Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is one of the hallmark enzymes used to evaluate the differentiation state and pluripotency of stem cells. As an early marker of osteogenic differentiation, ALP activity correlates with mineralization potential and serves as a practical readout in both basic stem cell research and applied therapeutic development.
At Creative Biolabs, we design and deliver reliable, reproducible, and customizable ALP activity assay protocols tailored for diverse stem cell models. This protocol provides a step-by-step guide to performing ALP assays in stem cells.
ALP is a hydrolytic enzyme that catalyzes the removal of phosphate groups from phosphate esters under alkaline conditions. This activity plays a central role in biomineralization, where ALP provides inorganic phosphate for hydroxyapatite crystal formation. Because of this function, ALP has become a key biomarker in stem cell biology. Its expression is strongly associated with pluripotency and is upregulated during osteogenic differentiation.
The assay principle relies on providing ALP with an artificial substrate that can be easily detected after enzymatic cleavage. Depending on the research objective, the readout may be colorimetric, fluorometric, or histochemical.
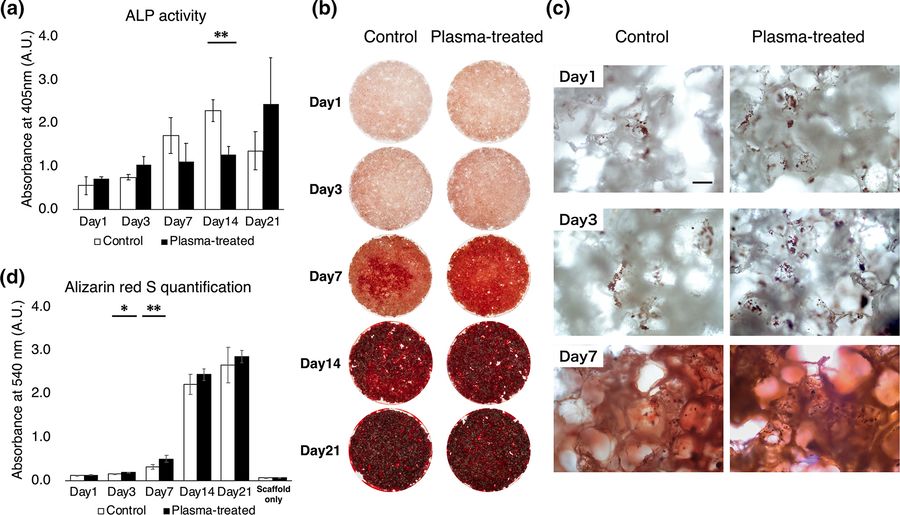 Fig.1 ALP activity of bone marrow stem cells.1,2
Fig.1 ALP activity of bone marrow stem cells.1,2
Our ALP assay platforms integrate precision detection technologies with tailored assay design. By offering multiple detection modes, we ensure that clients obtain the most relevant and reproducible data for their specific research goals.
| Category | Reagents |
|---|---|
| Stem Cell Culture |
Human or murine stem cell lines (ESCs, iPSCs, or MSCs) Differentiation media (osteogenic or other lineage-specific induction medium) Basal medium (DMEM, RPMI, or equivalent) Fetal bovine serum (FBS), growth factors, supplements |
| Assay Reagents |
pNPP substrate solution ALP buffer Stop solution ELF-97 phosphatase substrate BCIP/NBT staining solution |
| Controls |
Positive control: ALP-rich osteoblasts or commercial ALP enzyme standard Negative control: undifferentiated fibroblasts or ALP inhibitor-treated cells |
Seed stem cells at optimal density. Allow cells to adhere overnight in complete growth medium. For osteogenic differentiation assays, replace with induction medium containing ascorbic acid, β-glycerophosphate, and dexamethasone. Maintain cultures for 7–21 days, changing medium every 2–3 days.

Use the colorimetric assay (pNPP method), fluorescent assay (ELF-97 method), or histochemical staining (BCIP/NBT method).

Normalize ALP activity to total protein content. Alternatively, normalize to DNA content for more precise cell number adjustment. Include negative controls (substrate only, no cells) to correct for background absorbance. Positive control enzyme standards allow calibration and cross-experiment comparison.

Plot absorbance (OD405) or fluorescence intensity versus time. Calculate relative activity (fold increase vs control). Perform statistical analysis (ANOVA, Student's t-test) to evaluate significance.
At Creative Biolabs, we routinely refine assay conditions for our partners to ensure reproducibility, sensitivity, and scalability.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low signal |
|
|
| Excessively high signal |
|
|
| High background absorbance/fluorescence |
|
|
| Uneven staining (Histochemical assay) |
|
|
| Poor correlation with mineralization data |
|
|
Our experts employ advanced troubleshooting and assay optimization workflows, such as:
We understand that the ALP activity assay is only one step in a much broader workflow of stem cell research and development. To provide clients with end-to-end support, we have developed a comprehensive suite of related services that seamlessly integrate with ALP testing.
Our services offer a comprehensive repertoire of features to ensure your iPSCs are properly characterized, ensuring their pluripotency and usability in different research contexts.
Generation of high-quality human iPSCs from somatic cells using non-integrative methods.
We have extensive expertise in iPSC differentiation and can provide the most flexible, adaptable, and customizable solutions for your project. Different cell types are available, such as hepatocytes, cardiomyocytes, and neural cells.
Gene knock-out, knock-in, or correction services for iPSC lines using precise strategies with clone validation.
Interested in integrating ALP activity assay into your neurobiology workflow? Let our experts help you build a solution tailored to your research questions.
A: For quantitative data, pNPP colorimetric assays are standard. For higher sensitivity, ELF-97 fluorescence is recommended. For qualitative colony analysis, BCIP/NBT staining is ideal.
A: With proper normalization and optimized protocols, reproducibility is high. Creative Biolabs validates all assays with control cell lines to ensure cross-line consistency.
A: Yes, fluorometric substrates like ELF-97 allow live-cell staining while maintaining cell viability. This enables researchers to track differentiation in real time and conduct downstream assays on the same culture. Creative Biolabs offers optimized live-cell ALP detection formats for labs requiring non-destructive monitoring.
A: Typical issues include weak signals, high background noise, and batch-to-batch variability. These problems can stem from substrate degradation, inconsistent differentiation induction, or improper washing steps. Our experts at Creative Biolabs troubleshoot and optimize every step, from substrate choice to culture conditions, to deliver reliable data packages.
References
Created August 2025
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.