Creative Biolabs has a tradition of commitment. To achieve efficient execution and regulatory approval, we offer careful considerations of your program for the development of a cellular or gene therapy product – now and in the future.
EXPLORE MORE HighlightsWe focus on unmet needs and develop novel cellular and gene drugs and solutions that offer significant benefits over existing options.
EXPLORE MORE HighlightsThe advent of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapies has revolutionized the field of oncology, providing new avenues for treating various forms of cancer. Our 20 years of experience in the biotechnology sector have equipped us with the expertise and technological capabilities to support the entire lifecycle of CAR-T products, from early development to commercialization.
EXPLORE MORETo accelerate advanced breakthroughs of your projects, we offer broad range of platforms which enable our clients be free to tackle problems with cutting-edge technologies from different angles and in different methods.
EXPLORE MORE HighlightsUse the resources in our library to help you understand your options and make critical decisions for your study. We offer oncolytic virus, CAR-T, and dendritic cell related documents, as well as newsletter. If you don't find the answers you're looking for, contact us for additional assistance.
EXPLORE MORE HighlightsGet a real taste and understanding of the business and culture of one of the world's great research-based cellular and gene therapy discovery and development companies.
EXPLORE MOREAll products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
Creative Biolabs is your trusted partner for anti-GD2 CAR-T therapy development. We provide a comprehensive range of products, such as anti-GD2 vectors, cells, and viral particles. Our team understands each researcher's needs and we also offer customized CAR-T cell development services tailored to your specific requirements.
GD2 is known as ganglioside G2 or GRD2, which is used as a target for immunotherapy in patients with malignant melanoma and neuroblastoma. This protein is expressed on tumors of neuroectodermal origin, including human neuroblastoma and melanoma, with highly restricted expression on normal tissues. Therefore, GD2 is associated with human neuroblastoma and melanoma. GD2-targeted immunotherapy has shown promising results in clinical trials for the treatment of melanoma and neuroblastoma patients.
Human neuroblastoma
Anti-GD2 CAR-T Expression Test
The anti-GD2 CAR-T expression test is designed to monitor the expression of the anti-GD2 CAR-T receptor and its components in T cells. At Creative Biolabs, we utilize diverse detection techniques such as flow cytometry, western blotting, and QPCR to analyze CAR expression.
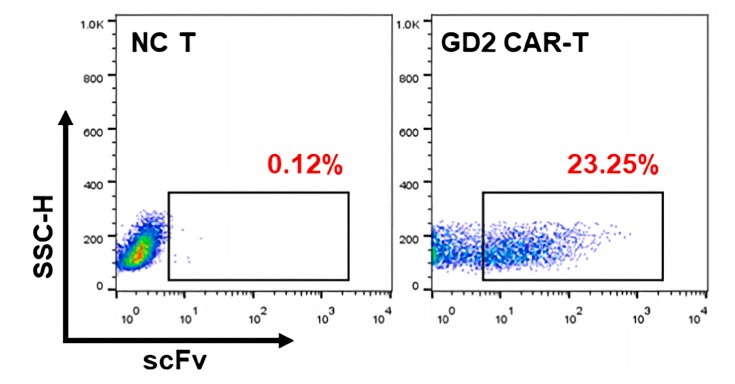 Fig.1 Flow cytometry analysis of cell-surface expression of anti-GD2-CAR on transduced T cells.1
Fig.1 Flow cytometry analysis of cell-surface expression of anti-GD2-CAR on transduced T cells.1
Anti-GD2 CAR-T Cytokine Release Test
Our comprehensive cytokine release test services detect a wide range of cytokines, including IL-2, TNF-α, and IFN-γ. There are several techniques available for quantifying the levels of released cytokines including ELISAs, ELISPOT, and multiplex bead array.
