As a pioneer in stem cell technology and neuroglial research, Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive and standardized protocol for generating functional oligodendrocytes from human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). This cutting-edge workflow supports drug discovery, neurodevelopmental research, and disease modeling for demyelinating disorders such as multiple sclerosis and leukodystrophies.
As the primary myelinating cells of the central nervous system (CNS), oligodendrocytes are indispensable for axonal insulation, electrical signal propagation, and trophic support of neurons. iPSCs provide an ethically sound, renewable, and patient-specific source for generating human oligodendrocytes in vitro. This enables researchers to bypass limitations of primary glial cells, such as poor accessibility, variability, and limited scalability.
Through a precisely staged differentiation protocol, iPSCs can be directed to recapitulate embryonic development—progressing from pluripotency through neural induction, ventral forebrain or spinal cord patterning, specification of oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs), and finally, maturation into functional myelin-producing cells.
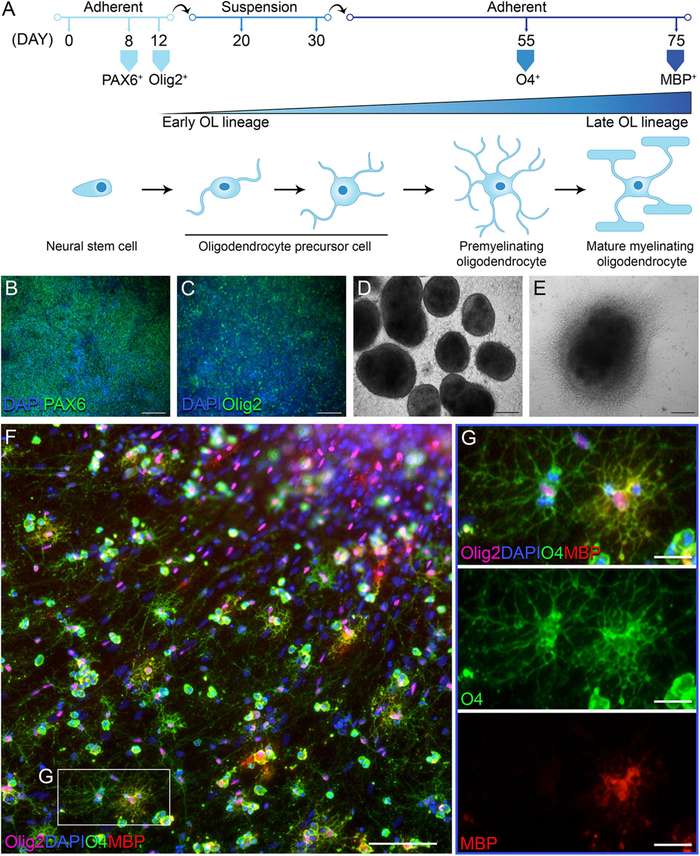 Fig.1 Differentiation of hiPSCs into oligodendrocytes.1,2
Fig.1 Differentiation of hiPSCs into oligodendrocytes.1,2
The differentiation process is guided through neural lineage commitment, expansion of OPCs, and terminal maturation into myelinating oligodendrocytes. Key signaling pathways involved include SHH, FGF2, PDGF, and T3-mediated thyroid hormone signaling.
| Category | Items |
|---|---|
| iPSC culture | Feeder-free iPSC line, mTeSR1 medium, Matrigel-coated plates |
| Neural induction | Dual-SMAD inhibitors: SB431542, LDN-193189 |
| OPC induction | SHH, FGF2, Retinoic acid, Purmorphamine |
| OPC expansion | PDGF-AA, NT-3, IGF-1 |
| Terminal differentiation | T3 (triiodothyronine), cAMP, Noggin, B27 supplement |
| Analytical tools | qPCR primers, ICC antibodies (OLIG2, NKX2.2, MBP, CNPase) |
Plate feeder-free iPSCs on Matrigel in mTeSR1 medium. Maintain at 60-80% confluence for optimal neuroectodermal induction. Replace medium daily; passage when reaching 80-90% confluence.

Replace medium with N2B27 + SB431542 and LDN193189. Culture for 7–10 days to generate neuroepithelial cells. Confirm rosette formation morphologically.

Add SHH and Purmorphamine to pattern ventral identity. Supplement with Retinoic Acid and FGF2 . Maintain for 20 days with daily medium changes. Monitor expression of OLIG2 and NKX2.2 via ICC/qPCR.

Switch to OPC expansion medium containing PDGF-AA, NT-3, and IGF-1. Passage cells every 5–7 days. Monitor OPC morphology (bipolar/tri-polar processes) and expression of NG2 and PDGFRα.

Induce maturation by withdrawing PDGF-AA and supplementing with T3, cAMP, and B27. Maintain in differentiation medium for 2–4 weeks. Evaluate MBP and CNPase expression and membrane sheet formation.
At Creative Biolabs, quality assurance is integrated at every stage of oligodendrocyte generation.
| Detection Methods | |
|---|---|
| Identity verification |
|
| Functional validation |
|
| Genomic stability |
|
We emphasize proactive troubleshooting and continual optimization to ensure high-yield and high-purity oligodendrocyte populations. Below are detailed troubleshooting insights based on extensive empirical experience.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low neural induction efficiency |
|
|
| Poor neural rosette formation |
|
|
| Insufficient OLIG2+/NKX2.2+ OPCs |
|
|
| OPC proliferation arrest |
|
|
| Premature differentiation during OPC expansion |
|
|
| Poor morphological maturation |
|
|
| Low MBP/MOG expression |
|
|
By systematically applying these troubleshooting strategies, you can dramatically improve differentiation efficiency, ensure functional maturity, and minimize experimental failure.
To complement our iPSC-derived oligodendrocyte differentiation services, we proudly offer a comprehensive portfolio of related solutions, enabling our clients to streamline research workflows, reduce technical burden, and accelerate time-to-discovery.
Generation of integration-free iPSC lines from somatic tissues.
CRISPR/Cas9 knock-in/knock-out strategies for isogenic controls.
Our iPSC-derived neural cell services are tailored to support CNS disease modeling and drug screening pipelines with unmatched precision and consistency.
Ready to elevate your neuroglial research with validated human oligodendrocytes and tailored support?
Contact us today at info@creative-biolabs.com or visit our services page to request a quote or a free scientific consultation.
References
Created July 2025
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.