The human blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a highly specialized interface that regulates molecular traffic between the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral circulation. At the core of this barrier lie brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs), which possess tight junctions, polarized transporters, and low transcytosis activity. Deriving BBB endothelial cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) offers a renewable and patient-specific platform for modeling neurological diseases, drug screening, and studying BBB physiology.
At Creative Biolabs, we have optimized a robust, scalable, and reproducible protocol for the generation of functional BBB endothelial cells from iPSCs.
The generation of BBB endothelial cells from iPSCs represents a major breakthrough in in vitro modeling of the CNS. This differentiation process is typically accomplished through a series of well-orchestrated developmental stages that mimic early embryogenesis, including mesodermal induction, endothelial commitment, and subsequent BBB-specific maturation. The key to success lies in the precise timing and concentration of signaling cues such as BMP4, Activin A, VEGF, retinoic acid, and cAMP analogs, as well as in the use of defined extracellular matrix substrates that support endothelial morphogenesis and barrier assembly.
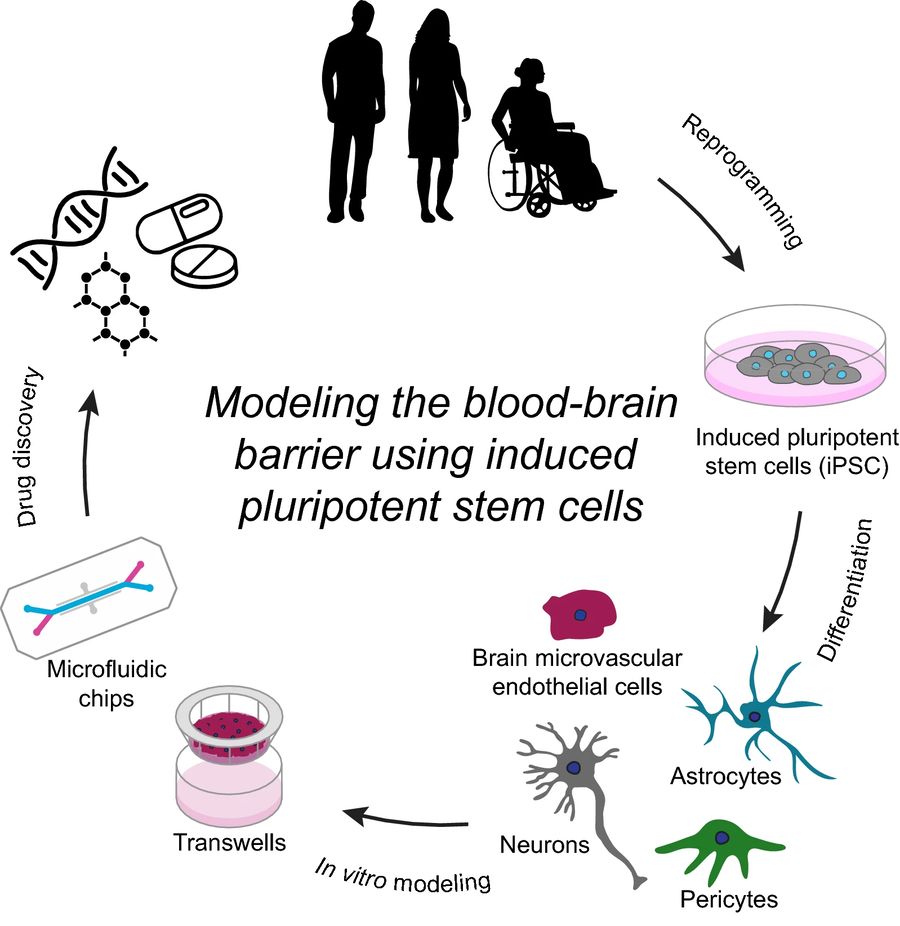 Fig.1 Overview of modeling the BBB using iPSC.1,2
Fig.1 Overview of modeling the BBB using iPSC.1,2
This approach has opened the door to diverse applications, including modeling of neurodegenerative and neuroinflammatory diseases, studying CNS drug permeability, evaluating gene therapy vectors, and assessing nanoparticle translocation across the BBB. Furthermore, iPSC technology enables the generation of BBB cells from patients with genetic conditions or specific mutations, providing a highly personalized platform for disease modeling and precision medicine.
At Creative Biolabs, we have refined this process into a standardized, scalable workflow that consistently yields cells expressing hallmark BBB markers.
| Category | Reagents |
|---|---|
| iPSC culture | Matrigel, mTeSR1 medium, ROCK inhibitor |
| Differentiation | BMP4, Activin A, bFGF, VEGF-A, Retinoic Acid |
| Endothelial maturation | cAMP analogs, hydrocortisone, astrocyte-conditioned medium (optional) |
| ECM coating | Collagen IV, Fibronectin |
| Assays | TEER measurement system, FITC-dextran permeability kit, Immunofluorescence antibodies (CD31, ZO-1, Claudin-5) |
Plate iPSCs on Matrigel-coated plates in mTeSR1 with ROCK inhibitor for the first 24 hours. Refresh media daily. Monitor confluency until 70–80% is reached for differentiation initiation.