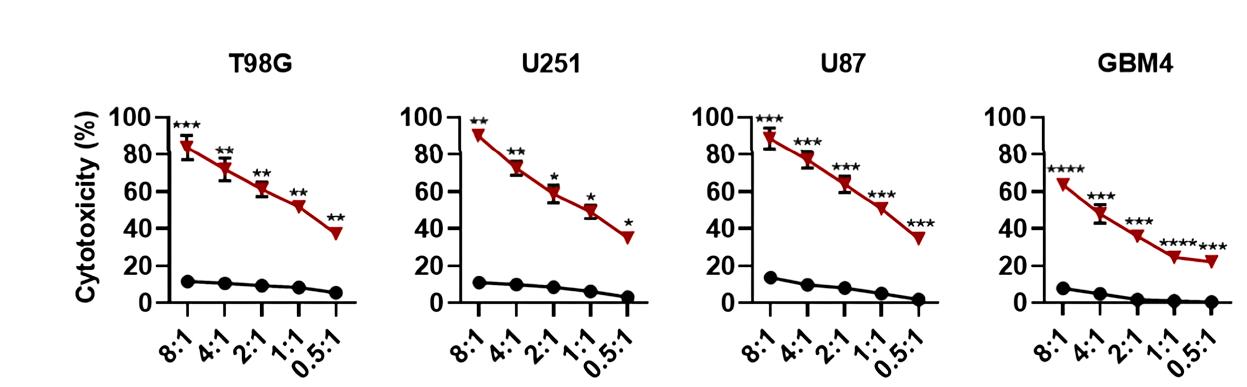 Fig.2 ELISA analysis of cytokine release (IFN-γ and TNF-α) in GD2 CAR-T cells co-cultured with various glioblastoma cell lines.1
Fig.2 ELISA analysis of cytokine release (IFN-γ and TNF-α) in GD2 CAR-T cells co-cultured with various glioblastoma cell lines.1
Anti-GD2 CAR-T In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
We provide CAR-T cytotoxicity assays that enable researchers to determine the efficiency of anti-GD2 CAR-T cells in targeting and eliminating cancer cells expressing GD2.
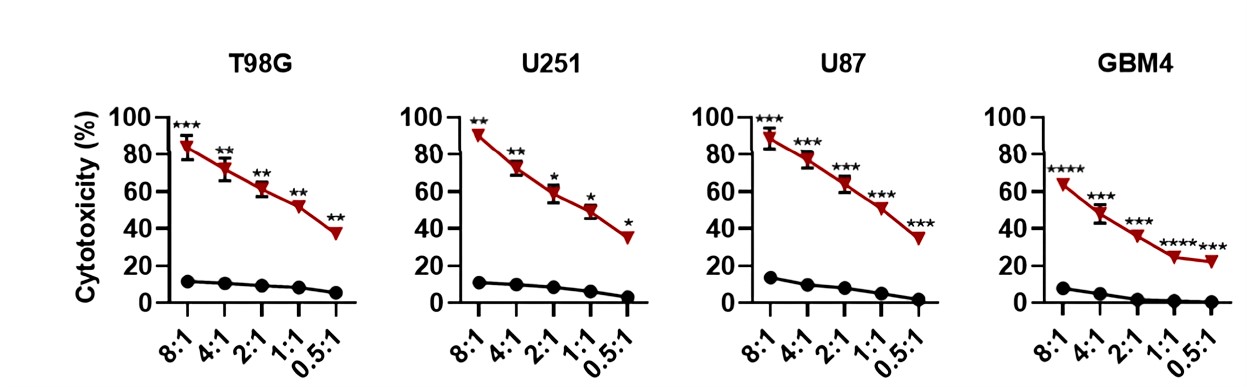 Fig.3 The cytotoxicity of anti-GD2 CAR-T against various glioblastoma cell lines. GD2 CAR-T cells exhibited antigen-specific cytotoxicity against GD2+ glioblastoma cells.1
Fig.3 The cytotoxicity of anti-GD2 CAR-T against various glioblastoma cell lines. GD2 CAR-T cells exhibited antigen-specific cytotoxicity against GD2+ glioblastoma cells.1
Anti-GD2 CAR-T Cell Therapy Animal Models
We offer in vivo anti-GD2 CAR-T cell therapy testing services in animal models. Our animal models, including xenograft, humanized, syngeneic, and transgenic models, enable researchers to assess the therapeutic efficacy and safety of CAR-T cell therapies in vivo.
