Glycans in Immunity
As an irreplaceable global leader in glycan research, Creative Biolabs provides diversified and high-quality glycan analysis services to meet customers’ needs.
The effects of glycans on biology are complicated and diverse. In the immune system, glycans or glycoconjugates are involved in most immune functions. In fact, all cell surface receptors are glycoproteins. In addition, the glycosylation of antibodies also has a profound effect on antibody function, and changes in glycan structure are also related to inflammation and infection. Therefore, glycans are regarded as the core of a functioning immune system. Broadly speaking, pathways that influence the structure and activity of glycans will have an impact on immunity.
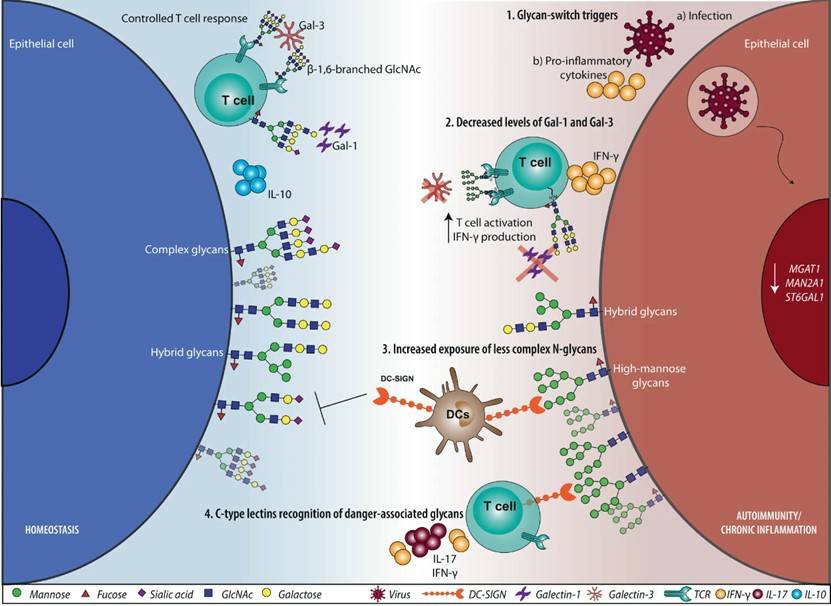 Fig.1 Glycan and glycan-binding protein-mediated immune network.1
Fig.1 Glycan and glycan-binding protein-mediated immune network.1
Direct Effects of Glycans on Immunity
Cell surface glycosylation is ubiquitous in all living cells and is positioned to mediate the process of immune recognition. A well-known example is the selectin family of surface proteins mainly found on white blood cells, which bind to endothelin near the site of infection or inflammation and can penetrate tissues. In invertebrates, glycans are usually terminated with sialic acid. Sialic acid is a normal self-marker and can be recognized by various receptors that mediate intercellular and intracellular communication.
Indirect Effects of Glycans on Immunity
In addition to the recognition function, glycans can indirectly reduce or prevent the attachment of microorganisms and cell entry. Many epithelial cells are coated with mucins. Based on the malleability of mucins, microorganisms in the external world can form a viscous physical barrier with potential epithelial cells in the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts to prevent harmful substances. Additionally, the indirect effects of glycans on immunoglobulins also affect the signal transduction of immune cell Fc receptors.
Other Effects of Glycans
In recent years, there has been an increased interest in the regulatory functions of glycans for molecules and cells. The specific glycosylation pattern is the basis of the normal activities of numerous immune molecules. Glycans play an important role in regulating antibody function and immune signal cascade. Moreover, changes in glycosylation patterns may lead to impaired protein expression, changes in protein ligand functions, and significant changes in immune pathway signals.
Altered Glycosylation in Clinical Immunology
Protein glycosylation is an epigenetic modification process that has received a lot of attention, which affects the expression and function of many proteins required for normal immune function. It is worth noting that mutations in genes that affect the glycosylation immune signaling pathway can lead to diseases. In addition, recessive mutations in genes responsible for protein glycosylation can cause congenital glycosylation disorders and may have immunological effects.
Creative Biolabs is confident to provide first-class glycan detection services based on our excellent platform, aiming to help our customers carry out glycan related structure and function research. If you have difficulties in glycan research, please contact us for help.
Reference
-
Pinho, Salomé S., et al. "Immune regulatory networks coordinated by glycans and glycan-binding proteins in autoimmunity and infection." Cellular & Molecular Immunology 20.10 (2023): 1101-1113. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Resources

 Fig.1 Glycan and glycan-binding protein-mediated immune network.1
Fig.1 Glycan and glycan-binding protein-mediated immune network.1

