Glycosaminoglycan Microarray
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) play critical roles in many cellular processes, ranging from viral invasion and angiogenesis to spinal cord injury. Glycosaminoglycan microarray provides a high-throughput method to elucidate glycosaminoglycan-protein interactions which just requires a few GAGs sample. Creative Biolabs offers high-quality services in Glycosaminoglycan Microarray. We can provide commercial, customized and semi-customized microarray services of GAGs. Combined with various kinds of support technologies such as Lectin Microarray, matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS), surface plasmon resonance imaging (SPRi), thin layer chromatography (TLC), and Flow Cytometry, we can provide comprehensive service of glycosaminoglycan-protein research. Moreover, we also provide general or customized Heparin Sulfate Microarray service to support more specific studies furtherly. With a large and well-equipped scientist team, we are dedicated to collaborating with our clients around the world to meet your requirements.
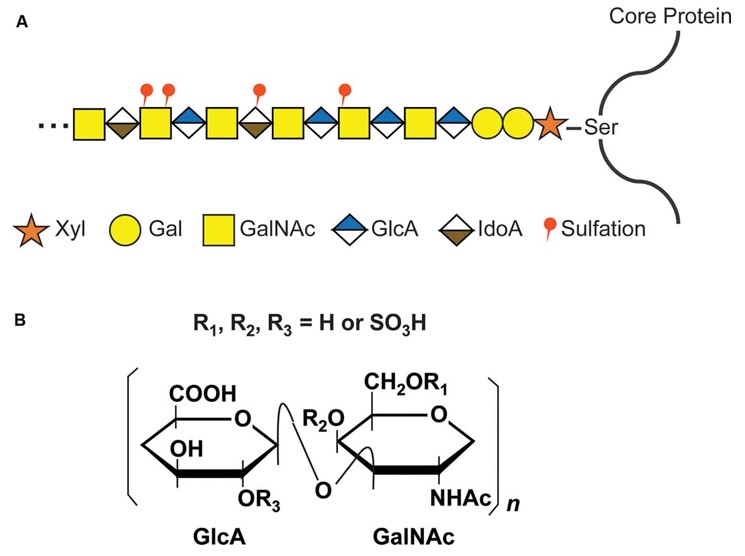 Fig.1 Structure of GAG.1, 3
Fig.1 Structure of GAG.1, 3
Introduction of Glycosaminoglycan Microarray
Glycosaminoglycans are extracellular matrix and cell surface sulfated glycans crucial to the regulation of various signaling proteins whose functions are essential in many pathophysiologycal systems. GAGs are structurally composed of alternating hexosamine and uronic acid or galactose. Assembled from repeating disaccharide units, GAGs display diverse patterns of sulfation, which contribute to the high structure flexibility of GAGs. According to the type of monosaccharides and glycosidic bonds, GAGs are classified to heparin, heparan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, hyaluronan or hyaluronic acid, keratan sulfate and so on.
Recent researches suggested that GAGs take part in numerous biological processes by binding to protein molecules and functionally regulating protein-ligand interactions. Because structural heterogeneity is high in GAG chains and purification is difficult, the use of structurally defined GAG oligosaccharides from natural sources as molecular models in both biophysical and pharmacological assays is limited. Therefore, the establishment of glycosaminoglycan microarray platform with synthetic GAG oligosaccharides is a novel approach to overcome this obstacle and serve as useful molecular tools in studies of GAG-protein interactions.
Applications of Glycosaminoglycan Microarray
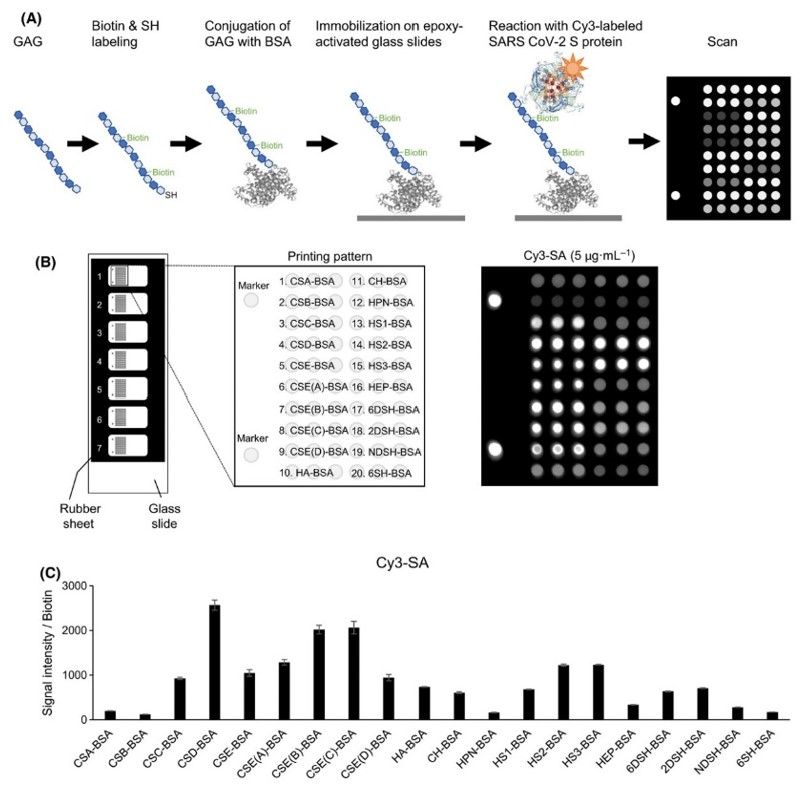 Fig.2 Construction of GAG microarrays.2, 3
Fig.2 Construction of GAG microarrays.2, 3
Because of GAGs extracellular location, high anionic character and rich structural diversity, GAGs are capable of interacting with and regulating many proteins whose functions are essential to pathophysiology. In particular, GAGs are known to modulate wound repair, coagulation, thrombosis, cancer growth and metastasis, inflammation, neovascularization, tissue regeneration and repair, cellular growth and migration. Since the first report of dedicated GAG microarray created using synthetic GAG oligosaccharides appeared in 2006, many novel immobilization methods are used to build glycosaminoglycan microarray chips. Nowadays, the application of glycosaminoglycan microarray to discover new interactions between proteins and GAGs is widely accepted in the immunology field. Creative Biolabs also established a mature glycosaminoglycan microarray platform in Tumor Glyco-diag, glycoprotein vaccine development and Anti-Glycoprotein Antibody Development. Particularly, because of the importance of heparin sulfate (HS) in vivo, we specially launched Heparin Sulfate Microarray service based on general glycosaminoglycan microarray.
Glycosaminoglycan microarray overcame the difficulties of traditional methods and provide a rapid and low-cost way to research GAG-protein interactions. If you are interested in our Glycosaminoglycan Microarray services or learn more about our Heparin Sulfate Microarray service, please contact us for more details.
Publication data
GAG is a linear polysaccharide containing four types that interact with a wide range of proteins and participate in various biological processes. This study developed fluorescence detection-based GAG microarrays to analyze SARS-CoV-2 spiny (S) proteins and screen proteins with high sensitivity for GAG binding specificity. The researchers immobilized 20 GAGs on an immobilized microarray platform and utilized fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 1 to validate the effectiveness of the GAG microarray. Then they used the microarray to analyze the specificity of each subunit of the S protein. The results showed that the S2 subunit might be important in the interaction between GAG and S proteins. This study not only provides data support for the interaction between S protein and GAG but also guides the construction and application of GAG microarrays.