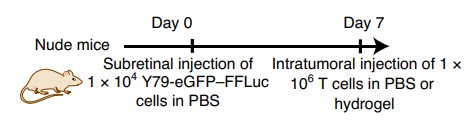 Fig.4 A schematic of in situ xenograft nude mouse model.2
Fig.4 A schematic of in situ xenograft nude mouse model.2
Efficacy Test of Anti-GD2 CAR-T
Creative Biolabs provide in vivo assays to test GD2 CAR-T cell efficacy and safety. These assays allow us to evaluate the ability of CAR-T cells to target and eliminate tumor cells, providing crucial information for assessing the efficacy of GD2 CAR-T cell therapy.
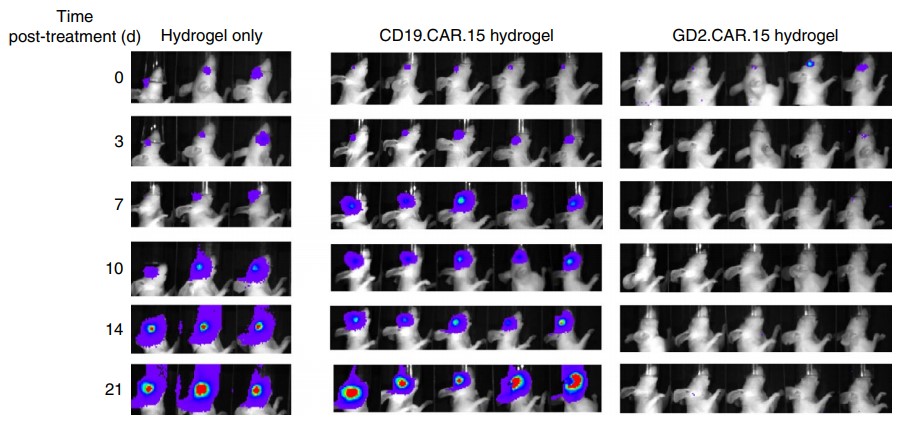 Fig.5 In vivo evaluation of the antitumor activity of anti-GD2 CAR-T. The results showed that GD2 CAR-T cells specifically eliminated tumors as measured by either bioluminescence (BLI).2
Fig.5 In vivo evaluation of the antitumor activity of anti-GD2 CAR-T. The results showed that GD2 CAR-T cells specifically eliminated tumors as measured by either bioluminescence (BLI).2
Toxicity Evaluation Anti-GD2 CAR-T
Furthermore, we recognize the importance of understanding the immune response generated by the anti-GD2 CAR T cell therapy. Therefore, we offer in vivo toxicity study services. These studies help to characterize potential side effects of the anti-GD2 CAR T cell therapy.
References
 Loading...
Loading...
