Creative Biolabs provides advanced protocols and customized services for differentiating induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) into functional adipocytes. This protocol outlines the stepwise induction of adipogenic lineage from human iPSCs, offering a powerful model for studying adipogenesis, metabolic diseases, and obesity-related drug screening.
Adipocytes, or fat cells, are central players in energy storage, thermogenesis, insulin sensitivity, and endocrine signaling. Dysfunction of these cells is closely associated with major public health issues, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and lipodystrophy. Conventional models relying on animal-derived adipocytes or immortalized preadipocyte lines often fail to recapitulate human-specific adipogenic pathways and disease phenotypes.
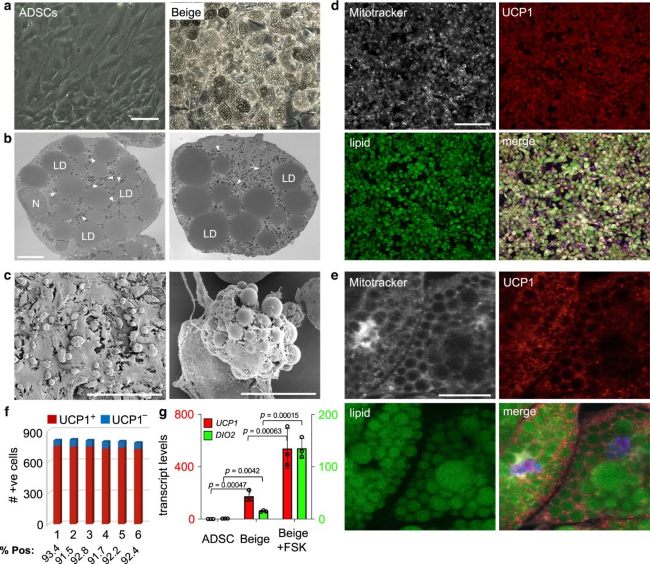 Fig.1 Efficient generation of beige adipocytes from adipose-derived stem/stromal cells (ADSCs).1,2
Fig.1 Efficient generation of beige adipocytes from adipose-derived stem/stromal cells (ADSCs).1,2
By contrast, iPSC-derived adipocytes provide a renewable, patient-specific, and genetically customizable cell source that closely mimics native adipose tissue functionality. The directed differentiation process involves stage-specific activation of signaling pathways—such as WNT, TGF-β, and PPARγ—that guide the pluripotent cells through mesodermal and mesenchymal progenitor stages into mature adipocytes. These iPSC-derived adipocytes display hallmark features, including intracellular lipid accumulation, expression of adipogenic transcription factors (PPARγ, C/EBPα), and secretion of key adipokines (adiponectin, leptin).
At Creative Biolabs, we have established a robust and highly reproducible protocol for adipocyte generation from iPSCs. Our platform ensures high differentiation efficiency, phenotypic consistency, and compatibility with downstream applications such as transcriptomic profiling, lipidomics, insulin responsiveness assays, and gene editing.
| Component | Details |
|---|---|
| iPSCs | Maintained under feeder-free conditions |
| Matrigel or vitronectin coating | Basement membrane substrate |
| Medium | Adipogenic differentiation medium |
| Insulin | Promotes lipid accumulation |
| Dexamethasone | Induces adipogenic gene expression |
| IBMX | cAMP phosphodiesterase inhibitor |
| Rosiglitazone | PPARγ agonist |
| B27 Supplement | Supports cell survival and differentiation |
| Oil Red O | Lipid staining reagent |
Culture iPSCs on Matrigel-coated plates in mTeSR1 medium. Ensure cells maintain pluripotency (check markers: OCT4, NANOG). Passage when 80–90% confluent.

Replace medium with mesoderm induction medium. Add WNT activator and BMP4. Incubate for 6 days, changing media daily. Switch to MSC-induction medium containing TGF-β inhibitors. Monitor spindle-shaped morphology development. Confirm MSC-like phenotype via surface markers.

Seed MSC-like cells at ~70% confluency. Replace with adipogenic differentiation medium. Change medium every 2–3 days.

Lipid droplet accumulation: Oil Red O staining.
Gene expression: RT-qPCR for PPARγ, C/EBPα, FABP4.
Immunostaining: Adiponectin, perilipin.
At Creative Biolabs, we implement a multi-tiered QC framework to verify the identity, functionality, and purity of differentiated adipocytes.
| Evaluation Category | Assay Type | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Morphology | Phase-contrast microscopy | Round/polygonal shape with visible lipid droplets |
| Viability | Trypan Blue or AO/PI staining | ≥90% viable cells post-differentiation |
| Lipid Accumulation | Oil Red O, Nile Red, BODIPY staining | >70% cells with neutral lipid content |
| Adipogenic Markers | RT-qPCR, Western blot | Upregulation of PPARγ, FABP4, C/EBPα, AdipoQ |
| Adipokine Secretion | ELISA | Detectable levels of adiponectin, leptin, resistin |
| Functional Response | Insulin-stimulated glucose uptake | Dose-dependent glucose uptake confirming metabolic function |
| Karyotype Stability | G-banding or aCGH | No chromosomal aberrations in parental or differentiated cells |
While the protocol is robust, technical challenges may arise due to biological variability, suboptimal reagents, or procedural inconsistencies. Below is a troubleshooting guide addressing common issues.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low differentiation efficiency | Suboptimal iPSC quality or MSC induction step |
|
| Poor lipid droplet formation | Ineffective induction medium |
|
| Cell detachment or high mortality | Overconfluence or improper seeding density |
|
| Weak expression of adipocyte markers | Insufficient induction duration |
|
| Heterogeneous morphology | Uneven matrix coating or cell seeding |
|
Enhancing the efficiency and reproducibility of adipocyte differentiation can be achieved through several critical optimization strategies.
As a pioneer in stem cell differentiation and metabolic disease modeling, Creative Biolabs offers a suite of integrated services to support your adipocyte research pipeline.
Reprogramming of patient-derived somatic cells into high-quality iPSCs
Full-process iPSC-to-adipocyte differentiation with QC documentation
Knock-in/knock-out of adipogenesis-related genes for disease modeling or target validation
Multiplex profiling of secreted factors including adiponectin, leptin, and resistin
Our team provides end-to-end support, from cell line selection to data interpretation, ensuring your adipogenesis project is successful and scientifically impactful.
References
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.