As a global leader in iPSC-based research services, Creative Biolabs offers state-of-the-art solutions for hematopoietic lineage differentiation. This protocol outlines a robust, stepwise strategy for the generation of hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs) from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs).
Unlike traditional hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) sources that are limited by donor availability, immunogenicity, and ethical concerns, iPSC-derived HPCs offer a patient-specific, renewable, and highly controllable platform for modeling blood development, screening hematopoietic disorders, and evaluating candidate therapeutics in vitro.
Mimicking embryonic hematopoiesis through stepwise differentiation, this protocol guides pluripotent cells through mesoderm specification and hematopoietic induction using tightly timed cytokine cocktails and defined culture conditions. The method reliably produces CD34⁺/CD43⁺ progenitor populations with multilineage potential, forming the basis for downstream differentiation into myeloid, erythroid, and lymphoid lineages.
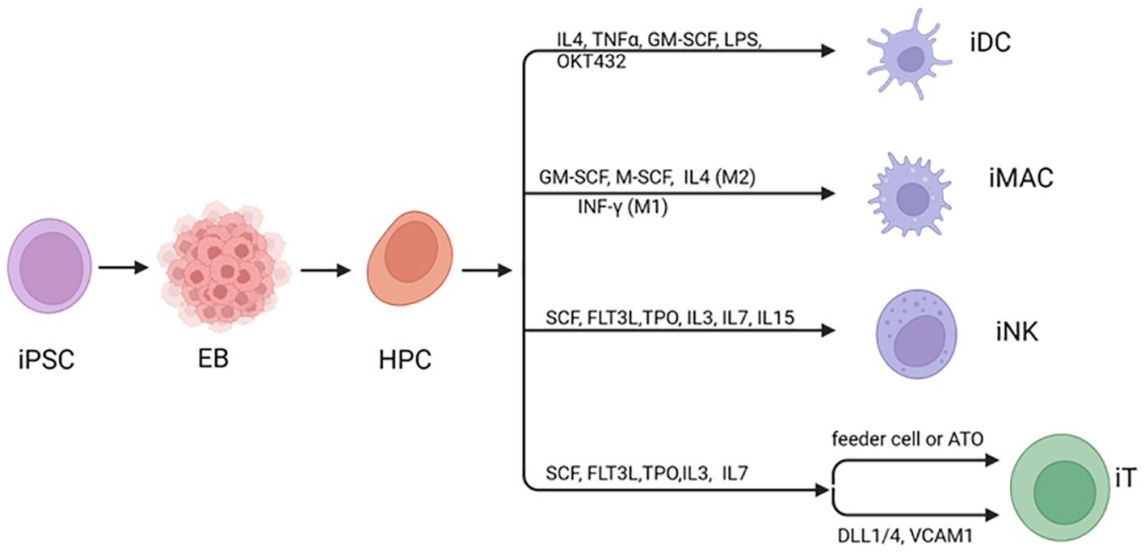 Fig.1 Human iPSC can be induced to differentiate to hematopoietic cells.1,2
Fig.1 Human iPSC can be induced to differentiate to hematopoietic cells.1,2
At Creative Biolabs, our stem cell division has developed and optimized lineage-specific differentiation protocols using feeder-free, xeno-free systems. Whether you require a ready-to-use HPC population for disease modeling, or wish to integrate HPC generation into a custom screening platform, our services offer:
Below is the list of recommended materials and reagents used throughout the protocol.
| Item | Specification |
|---|---|
| iPSC lines | Pluripotent, feeder-free, karyotypically normal |
| Medium | Chemically defined, feeder-free medium |
| Accutase | Gentle enzymatic detachment |
| ROCK Inhibitor | For enhancing survival |
| Cytokine | BMP4, VEGF-165, FGF2, stem cell factor, IL-3, IL-6, TPO, Flt3 ligand |
| Flow Cytometry Antibody | Anti-CD34, CD43, CD45 antibody |
Coat plates with Matrigel or Vitronectin and incubate for at least 1 hour at room temperature. Thaw or expand iPSCs in medium until they reach ~70–80% confluence. Prior to differentiation, treat with ROCK inhibitor for 1 hour to enhance survival during passaging. Dissociate iPSCs into small clumps using Accutase, avoiding full single-cell dissociation.

Seed iPSC aggregates into low-attachment plates in medium. Incubate for 2 days, replacing medium daily. This stage primes iPSCs toward mesoderm.

Switch to Hematopoietic Specification Medium. Continue culturing in low-attachment plates with the cytokines. Maintain for 3–4 days, gently swirling every 24 hours to prevent cell clumping.

Transfer suspension cells to fresh low-attachment plates with hematopoietic maturation medium. Monitor morphology and perform flow cytometry at Day 10–12 for CD34⁺, CD43⁺, and CD45⁺ markers.
At Creative Biolabs, rigorous quality control (QC) is integrated into each stage of the iPSC-to-HPC workflow to ensure reproducibility, functional relevance, and compatibility with downstream applications. Comprehensive phenotypic and functional assays are employed to verify cell identity, purity, and differentiation potential.
| Marker | Description | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| CD34⁺ | Hematopoietic stem and progenitor marker | High expression confirms progenitor identity |
| CD43⁺ | Marker of early hematopoietic commitment | Indicates transition from mesoderm to hematopoietic fate |
| CD45⁺ | Pan-leukocyte marker | Expressed at later maturation stages |
Cells are seeded into methylcellulose-based semi-solid media to assess their capacity to form hematopoietic colonies.
qRT-PCR is performed to evaluate transcriptional activation of key hematopoietic regulators.
Daily microscopy allows evaluation of embryoid body (EB) integrity, cell aggregation, and emergence of round, refractile HPC-like cells in suspension.
Efficient differentiation depends on precise control of multiple parameters. The following table outlines common issues, potential causes, and recommended solutions.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low CD34⁺ yield | Suboptimal cytokine activity or timing |
|
| Excessive cell death post-seeding | Incomplete ROCK inhibitor pre-treatment |
|
| Heterogeneous colony morphology | Inconsistent EB formation or plating density |
|
| Poor mesoderm induction | BMP4 or VEGF degradation |
|
| Loss of iPSC pluripotency | Over-confluence or late passage |
|
Drawing from over two decades of experience, Creative Biolabs provides the following expert recommendations to improve outcomes and minimize variation.
Creative Biolabs is committed to delivering precision-engineered solutions for your stem cell research and drug discovery needs. We provide a comprehensive suite of services designed to support the full translational research pipeline.
Tailored differentiation into hematopoietic, neural, cardiac, and other lineages
From somatic cell reprogramming to pluripotency and genomic validation
iPSC production for cell-based research and preclinical pipelines
Partner with us to accelerate your project with confidence.
Reference
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.