Glycosphingolipid Microarray
Glycosphingolipids (GSLs) are ubiquitous glycoconjugates present on the cell membrane which play significant roles in many bioprocesses such as cell adhesion, embryonic development, signal transduction and carcinogenesis. Therefore, the research of GSL diversity and carbohydrate-protein interactions could increase understanding of GSL-related mechanisms. Among various analysis techniques, glycosphingolipid microarrays occupy an important position because of their high throughput and low required amount of GSL samples. Creative Biolabs offers high-quality services in glycosphingolipid microarray rely on our large and well-equipped scientist team. We are glad to provide a broad and integrated microarray service to meet your specific requirements.
Introduction of GSL Microarray
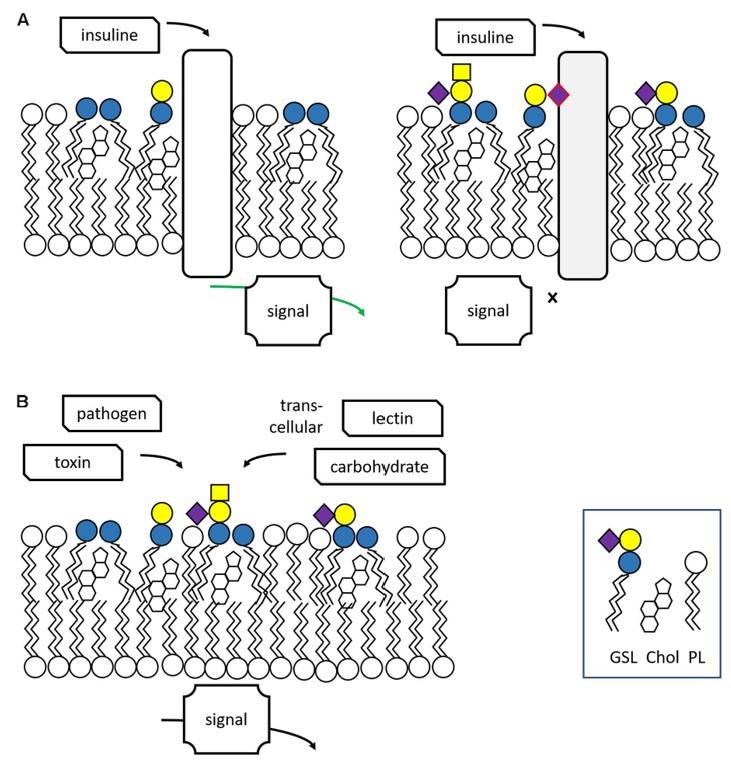 Fig.1 Synthesis and structure of glycosphingolipid.1, 3
Fig.1 Synthesis and structure of glycosphingolipid.1, 3
GSLs are important components of the plasma membranes of all eukaryotic cells. GSLs are composed of a glycan structure attached to a lipid tail, this combination results in an amphiphilic molecule with a hydrophilic carbohydrate moiety and a hydrophobic lipid moiety. The glycosylation and metabolism of GSL affect homeostasis in living organisms. Although various changes in GSLs have been proven to be closely correlated to various metabolic diseases, neurological dysfunctions and cancer, the clear biological mechanism of GSLs is not fully understood. The amphiphilicity and difficulty in preparation is a major challenge in the field of GSL analysis. However, glycosphingolipid microarray provides a novel effective platform for in vitro study of their functional interactions combined with other technologies such as SPRi, MS, MALDI-TOF MS or Flow Cytometry. This method is high-throughput, low cost and easy to conduct, and it provides detailed information about glycan linkages.