| CAT | Product Name | Target Species | Antibody Clone | Antibody Host | Receptor Construction | Vector Type | Targeting Cell Type | CAR Vector Type | Inquiry & Datasheet |
| CAR-YF108 | Anti-GD2 (CBL-YF036) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBL-YF036 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CAR-YF109 | Anti-GD2 (CBL-YF036) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBL-YF036 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CAR-YF203 | Anti-GD2 (3F8) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 3F8 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CAR-YF204 | Anti-GD2 (3F8) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 3F8 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CAR-YF205 | Anti-GD2 (h3F8) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | h3F8 | Humanized | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CAR-YF206 | Anti-GD2 (h3F8) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | h3F8 | Humanized | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CAR-YF207 | Anti-GD2 (CBL-YF063) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBL-YF063 | Human | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CAR-YF208 | Anti-GD2 (CBL-YF063) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | CBL-YF063 | Human | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CAR-YF209 | Anti-GD2 (KM666) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | KM666 | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CAR-YF210 | Anti-GD2 (KM666) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | KM666 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CAR-YF211 | Anti-GD2 (hKM666) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | hKM666 | Humanized | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CAR-YF212 | Anti-GD2 (hKM666) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | hKM666 | Humanized | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CAR-ZP017 | Anti-GD2 (8TMBBZ.2bg.150A) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 8TMBBZ.2bg.150A | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CAR-ZP043 | Anti-GD2 (8TMBBZ.2bg.150A) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 8TMBBZ.2bg.150A | Mouse | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CAR-ZP4249 | Anti-GD2 (7A4) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 7A4 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CAR-ZP4250 | Anti-GD2 (7A4) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 7A4 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CAR-ZP4251 | Anti-GD2 (ME36.1) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | ME36.1 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CAR-ZP4252 | Anti-GD2 (ME36.1) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | ME36.1 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CAR-ZP4253 | Anti-GD2 (5F11) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 5F11 | Mouse | scFv-CD28-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CAR-ZP4254 | Anti-GD2 (5F11) h(41BB-CD3ζ) CAR, pCDCAR1 | Human | 5F11 | Mouse | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Lentiviral vector | T cell | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CAT | Product Name | Target Species | Antibody Clone | Fab-Host Animal | Vector Type | Targeting Cell Type | Inquiry & Datasheet |
| XS-0722-ZP3811 | Anti-GD2 X CD3 BsAb Secreting T Cell Redirecting Vector (GD2xCD3) | Human | T Cells | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CAT | Product Name | Host Cell Type | Target | scFv Clone | CAR Construction | CAR Cell Type | Inquiry & Datasheet |
| CARJ-ZP461 | Anti-GD2 (hu14.18K322A) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, Jurkat Cell | T lymphocyte | GD2 | hu14.18K322A | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CARJ-ZP462 | Anti-GD2 (hu14.18K322A) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, Jurkat Cell | T lymphocyte | GD2 | hu14.18K322A | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CARJ-ZP463 | Anti-GD2 (TAB-078CQ) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, Jurkat Cell | T lymphocyte | GD2 | TAB-078CQ | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CARJ-ZP464 | Anti-GD2 (TAB-078CQ) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, Jurkat Cell | T lymphocyte | GD2 | TAB-078CQ | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CARJ-ZP465 | Anti-GD2 (TAB-077CQ) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, Jurkat Cell | T lymphocyte | GD2 | TAB-077CQ | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CARJ-ZP466 | Anti-GD2 (TAB-077CQ) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, Jurkat Cell | T lymphocyte | GD2 | TAB-077CQ | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CARJ-ZP467 | Anti-GD2 (TAB-076CQ) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, Jurkat