide portfolio of related services.
For the most stringent validation, we provide teratoma assays in immunodeficient mice. This gold-standard test demonstrates the ability of your iPSCs to differentiate into tissues of all three germ layers.
Generation of high-quality human iPSCs from somatic cells using non-integrative methods.
Our differentiation assays include both directed protocols and spontaneous differentiation assays, complete with lineage-specific marker verification.
Gene knock-out, knock-in, or correction services for iPSC lines using precise strategies with clone validation.
A: Fully reprogrammed iPSCs express pluripotency markers at levels comparable to hESCs, with consistent expression across multiple detection methods (qPCR, ICC, flow cytometry). Partial reprogramming often shows incomplete marker profiles and reduced self-renewal capacity.
A: For a full multi-platform analysis, we generally recommend 1–2 million cells. However, with optimized protocols, we can work with as few as 200,000 cells using microfluidics and high-sensitivity antibody assays.
A: We recommend validation every 3–5 passages, before differentiation experiments, or whenever cells undergo significant environmental changes (e.g., switch of feeder system, media brand, or culture substrate).
A: The most widely accepted gold-standard markers are OCT4, SOX2, and NANOG at the transcriptional level, combined with surface markers such as SSEA-3/4 and TRA-1-60/TRA-1-81. Using a combination ensures robust and reproducible validation of pluripotency.
References
Created August 2025
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.