Creative Biolabs has developed a state-of-the-art WGS protocol tailored to stem cell populations, allowing scientists to trace genomic fidelity, identify subtle variations, and validate engineered cell lines with unmatched precision. Below, we share a detailed protocol that demonstrates not only the technical rigor but also the practicality of our approach.
Stem cells, particularly pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), hold immense potential for basic research, disease modeling, and cell-based product development. However, their genomic stability is often challenged by in vitro culture conditions, genome-editing interventions, or spontaneous mutations over passages.
WGS provides:
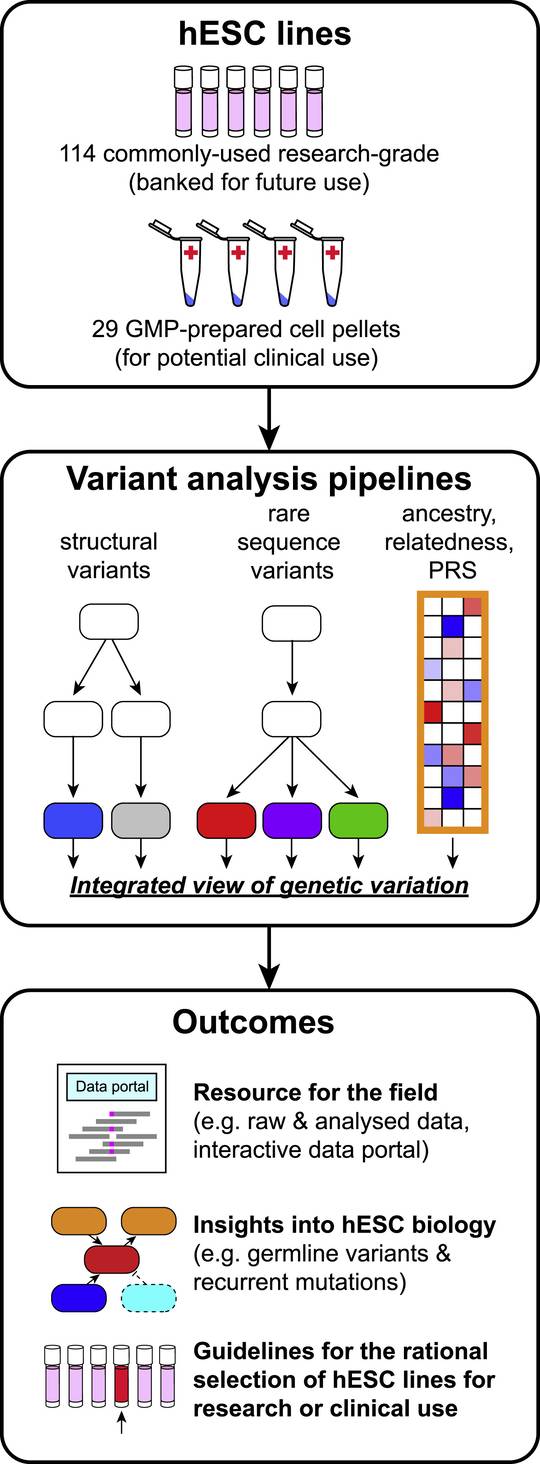 Fig.1 The genomic DNA of hESCs was analyzed by high-density SNP microarray and at the single-nucleotide level by WGS to call structural variants.1,2
Fig.1 The genomic DNA of hESCs was analyzed by high-density SNP microarray and at the single-nucleotide level by WGS to call structural variants.1,2
The principle of WGS is straightforward yet powerful: fragment the entire stem cell genome, sequence all fragments using next-generation sequencing (NGS) or third-generation long-read platforms, and computationally assemble the full genome to detect variants at single-base resolution.
For stem cells, this principle takes on extra weight because:
By applying WGS, researchers ensure their stem cell lines maintain fidelity, reproducibility, and translational relevance. Creative Biolabs combines deep sequencing technologies with bioinformatics pipelines optimized for stem cell samples, ensuring researchers receive a holistic and high-resolution genetic profile.
| Category | Item |
|---|---|
| Cell Material |
Human pluripotent stem cells (hESCs or iPSCs) Mesenchymal stem cells (bone marrow, adipose, cord-derived) Neural stem cells or other lineage-committed precursors |
| Reagents & Consumables |
High-quality DNA extraction kit RNase A Nuclease-free water Fragmentation system (sonicator or enzymatic kit) DNA quantification reagents Library preparation kits Magnetic beads Sequencing adapters and barcodes PCR master mix for library amplification |
Harvest ~1–2 million stem cells under sterile conditions. Extract genomic DNA using a commercial kit optimized for high molecular weight DNA. Treat with RNase A to remove RNA contamination. Quantify DNA and purity check. Verify DNA integrity via agarose gel electrophoresis.

Shear DNA into fragments (~350 bp for short-read sequencing, >10 kb for long-read). Use ultrasonication or enzymatic fragmentation. Confirm fragment size distribution.

End-repair fragmented DNA. Perform A-tailing to facilitate adapter ligation. Ligate sequencing adapters containing unique indexes. Purify with magnetic beads to remove small fragments. PCR-amplify (limited cycles to reduce bias).

Load libraries onto NGS platform. Perform paired-end sequencing (150 bp reads). For long-read sequencing, directly load libraries onto Nanopore flow cells.

Perform raw data QC. Trim low-quality bases and adapters. Align reads to human reference genome (hg38). Detect SNVs, insertions/deletions, CNVs, and structural variants. Annotate mutations using curated stem cell databases. Generate visual reports for variant distribution and genome integrity.
We have compiled decades of hands-on experience into a comprehensive troubleshooting guide to help scientists avoid common pitfalls and achieve reliable results.
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Low DNA yield from stem cells |
|
| Poor DNA integrity |
|
| Over-representation of small fragments or adapter dimers |
|
| Excessive PCR duplicates leading to reduced coverage diversity |
|
| Uneven coverage across the genome |
|
| Low sequencing quality |
|
Our WGS service is part of a comprehensive stem cell characterization platform. Researchers often need multi-dimensional insights that go beyond genomics, and we provide a full suite of complementary assays designed to ensure stem cells meet the highest standards of quality, reproducibility, and application readiness.
A: For general quality control, 30× coverage is sufficient. However, for engineered stem cells or projects requiring detection of rare off-target edits and subclonal mutations, we recommend ≥60× coverage. At Creative Biolabs, we adjust depth according to your research goals.
A: Typically, 1–2 million cells are sufficient to obtain high-quality genomic DNA for bulk sequencing. For single-cell WGS, Creative Biolabs offers ultra-low input library preparation kits and amplification strategies that preserve genomic fidelity.
A: WGS enables identification of single nucleotide variants (SNVs), insertions and deletions (InDels), copy number variations (CNVs), structural variants (SVs), and mitochondrial DNA mutations. Our pipelines are optimized for stem cells, ensuring accurate annotation of variants relevant to genomic stability.
A: Definitely. Many clients combine WGS with RNA-Seq, epigenomic profiling, and karyotyping. By leveraging our integrated multi-omics platform, you gain a comprehensive understanding of your stem cells at the genomic, transcriptomic, and epigenetic levels.
References
Created August 2025
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.