Cell | T lymphocyte | GD2 | TAB-076CQ | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CARJ-ZP468 | Anti-GD2 (TAB-076CQ) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, Jurkat Cell | T lymphocyte | GD2 | TAB-076CQ | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CARJ-ZP469 | Anti-GD2 (TAB-075CQ) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR, Jurkat Cell | T lymphocyte | GD2 | TAB-075CQ | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| CARJ-ZP470 | Anti-GD2 (TAB-075CQ) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR, Jurkat Cell | T lymphocyte | GD2 | TAB-075CQ | scFv-41BB-CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| XS-0722-ZP2068 | Anti-GD2 (XP808) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR-Treg Cells | CAR-Treg Cells | GD2 | XP808 | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| XS-0722-ZP2069 | Anti-GD2 (XP809) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR-Treg Cells | CAR-Treg Cells | GD2 | XP809 | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| XS-0722-ZP3183 | Anti-GD2 (XP228) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) TSCM CAR-T Cells | TSCM CAR-T Cells | GD2 | XP228 | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| XS-0722-ZP3184 | Anti-GD2 (XP229) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) TSCM CAR-T Cells | TSCM CAR-T Cells | GD2 | XP229 | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| XS-0722-ZP3185 | Anti-GD2 (XP230) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) TSCM CAR-T Cells | TSCM CAR-T Cells | GD2 | XP230 | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| XS-0722-ZP3186 | Anti-GD2 (XP231) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) TSCM CAR-T Cells | TSCM CAR-T Cells | GD2 | XP231 | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| XS-0722-ZP3187 | Anti-GD2 (XP232) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) TSCM CAR-T Cells | TSCM CAR-T Cells | GD2 | XP232 | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| XS-0722-ZP3464 | Anti-GD2 (XP509) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) TSCM CAR-T Cells | TSCM CAR-T Cells | GD2 | XP509 | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| XS-0722-ZP3623 | Anti-GD2 (XP668) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) TSCM CAR-T Cells | TSCM CAR-T Cells | GD2 | XP668 | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet | |
| XS-0722-ZP3710 | Anti-GD2 (XP755) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) TSCM CAR-T Cells | TSCM CAR-T Cells | GD2 | XP755 | scFv-4-1BB-CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CAT | Product Name | Target Species | Antibody Clone | Host | Hinge | TM | ICD | Inquiry & Datasheet |
| CARMA-W2305 | Anti-GD2 (14G2a) ICD(CD147) CAR-MA Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | 14G2a | Mouse | IgG1 | CD147 | CD147 | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARMA-W2306 | Anti-GD2 (14G2a) ICD(CD86+FcγRI) CAR-MA Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | 14G2a | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | CD86+FcγRI | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARMA-W2312 | Anti-GD2 (3F8) ICD(CD86+FcγRI) CAR-MA Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | 3F8 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | CD86+FcγRI | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARMA-W2313 | Anti-GD2 (3F8) ICD(CD3ζ) CAR-MA Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | 3F8 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARMA-W2314 | Anti-GD2 (3F8) ICD(Megf10) CAR-MA Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | 3F8 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | Megf10 | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARMA-W2315 | Anti-GD2 (3F8) ICD(FcRɣ) CAR-MA Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | 3F8 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | FcRɣ | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARMA-W2316 | Anti-GD2 (3F8) ICD(FcRɣ+PI3K) CAR-MA Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | 3F8 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | FcRɣ+PI3K | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARMA-W2317 | Anti-GD2 (ME36.1) ICD(CD147) CAR-MA Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | ME36.1 | Mouse | IgG1 | CD147 | CD147 | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARMA-W2318 | Anti-GD2 (ME36.1) ICD(CD86+FcγRI) CAR-MA Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | ME36.1 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | CD86+FcγRI | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARMA-W2319 | Anti-GD2 (ME36.1) ICD(CD3ζ) CAR-MA Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | ME36.1 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARMA-W2320 | Anti-GD2 (ME36.1) ICD(Megf10) CAR-MA Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | ME36.1 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | Megf10 | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARMA-W2321 | Anti-GD2 (ME36.1) ICD(FcRɣ) CAR-MA Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | ME36.1 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | FcRɣ | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARMA-W2322 | Anti-GD2 (ME36.1) ICD(FcRɣ+PI3K) CAR-MA Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | ME36.1 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | FcRɣ+PI3K | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARMA-W2323 | Anti-GD2 (hu3F8) ICD(CD147) CAR-MA Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | hu3F8 | Humanized | IgG1 | CD147 | CD147 | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARMA-W2324 | Anti-GD2 (hu3F8) ICD(CD86+FcγRI) CAR-MA Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | hu3F8 | Humanized | CD8 | CD8 | CD86+FcγRI | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARMA-W2325 | Anti-GD2 (hu3F8) ICD(CD3ζ) CAR-MA Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | hu3F8 | Humanized | CD8 | CD8 | CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARMA-W2326 | Anti-GD2 (hu3F8) ICD(Megf10) CAR-MA Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | hu3F8 | Humanized | CD8 | CD8 | Megf10 | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARMA-W2327 | Anti-GD2 (hu3F8) ICD(FcRɣ) CAR-MA Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | hu3F8 | Humanized | CD8 | CD8 | FcRɣ | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARMA-W2328 | Anti-GD2 (hu3F8) ICD(FcRɣ+PI3K) CAR-MA Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | hu3F8 | Humanized | CD8 | CD8 | FcRɣ+PI3K | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARMA-W2329 | Anti-GD2 (7A4) ICD(CD147) CAR-MA Plasmid, pCDCAR1 | Human | 7A4 | Mouse | IgG1 | CD147 | CD147 | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CAT | Product Name | Target Species | Antibody Clone | Host | Hinge | TM | ICD | Inquiry & Datasheet |
| CARTHP-W2306 | Anti-GD2 (14G2a) ICD(CD86+FcγRI) CAR THP1 Cell Line | Human | 14G2a | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | CD86+FcγRI | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARTHP-W2307 | Anti-GD2 (14G2a) ICD(CD3ζ) CAR THP1 Cell Line | Human | 14G2a | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARTHP-W2308 | Anti-GD2 (14G2a) ICD(Megf10) CAR THP1 Cell Line | Human | 14G2a | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | Megf10 | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARTHP-W2309 | Anti-GD2 (14G2a) ICD(FcRɣ) CAR THP1 Cell Line | Human | 14G2a | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | FcRɣ | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARTHP-W2310 | Anti-GD2 (14G2a) ICD(FcRɣ+PI3K) CAR THP1 Cell Line | Human | 14G2a | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | FcRɣ+PI3K | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARTHP-W2311 | Anti-GD2 (3F8) ICD(CD147) CAR THP1 Cell Line | Human | 3F8 | Mouse | IgG1 | CD147 | CD147 | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARTHP-W2312 | Anti-GD2 (3F8) ICD(CD86+FcγRI) CAR THP1 Cell Line | Human | 3F8 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | CD86+FcγRI | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARTHP-W2313 | Anti-GD2 (3F8) ICD(CD3ζ) CAR THP1 Cell Line | Human | 3F8 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARTHP-W2314 | Anti-GD2 (3F8) ICD(Megf10) CAR THP1 Cell Line | Human | 3F8 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | Megf10 | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARTHP-W2328 | Anti-GD2 (hu3F8) ICD(FcRɣ+PI3K) CAR THP1 Cell Line | Human | hu3F8 | Humanized | CD8 | CD8 | FcRɣ+PI3K | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARTHP-W2329 | Anti-GD2 (7A4) ICD(CD147) CAR THP1 Cell Line | Human | 7A4 | Mouse | IgG1 | CD147 | CD147 | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARTHP-W2330 | Anti-GD2 (7A4) ICD(CD86+FcγRI) CAR THP1 Cell Line | Human | 7A4 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | CD86+FcγRI | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARTHP-W2331 | Anti-GD2 (7A4) ICD(CD3ζ) CAR THP1 Cell Line | Human | 7A4 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARTHP-W2332 | Anti-GD2 (7A4) ICD(Megf10) CAR THP1 Cell Line | Human | 7A4 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | Megf10 | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARTHP-W2333 | Anti-GD2 (7A4) ICD(FcRɣ) CAR THP1 Cell Line | Human | 7A4 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | FcRɣ | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARTHP-W2334 | Anti-GD2 (7A4) ICD(FcRɣ+PI3K) CAR THP1 Cell Line | Human | 7A4 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | FcRɣ+PI3K | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARTHP-W2335 | Anti-GD2 (14.18) ICD(CD147) CAR THP1 Cell Line | Human | 14.18 | Mouse | IgG1 | CD147 | CD147 | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARTHP-W2336 | Anti-GD2 (14.18) ICD(CD86+FcγRI) CAR THP1 Cell Line | Human | 14.18 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | CD86+FcγRI | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARTHP-W2337 | Anti-GD2 (14.18) ICD(CD3ζ) CAR THP1 Cell Line | Human | 14.18 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | CD3ζ | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CARTHP-W2338 | Anti-GD2 (14.18) ICD(Megf10) CAR THP1 Cell Line | Human | 14.18 | Mouse | CD8 | CD8 | Megf10 | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| CAT | Product Name | Target Species | scFv Clone | Host | CAR Vector Name | CAR Vector Type | Targeting Diseases | Inquiry & Datasheet |
| MCAR-P459 | Anti-GD2 (hu14.18K322A) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR-T Cells [Humanized Mouse (CD34+ HSC)] | Human | hu14.18K322A | Humanized | pCDCAR1 | Lentiviral vector | Neuroblastoma | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| MCAR-P460 | Anti-GD2 (hu14.18K322A) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR-T Cells [Humanized Mouse (CD34+ HSC)] | Human | hu14.18K322A | Humanized | pCDCAR1 | Lentiviral vector | Neuroblastoma | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| MCAR-P461 | Anti-GD2 (32E2) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR-T Cells [Humanized Mouse (CD34+ HSC)] | Human | 32E2 | Human | pCDCAR1 | Lentiviral vector | Neuroblastoma | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| MCAR-P462 | Anti-GD2 (32E2) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR-T Cells [Humanized Mouse (CD34+ HSC)] | Human | 32E2 | Human | pCDCAR1 | Lentiviral vector | Neuroblastoma | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| MCAR-P463 | Anti-GD2 (31F9V2) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR-T Cells [Humanized Mouse (CD34+ HSC)] | Human | 31F9V2 | Human | pCDCAR1 | Lentiviral vector | Neuroblastoma | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| MCAR-P464 | Anti-GD2 (31F9V2) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR-T Cells [Humanized Mouse (CD34+ HSC)] | Human | 31F9V2 | Human | pCDCAR1 | Lentiviral vector | Neuroblastoma | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| MCAR-P465 | Anti-GD2 (3G6) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR-T Cells [Humanized Mouse (CD34+ HSC)] | Human | 3G6 | Human | pCDCAR1 | Lentiviral vector | Neuroblastoma | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| MCAR-P466 | Anti-GD2 (3G6) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR-T Cells [Humanized Mouse (CD34+ HSC)] | Human | 3G6 | Human | pCDCAR1 | Lentiviral vector | Neuroblastoma | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| MCAR-P467 | Anti-GD2 (2E12) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR-T Cells [Humanized Mouse (CD34+ HSC)] | Human | 2E12 | Human | pCDCAR1 | Lentiviral vector | Neuroblastoma | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| MCAR-P468 | Anti-GD2 (2E12) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR-T Cells [Humanized Mouse (CD34+ HSC)] | Human | 2E12 | Human | pCDCAR1 | Lentiviral vector | Neuroblastoma | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| MCAR-P469 | Anti-GD2 (1B7) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR-T Cells [Humanized Mouse (CD34+ HSC)] | Human | 1B7 | Human | pCDCAR1 | Lentiviral vector | Neuroblastoma | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| MCAR-P470 | Anti-GD2 (1B7) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR-T Cells [Humanized Mouse (CD34+ HSC)] | Human | 1B7 | Human | pCDCAR1 | Lentiviral vector | Neuroblastoma | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| MCAR-P471 | Anti-GD2 (Dinutuximab) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR-T Cells [Humanized Mouse (CD34+ HSC)] | Human | Dinutuximab | Human | pCDCAR1 | Lentiviral vector | Neuroblastoma | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| MCAR-P472 | Anti-GD2 (Dinutuximab) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR-T Cells [Humanized Mouse (CD34+ HSC)] | Human | Dinutuximab | Human | pCDCAR1 | Lentiviral vector | Neuroblastoma | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| MCAR-P1014 | Anti-GD2 (CB-P09) h(CD28-CD3ζ) CAR-T Cells [Mouse CAR-T Cells] | Mouse | CB-P09 | Rat | pCDCAR1 | Lentiviral vector | Neuroblastoma | Add to Cart Datasheet |
| MCAR-P1235 | Anti-GD2 (CB-P09) h(4-1BB-CD3ζ) CAR-T Cells [Mouse CAR-T Cells] | Mouse | CB-P09 | Rat | pCDCAR1 | Lentiviral vector | Neuroblastoma | Add to Cart Datasheet |
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION