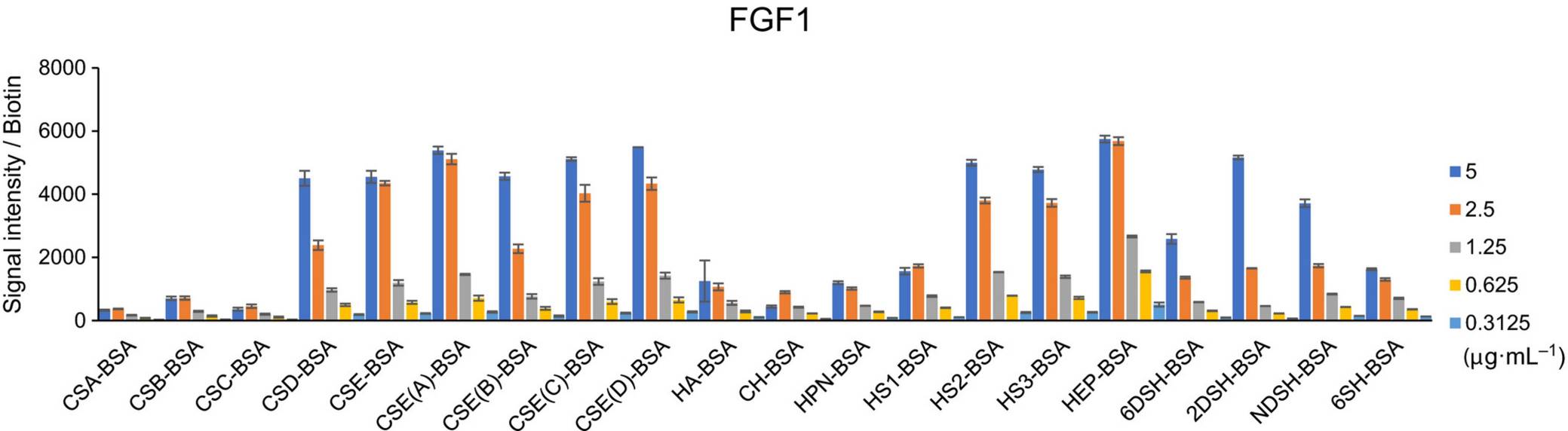 Fig.3 Detection of FGF1 binding specificity to GAG.2, 3
Fig.3 Detection of FGF1 binding specificity to GAG.2, 3
FAQs
Q1: What are the advantages of using GAG Microarrays?
A1: GAG microarrays enable high-throughput screening of binding interactions in a highly sensitive and high-throughput manner. Studying interactions by detecting the GAG binding properties of proteins can help accelerate the study of complex biological processes such as signal transduction and disease mechanisms.
Q2: Can GAG microarrays be customized?
A2: Yes, based on our extensive experience in microarray construction, we customize GAG microarrays according to the specific goals of our clients. We validate the GAG microarrays to ensure their quality and effectiveness.
Customer Review
Attention to Detail on GAG Microarrays
"Creative Biolabs utilized their GAG microarrays to help us study GAG-protein interactions. In addition to the detailed analysis report, they provided some valuable insights into the results to help us better analyze the binding activity. Their attention to detail was commendable."
Customized GAG Microarrays
"We utilized the GAG microarrays provided by Creative Biolabs to examine the GAG binding properties of proteins. Their researchers customized the microarrays to meet our needs. The final high throughput screening enabled us to fast GAG binding activity to proteins, which helped us to further advance our research. Highly recommend them for this service."
References
-
Hussein, Rowan K., et al. "Role of chondroitin sulfation following spinal cord injury." Frontiers in cellular neuroscience 14 (2020): 208.
-
Watanabe, Tomoko, et al. "A glycosaminoglycan microarray identifies the binding of SARS‐CoV‐2 spike protein to chondroitin sulfate E." Febs Letters 595.18 (2021): 2341-2349.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Structure of GAG.1, 3
Fig.1 Structure of GAG.1, 3 Fig.2 Construction of GAG microarrays.2, 3
Fig.2 Construction of GAG microarrays.2, 3 Fig.3 Detection of FGF1 binding specificity to GAG.2, 3
Fig.3 Detection of FGF1 binding specificity to GAG.2, 3