Commit iPSCs toward mesoderm lineage using a BMP4- and Activin A-based cocktail. Medium: DMEM/F12 + BMP4 + Activin A + bFGF. Replace iPSC medium with mesodermal induction medium. Incubate for 48 hours, changing media every 24 hours.

Drive mesoderm cells toward endothelial lineage using VEGF-A and bFGF. Medium: EGM-2 + VEGF-A + bFGF. Plate cells on collagen IV + fibronectin-coated plates. Change media daily. By Day 6, cells express CD31 and VE-cadherin.

Functionalize endothelial cells with BBB-specific properties including tight junctions and selective permeability. BBB induction medium: EGM-2 + Retinoic Acid + 8-Br-cAMP + hydrocortisone. Plate on Transwells pre-coated with collagen IV and fibronectin. Culture for 4–6 days.
We employ a comprehensive quality control (QC) framework combining phenotypic, functional, and molecular characterization methods to confirm BBB-specific endothelial differentiation and to verify model reproducibility across batches.
| Assay Type | Method | Key Readouts |
|---|---|---|
| Immunostaining | IF for CD31, ZO-1, Claudin-5 | Tight junction and endothelial identity |
| qPCR | Gene expression of SLC2A1, ABCB1 | Transporter profile |
| TEER | Electrical resistance across monolayer | Integrity & tightness |
| Permeability | FITC-dextran or sodium fluorescein | Paracellular leakage |
| Transport Assays | P-gp efflux activity | BBB efflux capability |
Ensuring the identity, purity, functionality, and barrier integrity of iPSC-derived BBB endothelial cells is critical for their downstream application in disease modeling, drug screening, and neurovascular research. Creative Biolabs offers optional validation reports for each batch of BBB endothelial cells, tailored to your specific application.
Despite the robustness of the iPSC-to-BBB endothelial differentiation protocol, minor variations in cell quality, reagent freshness, or culture conditions may affect the outcome. Below is a comprehensive troubleshooting guide to help researchers identify and resolve common issues, as well as best practices to fine-tune performance for high-end applications.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low differentiation efficiency | Overconfluent or unhealthy iPSCs; suboptimal mesoderm induction |
|
| Cells detach during transition to endothelial stage | ECM coating insufficient or uneven |
|
| Poor expression of tight junction markers | Incomplete maturation; lack of supporting signals |
|
| TEER remains low or unstable | Inconsistent seeding density or cell stress |
|
| High FITC-dextran leakage | Monolayer disruption or weak junctions |
|
| Batch variability | Cell line differences; reagent lot inconsistencies |
|
Creative Biolabs is here to help troubleshoot, customize, and scale your project with confidence. By integrating these troubleshooting and optimization strategies, researchers can achieve a highly reproducible and physiologically relevant in vitro BBB model.
Creative Biolabs offers an integrated suite of services tailored for researchers working on neurovascular biology, CNS drug delivery, and BBB modeling. Whether you need fully differentiated BBB endothelial cells, customized iPSC lines, or functional assays, our solutions cover the entire discovery-to-validation continuum.
Tailored differentiation into endothelial cells, astrocytes, pericytes, and neurons with lineage-specific protocols. Assembly of multi-cellular BBB models using iPSC-derived endothelial cells, astrocytes, and pericytes to mimic in vivo architecture.
CRISPR editing, karyotyping, and expansion of patient-specific or disease-modeling iPSC lines.
We understand that no two BBB modeling projects are alike. Our expert PhD-level team is available for:
At Creative Biolabs, we don't just provide protocols—we partner in your discovery. Whether you're building a BBB model from scratch or scaling up for high-throughput screening, our team of stem cell specialists is ready to support your goals with tailored, end-to-end solutions.
Ready to accelerate your CNS research? Contact us for a custom quote or consultation today.
References
Created July 2025
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.