Sensory neurons are responsible for converting external stimuli—such as heat, pressure, pain, and proprioception—into electrical signals processed by the central nervous system. Due to their inaccessibility in humans, sensory neurons derived from iPSCs offer a powerful alternative for modeling peripheral neuropathies, nociceptive pain, and for conducting toxicity screening of therapeutic compounds.
Creative Biolabs leverages advanced stem cell engineering and differentiation protocols to support the robust generation of peripheral sensory neurons. Our platform enables customization for patient-specific lines, disease modeling, and pharmaceutical research.
Sensory neurons derived from iPSCs are pivotal tools for modeling human neurological diseases, studying pain and sensory perception, and developing drug screening platforms. The generation of sensory neurons from iPSCs involves a multistage differentiation process that mimics in vivo embryonic development, guiding cells through:
These neurons can be subclassified into nociceptors, mechanoreceptors, and proprioceptors, depending on the signaling cues provided during differentiation. Precise temporal control of small molecules and growth factors such as CHIR99021, BMP4, NGF, and retinoic acid ensures lineage specificity.
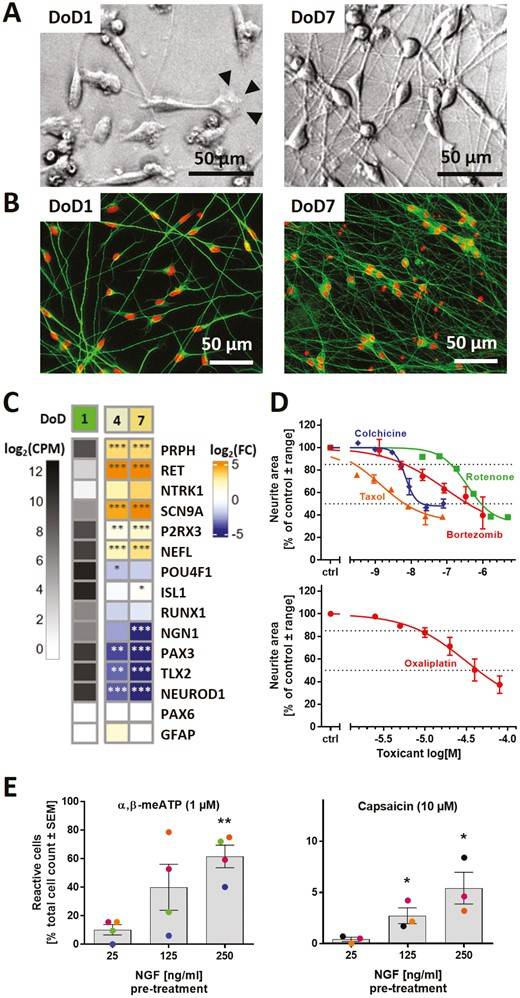 Fig.1 Human sensory neurons derived from iPSCs.1,2
Fig.1 Human sensory neurons derived from iPSCs.1,2
Key features of iPSC-derived sensory neurons:
At Creative Biolabs, we have developed an optimized, highly reproducible protocol to generate functional sensory neurons from iPSCs using chemically defined, feeder-free conditions.
Below is a non-exhaustive list of essential reagents and media required for sensory neuron differentiation.
| Category | Reagents |
|---|---|
| Cell culture | mTeSR1 medium, Matrigel (or vitronectin), Accutase |
| Neural induction | CHIR99021, SB431542, LDN193189 |
| Patterning | BMP4, Retinoic Acid, SU5402, DAPT |
| Neuronal maturation | NGF, BDNF, GDNF, NT-3, Ascorbic acid, dbcAMP |
| QC and staining | Anti-BRN3A, Anti-ISL1, Anti-PGP9.5, Anti-TRKA, DAPI |
Culture and expand iPSCs on Matrigel-coated plates in mTeSR1 medium. Passage using Accutase when 70–80% confluent. Confirm pluripotency via OCT4, NANOG, and SOX2 expression.

Replace mTeSR1 with Neural Induction Medium containing: CHIR99021 – Activates WNT signaling, SB431542 and LDN193189 – Dual SMAD inhibition. Refresh media daily. Cells will adopt a neuroepithelial morphology.

Switch to patterning medium supplemented with: BMP4 – Promotes neural crest fate, Retinoic Acid – Enhances posterior identity, SU5402 – Inhibits FGF to encourage sensory lineage. Monitor for crest-like rosette formation.

Dissociate and plate onto laminin/fibronectin-coated plates. Add maturation cocktail: NGF, BDNF, GDNF, NT-3, Ascorbic Acid, dbcAMP. Media changes every 2–3 days. Neurons extend axons and develop spontaneous activity.
To ensure functionality and lineage identity, several assays should be performed.
| Parameter | Methodology |
|---|---|
| Molecular Markers |
qPCR or IF Staining for:
|
| Electrophysiology |
Patch clamp recording to verify:
|
| Functional Assays |
Calcium imaging with:
|
| Morphological Assessment |
|
Generating high-quality, functional sensory neurons from iPSCs requires careful optimization of multiple variables across all stages of differentiation. Below, we provide a categorized list of common issues, potential causes, and actionable solutions.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Incomplete neuroepithelial conversion |
|
|
| Cell death during neural induction |
|
|
| Spontaneous differentiation in iPSC culture |
|
|
| Absence of neural crest morphology |
|
|
| Poor induction of ISL1/BRN3A expression |
|
|
| Rosette formation too sparse |
|
|
| Low neuronal yield |
|
|
| No axonal projection observed |
|
|
| High rate of apoptosis during maturation |
|
|
At Creative Biolabs, we offer consultation-based troubleshooting for clients working with custom iPSC lines, disease models, or drug testing pipelines. Whether you need to optimize neural crest yield or validate sensory subtypes like nociceptors or mechanoreceptors, our scientific team is ready to assist with protocol adaptation, performance tuning, and quality control strategies.
Leveraging two decades of stem cell innovation and neurobiology expertise, we offer a comprehensive portfolio of customizable services to support every stage of your iPSC-to-sensory neuron project.
Generate high-quality iPSCs from patient somatic cells using non-integrating methods (Sendai virus, episomal vectors).
Confirm iPSC identity through expression of OCT4, SOX2, NANOG, TRA-1-60, and normal chromosomal status.
Knock-in, knock-out, or point mutation to model inherited peripheral neuropathies or pain syndromes.
We also offer protocols for dopaminergic neurons, motor neurons, cortical neurons, and autonomic neurons.
Creative Biolabs is your trusted partner in human sensory neuron innovation. Learn more or request a custom quote.
References
Created July 2025
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.