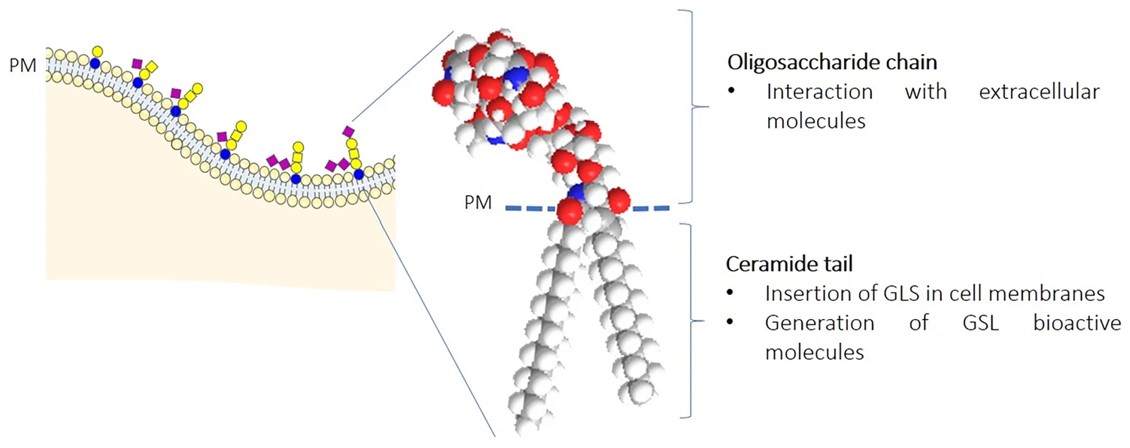 Fig.2 Plasma membrane glycosphingolipid structure.2, 3
Fig.2 Plasma membrane glycosphingolipid structure.2, 3
Applications of GSL Microarray
Although their normal biological functions are not fully understood, it has been appreciated for some time that the distribution of GSLs in neuronal and myelin membranes, and in other tissues and organs, makes them potential targets for involvement in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases, as well as potential diagnostic markers for autoimmune neuropathies, cancers and other disorders.
Recent research reported that a major GSL component of the islets of Langerhans expressed both on the surface and secretory granules of the insulin-producing β-cells named galactosylceramide-3-O-sulfate, has been implicated in type I diabetes. Therefore, elevated levels of IgG against sulfatide have been detected in newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes patients, while not those with type II diabetes. Based on these data, research groups have developed a glycosphingolipid microarray chip to detect the level of GSLs-binding antibodies and distinguish the type of diabete patients.
As an important part of the immune system, the biological functions and mechanisms of GSL are still unclear, which provides huge application potential. If you are interested in our glycosphingolipid microarray technologies, please feel free to contact us.
Published data
GSL plays an important role in regulating the substructure and mobility of lipid bilayers. This article provides us with a detailed overview of the structure, synthesis, degradation, and functions of GSLs. GSLs are formed by linking glycan chains and ceramides and have various types of core structures such as isoglobo-, ganglio-, and globo-. Its diversity correlates with the type of glycan chain and the sulfation of specific lipids. The synthesis of GSL is regulated by a variety of enzymes. After being modified at the Golgi, it is ultimately located at the plasma membrane. GSL is involved in a variety of signaling and interacts with other cells through carbohydrate-carbohydrate interactions or protein-carbohydrate interactions with other cells. Many bacteria, viruses, and toxins can bind to carbohydrates on the host cell surface GSL. Based on the structural diversity and functional properties, GSL microarrays play an important role in the identification of specific antibodies, and in disease therapy research. The profound analysis of GSL provides comprehensive theoretical support for the construction of GSL microarrays and related detection applications.
