Osteoblasts are specialized mesenchymal cells responsible for bone formation, playing a pivotal role in skeletal development, remodeling, and repair. Human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) offer a powerful platform for generating osteoblasts in vitro, enabling scalable production of osteogenic cells for disease modeling and drug screening.
At Creative Biolabs, we have developed a robust, chemically defined protocol to generate functional osteoblasts from iPSCs. This protocol ensures high yield, phenotypic fidelity, and compatibility with downstream applications.
Osteoblasts arise primarily from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which are multipotent progenitors capable of differentiating into osteoblasts, chondrocytes, adipocytes, and other cell types. During development and adulthood, osteoblasts can originate from various sources. In adult bones, BMSCs near blood vessels serve as important skeletal progenitor cells that contribute to osteoblast formation during bone remodeling.
The in vitro generation of osteoblasts from iPSCs offers a powerful platform to study skeletal development and design therapies. This differentiation process recapitulates key developmental stages observed in embryogenesis—transitioning from pluripotent stem cells to mesodermal progenitors, then to MSC-like intermediates, and ultimately to mature osteoblasts.
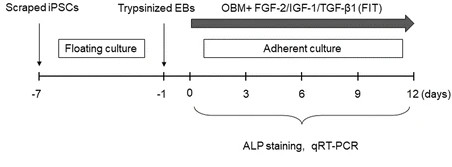 Fig.1 Schedule of osteogenic differentiation.1,2
Fig.1 Schedule of osteogenic differentiation.1,2
The ability to derive functional osteoblasts from iPSCs opens new horizons for bone biology and regenerative medicine. At Creative Biolabs, we provide not only a robust differentiation protocol but also fully integrated services tailored to your application, whether academic, pharmaceutical, or translational.
| Component | Details |
|---|---|
| iPSC lines | Validated, karyotypically normal |
| Matrigel or vitronectin | For coating |
| Medium | Feeder-free iPSC culture medium |
| Mesoderm induction reagents | RPMI 1640 + B27 supplement, Activin A, BMP4, CHIR99021 |
| MSC-like induction reagents | DMEM/F12 + FBS, FGF2, PDGF-BB, SB431542 |
| Osteoblast induction reagents | α-MEM + FBS, Ascorbic acid, β-Glycerophosphate, Dexamethasone |
Culture iPSCs on Matrigel-coated plates in medium. Passage at 80–90% confluency using EDTA and supplement with ROCK inhibitor for 24 hours post-passage. Ensure high viability and uniform colonies before starting differentiation.

Replace iPSC medium with RPMI 1640 + B27 minus insulin. Add Activin A, BMP4, and CHIR99021 to initiate mesoderm induction. Change medium every 24 hours for 4 days. Monitor morphology: cells will spread and elongate.

Switch to DMEM/F12 supplemented with 10% FBS, FGF2, PDGF-BB, and SB431542. Feed cells every other day. Cells acquire spindle-shaped MSC-like morphology. Confirm MSC markers (CD73+, CD90+, CD105+, CD34–, CD45–) via flow cytometry.

Change medium to osteogenic induction media (α-MEM + 10% FBS + osteogenic supplements). Maintain culture for 14–21 days. Replace medium every 2–3 days. Cells will exhibit cuboidal morphology and begin mineralizing matrix.
A successful iPSC-to-osteoblast differentiation process hinges on precise timing, consistent culture conditions, and responsive monitoring. Below, Creative Biolabs shares its expert-derived troubleshooting insights and optimization strategies.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low mesoderm induction efficiency | Suboptimal cell density, degraded growth factors, inefficient Wnt/BMP activation |
|
| Poor MSC-like cell transition | Inadequate medium exchange, contaminating feeder cells or debris, incomplete mesoderm induction |
|
| Low ALP or mineralization signal | Insufficient osteogenic stimulation, cell stress or passage-induced senescence, incorrect media composition |
|
| High cell death during transition | Harsh enzymatic dissociation, osmotic shock, media pH drift |
|
| Inconsistent differentiation across batches | Lot-to-lot variability in FBS, uncontrolled incubation conditions, inaccurate reagent pipetting |
|
Optimization Tips
Creative Biolabs is proud to offer a full spectrum of customized solutions to support your osteoblast-related research and development, from iPSC generation to osteogenic validation and application-specific optimization.
Reprogramming of somatic cells into integration-free, karyotypically stable iPSC lines.
Precise knock-in/knock-out of osteogenic genes (e.g., RUNX2, ALPL)
End-to-end protocol implementation to generate mature, mineralizing osteoblasts from any human iPSC line.
With cutting-edge facilities, experienced stem cell biologists, and translational know-how, Creative Biolabs is your trusted partner for generating, characterizing, and applying iPSC-derived osteoblasts. We invite you to explore our service suite or contact our experts to begin a customized journey toward high-impact skeletal research and innovation.
References
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.