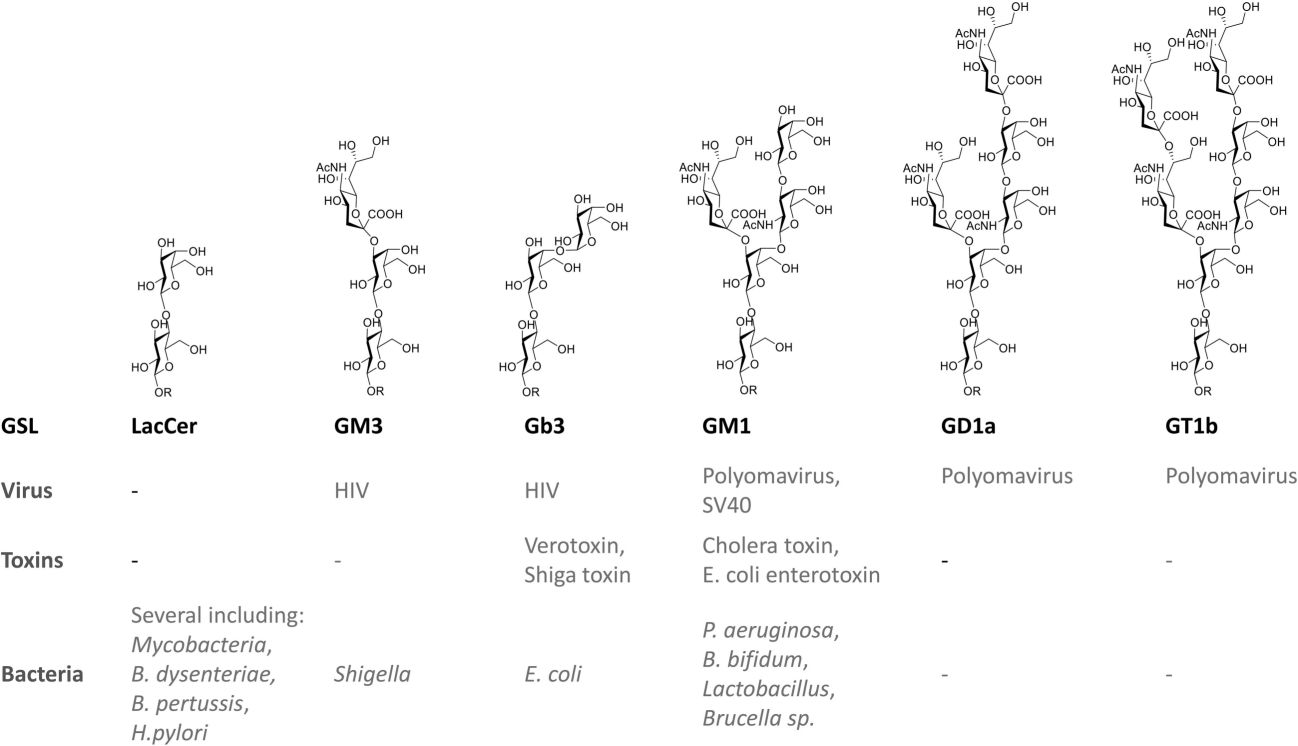 Fig.3 Examples of direct GSL interactions with toxins and pathogens.1, 3
Fig.3 Examples of direct GSL interactions with toxins and pathogens.1, 3
FAQs
Q1: What are the benefits of using GSL microarrays in glycobiology research?
A1: GSL microarrays provide researchers with a comprehensive view of the structure of GSLs and their interactions, which helps to further understand the cellular recognition processes, lipid signaling, and disease mechanisms associated with GSLs. It is an important tool for studying complex biological systems.
Q2: Can GSL microarrays be customized to meet specific research needs?
A2: Yes, we customize the GSL microarray to meet the specific research needs of our clients to ensure that our client's research needs are met to the fullest extent possible. The process includes isolating GSLs through advanced techniques, quantifying them, and coupling them to slides to create GSL microarrays.
Customer Review
Deep Understanding of GSL Microarray Technology
"Creative Biolabs' deep understanding of GSL microarray technology exceeded our expectations and helped us accelerate our GSL-related analysis. Their analysis team was also experienced and answered some of our questions about the experimental data. This collaboration was a very valuable experience for us."
High-quality GSL Microarray
"Creative Biolabs helped us analyze GSL interactions with their high-quality GSL microarray. Their after-sales service was also excellent, providing valuable insights into the analysis of the experimental data. The GSL microarray technology was highly recommended."
References
-
Aerts, Johannes MFG, et al. "Glycosphingolipids and infection. Potential new therapeutic avenues." Frontiers in cell and developmental biology 7 (2019): 324.
-
Chiricozzi, Elena. "Plasma membrane glycosphingolipid signaling: a turning point." Glycoconjugate Journal 39.1 (2022): 99-105.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Synthesis and structure of glycosphingolipid.1, 3
Fig.1 Synthesis and structure of glycosphingolipid.1, 3
 Fig.2 Plasma membrane glycosphingolipid structure.2, 3
Fig.2 Plasma membrane glycosphingolipid structure.2, 3
 Fig.3 Examples of direct GSL interactions with toxins and pathogens.1, 3
Fig.3 Examples of direct GSL interactions with toxins and pathogens.1, 3

